Difference Between DNA and RNA: The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA stands for Ribonucleic acid are the two types of nucleic acids found in ecosystems. DNA acts as the genetic material in most living organisms. RNA though also acts as genetic material in some viruses( such as Tobacco mosaic, Bacteriophage, etc.) but most of its function is as a messenger. RNA also had an additional role as well. It functions as an adapter, structural, and also in some cases as a catalytic molecule. Though both carry genetic material there are also other differences between the two.
Difference Between DNA and RNA
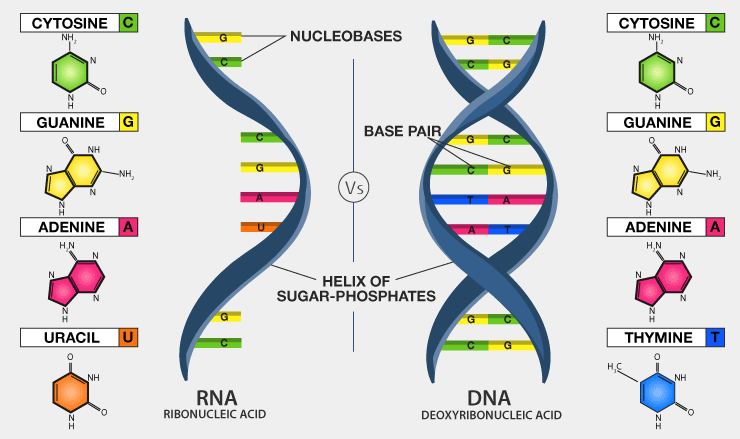
The difference between the two is that DNA is a double-stranded structure while RNA is a single-stranded structure. The other differences between the two are given in the table below-
| Parameter | DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) | RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) |
| Definition | It is a long polymer. It has a deoxyribose and phosphate backbone having four distinct bases namely thymine, adenine, cytosine, and guanine. | Is a polymer with a ribose and phosphate backbone with four varying bases namely uracil, cytosine, adenine, and guanine. |
| Location | It is located in the nucleus of a cell and in the mitochondria. | It is found in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and in ribosomes. |
| Predominant Structure | DNA is a double-stranded molecule that has a long chain of nucleotides. | RNA is a single-stranded molecule which that has a shorter chain of nucleotides. |
| Sugar portion | It has 2-deoxyribose. | It has Ribose. |
| Nitrogenous Bases and Pairing | The base pairing is as follows: GC (Guanine pairs with Cytosine) A-T (Adenine pairs with Thymine). | The base pairing is as follows: GC (Guanine pairs with Cytosine) A-U (Adenine pairs with Uracil). |
| Propagation | DNA replicates on its own, it is self-replicating. | RNA does not replicate on its own. It is synthesized from DNA when required.
|
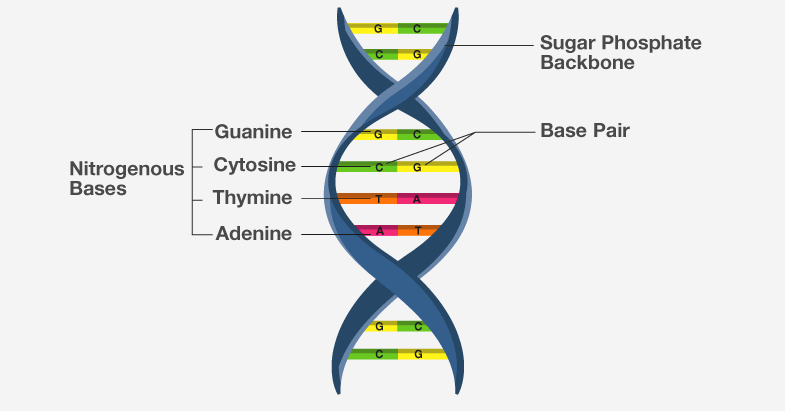
Structure of DNA
DNA as an acidic substance present in the nucleus was first discovered by Friedrich Meischer in 1869. The DNA structure is like a spiral staircase. Such structure is called a double-helix. The DNA molecule consists of two polynucleotide chains, in the backbone is composed of sugar and phosphate groups, and nitrogen bases projects inside.
The components of DNA are nucleotides, which are composed of a sugar group, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. The sugar and phosphate groups connect the nucleotides together to form each strand of DNA. Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), and Cytosine (C) are four types of nitrogen bases.
Types Of DNA
DNA is the genetic material that carries genetic information. Genes are small units of DNA consisting of million of base pairs. A gene code for a polypeptide molecule, where three nitrogenous bases sequence stands for one amino acid. Polypeptide chains are further folded in secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures to form different proteins.
1. A-DNA:
It is a right-handed double helix similar to the B-DNA form. Dehydrated DNA takes an A form that protects the DNA during extreme conditions such as desiccation. Protein binding also removes the solvent from DNA, and the DNA takes an A form.
2. B-DNA:
This is the most common DNA conformation and is a right-handed helix. The majority of DNA has a B-type conformation under normal physiological conditions.
3. Z-DNA:
Z-DNA is a left-handed DNA where the double helix winds to the left in a zig-zag pattern. It was discovered by Andres Wang and Alexander Rich. It is found ahead of the start site of a gene and hence is believed to play some role in gene regulation.
Functions of DNA
As every organism contains many genes in its DNA different types of proteins can be formed. Proteins are the main functional and structural molecules in most organisms. Apart from storing genetic information, DNA is also involved in the process of-
- Replication process: Transfer of genetic information from one cell to its daughter cells and from one generation to the next and equal distribution of DNA during the cell division.
- Mutations: The changes which occur in the DNA sequences.
- Transcription
- Cellular Metabolism
- DNA Fingerprinting
- Gene Therapy
Structure of RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a nucleic acid that involves the process of protein synthesis. Ribonucleic acid is a long chain of nucleic acid present in all living organisms. Its main function is to act as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling protein synthesis.
RNA is composed of the sugar ribose, phosphates, and nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U). Thymine is usually only present in DNA and uracil is usually only present in RNA.

Types of RNA
1. tRNA – Transfer RNA
The transfer RNA is held responsible for choosing the correct protein or the amino acids required by the body in turn helping the ribosomes. It is located at the endpoints of each amino acid. This is also called as soluble RNA and it forms a link between the messenger RNA and the amino acid.
2. rRNA-Ribosomal RNA
The rRNA is the component of the ribosome and is located within the cytoplasm of a cell, where ribosomes are found. In all living cells, the ribosomal RNA plays a fundamental role in the synthesis and translation of mRNA into proteins. The rRNA is mainly composed of cellular RNA and are the most predominant RNA within the cells of all living beings.
3. mRNA – Messenger RNA
This type of RNA functions by transferring the genetic material into the ribosomes and passing the instructions about the type of proteins, required by the body cells. Based on the functions, these types of RNA is called messenger RNA. Therefore, the mRNA plays a vital role in the process of transcription or during the protein synthesis process.
Functions of RNA
The ribonucleic acid – RNA, which is mainly composed of nucleic acids, is involved in a variety of functions within the cell and is found in all living organisms including bacteria, viruses, plants, and animals. These nucleic acid functions as structural molecule in cell organelles and are also involved in the catalysis of biochemical reactions. The different types of RNA are involved in various cellular processes. The primary functions of RNA:
- Facilitate the translation of DNA into proteins
- Functions as an adapter molecule in protein synthesis
- Serves as a messenger between the DNA and the ribosomes.
- They are the carrier of genetic information in all living cells
- Promotes the ribosomes to choose the right amino acid which is required in the building up of new proteins in the body.
