The Union Budget 2026–27, presented in February 2026, outlines India’s roadmap towards achieving the vision of Viksit Bharat, balancing high economic ambition with inclusive growth. The budget focuses on action over ambivalence, reform over rhetoric, and people over populism, while maintaining fiscal discipline and economic stability.
Union Budget 2026-27
The Union Budget 2026–27, presented by the Ministry of Finance, is not limited to the Finance Minister’s Budget Speech alone. It is accompanied by a comprehensive set of documents that collectively explain the government’s revenue, expenditure, fiscal strategy, taxation proposals, and policy priorities. To help Parliament members, policymakers, students, and citizens understand these documents, the government releases an explanatory guide titled “Key to the Budget Documents 2026–27.”
Union Budget 2026- 27 Overview |
|
| Parameters | Details |
| Budget Name | Union Budget 2026–27 |
| Presented By | Union Finance Minister |
| Presented In | Parliament of India |
| Budget Type | Annual Financial Statement |
| Key Objective | Inclusive growth with fiscal discipline |
| Financial Year | 1 April 2026 – 31 March 2027 |
| Focus Theme | Economic growth, infrastructure, employment, social welfare |
| Major Sectors Covered | Agriculture, Education, Health, Infrastructure, Defence, MSME |
| Tax Structure | Income Tax, Corporate Tax, Indirect Taxes (GST-related measures) |
| Capital Expenditure | Increased allocation for roads, railways, digital infrastructure |
| Revenue Expenditure | Subsidies, salaries, pensions, welfare schemes |
| Fiscal Deficit Target | As per FRBM roadmap (expected reduction focus) |
| Agriculture Push | Farmer income support, irrigation, agri-infrastructure |
| Employment Measures | Skill development, startup incentives, MSME support |
| Social Welfare | Health insurance, women & youth schemes |
| Green Economy | Renewable energy, EVs, climate action |
| Digital Initiatives | AI, fintech, Digital India expansion |
| Defence Allocation | Strengthening border security & indigenous production |
Union Budget 2026–27 Vision: Viksit Bharat with Inclusion
The central vision of Budget 2026–27 is to build a developed and self-reliant India by ensuring that economic growth reaches all sections of society. The budget follows the guiding principle of “Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas”, focusing particularly on the poor, underprivileged, and disadvantaged communities.
The government’s approach reflects a clear commitment to:
- Strengthening people’s capacity
- Enhancing productivity and competitiveness
- Building resilience against volatile global economic conditions
List of Budget Documents Presented with Union Budget 2026–27
Apart from the Finance Minister’s Budget Speech, the following documents are presented in Parliament:
- Annual Financial Statement (AFS)
- Demands for Grants (DG)
- Finance Bill
- Fiscal Policy Statements under the FRBM Act
- Expenditure Budget
- Receipt Budget
- Expenditure Profile
- Budget at a Glance
- Memorandum Explaining the Finance Bill
- Output Outcome Monitoring Framework
- Key Features of Budget 2026–27
- Implementation of Budget Announcements 2025–26
Union Budget 2026-27 Key Details- Click to Check
Revenue Budget and Capital Budget Classification
The Union Budget is further divided into the Revenue Budget and the Capital Budget. The Revenue Budget includes revenue receipts, such as tax and non-tax revenue, and revenue expenditure, which covers salaries, subsidies, interest payments, and grants. This type of expenditure does not result in the creation of assets.
The Capital Budget, on the other hand, deals with capital receipts and capital expenditure. Capital receipts include borrowings, disinvestment proceeds, and recovery of loans, while capital expenditure involves asset creation, investments, and loans given by the central government. Capital expenditure plays a vital role in long-term economic growth and infrastructure development.
Yuva Shakti–Driven Budget: Focus on Youth and Employment
A major highlight of Budget 2026–27 is its strong emphasis on Yuva Shakti (youth power). The government recognises the youth as the driving force behind India’s economic transformation.
Key objectives include:
- Enhancing employability through skill development
- Encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship
- Building future-ready human capital
- This approach aims to convert India’s demographic dividend into a productive economic advantage.

Economic Outlook and Growth Strategy
The government aims to ensure macroeconomic stability while accelerating growth through long-term reforms rather than short-term populist measures. Budget 2026–27 projects a high growth rate of around 7%, supported by:
- Sustained public investment
- Fiscal prudence
- Monetary stability
Key Economic Pillars:
- Moderate inflation to protect purchasing power
- Fiscal discipline to ensure sustainable public finances
- Strong domestic demand driven by public capital expenditure
Union Budget 2026: Government’s Three Kartavya (Duties)
The budget framework is guided by three core Kartavya (duties). These duties collectively aim to transform India’s economic potential into tangible performance.
- Accelerating and sustaining economic growth
- Fulfilling the aspirations of the people
- Building long-term national resilience
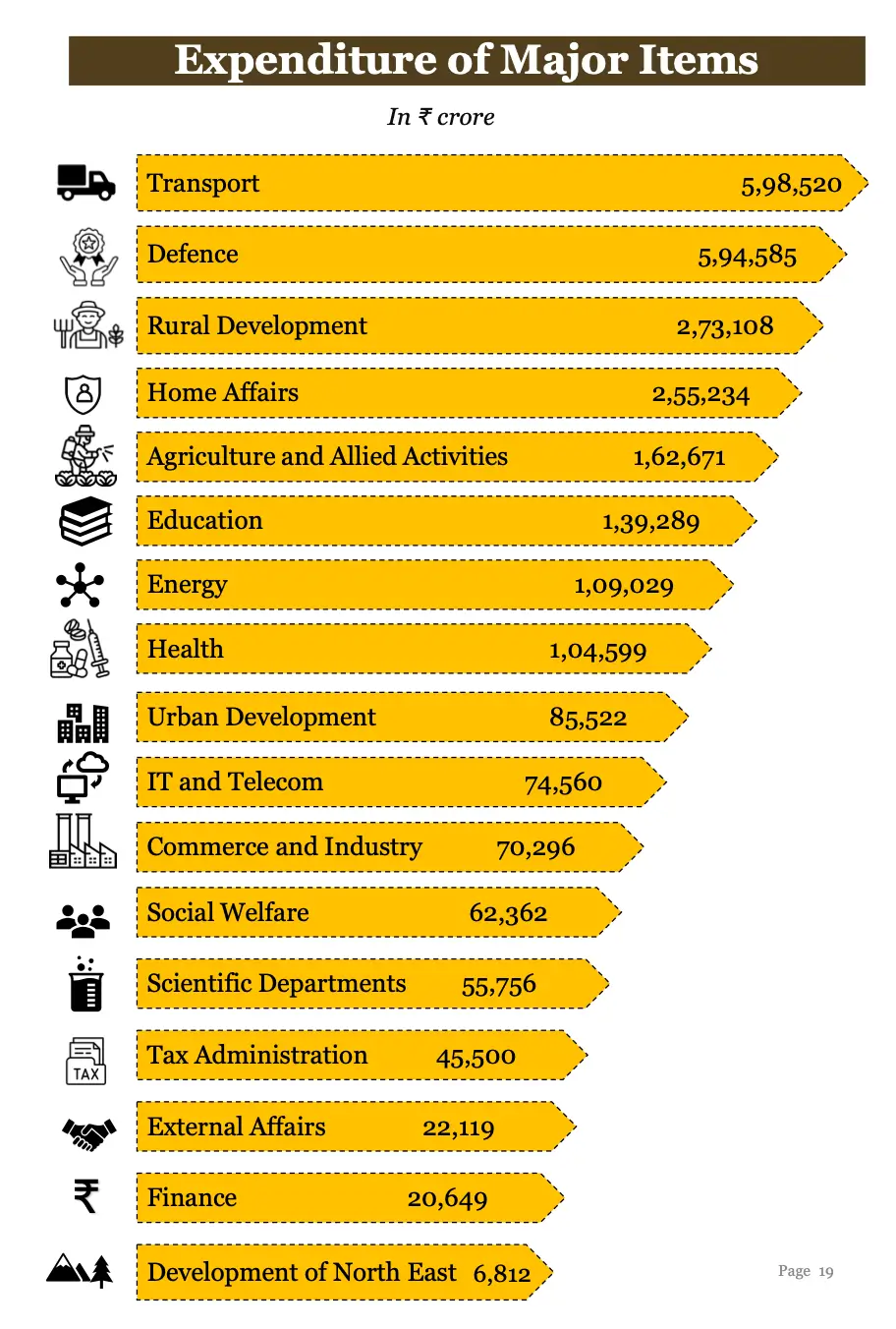
Expenditure of Major Items
Structural Reforms and Domestic Manufacturing Push
The budget announces far-reaching structural reforms to strengthen India’s economic foundation. A key focus area is reducing critical import dependencies by boosting domestic manufacturing capacity. These measures are expected to enhance India’s position as a global manufacturing hub.
Major Reform Areas:
- Expansion of domestic manufacturing ecosystems
- Support for industrial competitiveness
- Strengthening supply chains
Conclusion
The Union Budget 2026–27 presents a forward-looking and reform-oriented roadmap focused on growth with stability, inclusion with ambition, and reforms with responsibility. By prioritising youth empowerment, structural reforms, fiscal prudence, and public investment, the budget reinforces India’s journey towards becoming a developed and resilient economy.
Overall, Budget 2026–27 reflects a clear shift from short-term populism to long-term nation-building, ensuring that economic progress translates into real benefits for citizens.



 Important Days in March 2026, Complete L...
Important Days in March 2026, Complete L...
 UGC Protest Live Updates: Supreme Court ...
UGC Protest Live Updates: Supreme Court ...
 Indian Army Agniveer Compensation, Ajay'...
Indian Army Agniveer Compensation, Ajay'...







