The UGC Bill 2026 is currently a trending topic of discussion among many in India. The University Grants Commission has recently introduced a bill for “Promotion of Equity in Higher Education Institutions) Regulations, 2026, often referred to as the UGC Act 2026 or UGC Bill 2026. This bill is replacing the 2012 framework. However,
University students, faculty members, and those preparing for the UGC NET exam are particularly keenly interested in UGC New Bill and Rules. Read on the article to understand why UGC Bill is introduced and why it is causing much trouble
Issue: Caste-based discrimination is prevalent in Indian universities and colleges, affecting students from marginalised communities.
Action: The UGC introduced the UGC Bill 2026 and stricter rules under the Promotion of Equity Regulations 2026.
Goal: The goal is to develop a “standard operating procedure” for every campus across India, ensuring that students in small towns have the same protections as those in major cities.
UGC Protest Live Updates- Supreme Court Stays on New Regulations
What is UGC?
The University Grants Commission (UGC), established by the Indian government in 1956, heads higher education standards across colleges and universities in India. Its responsibilities include facilitating collaboration among institutions, providing funding, and ensuring quality education for students. Understanding the UGC’s role, functions, and significance is crucial, as it has the authority to implement reforms like the University Grants Commission Bill 2026 and set regulations for all higher education institutions nationwide. The UGC plays a vital role in shaping the future of education in India
UGC Bill 2026 (New)
Under the UGC Bill 2026, the Promotion of Equity Regulations, 2026 have been formally implemented. These regulations are meant to replace the earlier 2012 guidelines and introduce a newly structured framework to address caste-based discrimination within educational institutions. The updated UGC Rules are framed in response to alarming data indicating a significant increase in reported caste discrimination cases between 2019 and 2024.
The primary objective of this new law is to completely eliminate discrimination based on caste, religion, gender, place of birth, and disability in higher education institutions (HEIs) such as colleges and universities.
The new UGC Act 2026 mainly focuses to:-
- Prevent caste-based, gender-based, religious, and social discrimination-
- Guarantee equal opportunities for all students-
- Implement effective monitoring, grievance redressal, and accountability systems- Enhance institutional governance and compliance.
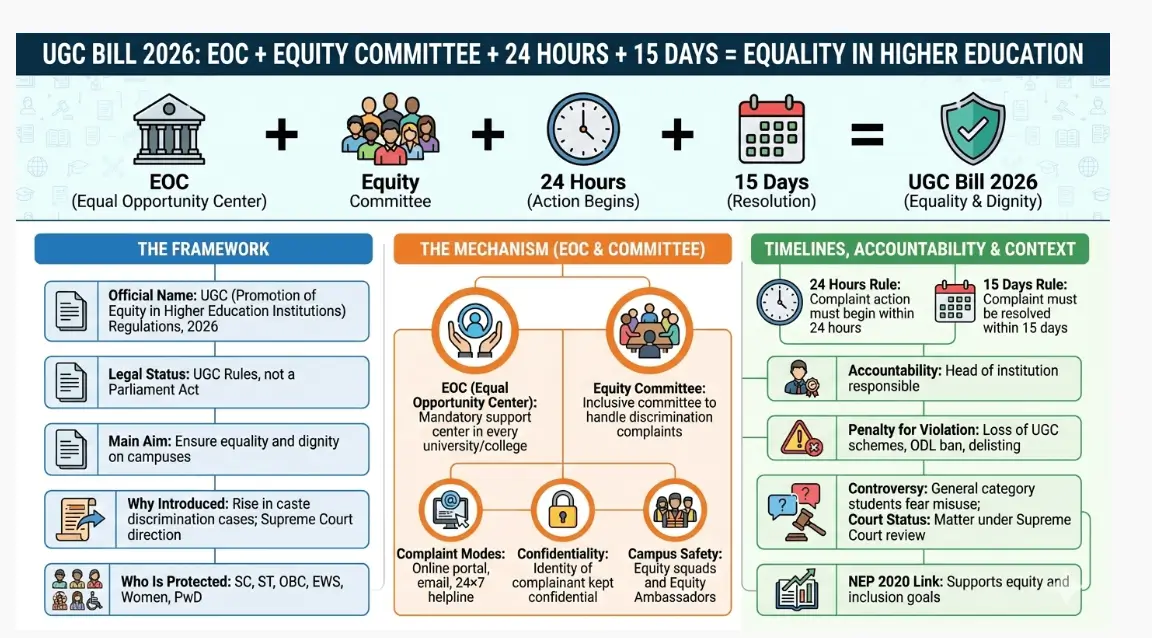
UGC New Bill 2026 Highlights
The University Grants Commission plays an important role, in shaping Indias higher education system. This article explains the major features, objectives, provisions, benefits, challenges, and expected impact of the UGC Bill 2026 in detail.
| Features | Details |
| Regulation Name | Promotion of Equity in HEIs Regulations 2026 |
| Implementation | 13th January 2026 |
| Protected Groups | SC, ST, OBC, EWS, PwBD, and Women. |
| Core Focus | Equity, inclusion, grievance redressal |
| New Bodies | EOC, Equity Committee, Equity Squads |
| Coverage | All universities & colleges |
| Penalty | Funding cut, derecognition |
UGC Bill New Vs Old
Let’s understand what is the difference between old rules and new rules.
| Parameter | Old Rules (2012) | UGC Bill 2026 |
| Definition of Discrimination | Vague | Clearly defined |
| Complaint Timeline | Not fixed | 24 hrs + 15 days |
| Accountability | Limited | Direct institutional liability |
| Monitoring | Internal | National-level oversight |
| Enforcement | Weak | Strict penalties |
Top 5 Major Changes in the 2026 Framework
1. Formal Inclusion of OBCs- One of the most significant updates is the explicit inclusion of Other Backwards Classes (OBCs) under the anti-discrimination umbrella. Previously, protections were primarily focused on SC/ST categories. The 2026 rules ensure OBC students and staff have the same grievance redressal rights.
2. Mandatory Equal Opportunity Centres (EOC)- Every university and college must now establish an Equal Opportunity Centre.
- Function: To provide academic, financial, and social guidance to disadvantaged groups.
- Composition: If a college lacks enough faculty, the parent university’s EOC will take over its functions.
3. The “Equity Committee” & Squads- Institutions must form a 10-member Equity Committee chaired by the Head of the Institution.
- At least 50% of the members must represent SC, ST, OBC, PwBD, or Women categories.
- Equity Squads: Mobile units that visit “vulnerable spots” on campus to prevent discrimination in real-time.
4. 24/7 Equity Helpline- Institutions are now mandated to operate a round-the-clock helpline and an online portal for reporting incidents. Students can also appoint “Equity Ambassadors” to act as peer-to-peer support systems.
5. Strict Time-Bound Redressal- Justice delayed is justice denied. The new rules mandate:
- 24 Hours: The Equity Committee must meet within a day of receiving a complaint.
- 15 Days: A full inquiry report must be submitted.
- 30 Days: Complainants can appeal to an Ombudsperson if dissatisfied.
What are Penalties for Non-Compliance?
Unlike the 2012 guidelines, the 2026 regulations have “penalties.” If an institution fails to implement these rules as mentioned in UGC Bill 2026, the penalities are as follows-
- Withdraw Grants: Stop all central funding and schemes.
- Revoke Degrees: Bar the institution from awarding degrees.
- De-recognition: Remove the institution from the official UGC-recognised list.
- Online Programs: Suspend permission for distance and online learning.
Why Were New UGC Rules Introduced in 2026?
The UGC Rules 2026 were formulated in compliance with directives issued by the Supreme Court of India. In 2025, while hearing petitions related to the tragic cases of Rohith Vemula and Payal Tadvi, the apex court highlighted major shortcomings in the existing anti-discrimination framework within higher educational institutions.
The court instructed the UGC to replace the outdated 2012 guidelines with more robust, time-bound, and enforceable regulations within eight weeks. Both cases involved allegations of caste-based discrimination and institutional negligence, which resulted in heartbreaking losses and sparked widespread public concern about campus safety, social justice, and institutional accountability.
What is the UGC Bill Controversy?
The UGC Bill Controversy reflects a broader debate between social justice and institutional autonomy. The UGC Bill Controversy refers to the nationwide debate and opposition triggered by the newly introduced UGC Bill 2026, especially its Promotion of Equity Regulations, 2026. While the bill aims to eliminate caste-based discrimination and promote inclusiveness in higher education, several political parties, academic bodies, teachers’ associations, and student organizations have raised serious concerns over its provisions, implementation, and potential misuse.
The UGC Bill 2026 is a sensitive topic when it comes to education.
- Reasons Behind the Controversy
- Perception of biased provisions
- Fear of misuse of complaint mechanisms
- Broad definition of discrimination
- Concerns about excessive monitoring
- Political and social reactions
Main Reasons for the UGC Act 2026 Controversy
- Definition of Discrimination: Critics argue that the definition of “indirect discrimination” is unclear, which could lead to its misuse.
- Unbalanced Representation: Some organisations argue that the lack of explicit representation for the general category in the ‘Equity Committee’ could make it biased.
- Legal Challenge: Several student groups have challenged this in the Supreme Court, arguing that caste-based protections should be applied equally to all students.



 Common Recruitment Exam for KVS & NV...
Common Recruitment Exam for KVS & NV...
 Rajasthan PTET 2025 Counselling, 2nd Col...
Rajasthan PTET 2025 Counselling, 2nd Col...







