The CBSE Class 10 Social Science Practice Model Paper 2024 for all the CBSE Class 10 students has been released at the official website of the Central Board of Secondary Education www.cbseacademic.nic.in. This year the CBSE has decided to conduct a single board examination and there will be no term from this section onwards. The students appearing for the CBSE Class 10th SST examination on March 07, 2024 are advised to carefully go through these Additional sample papers. As these sample papers will help them to understand and familiarize themselves with the actual board exam pattern and real exam-level questions. Students can also download the CBSE Class 10 SST Model Paper 2024 PDF with Solutions from the direct link shared below.
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Model Paper 2024
The newly released CBSE Class 10 Social Science Model Paper 2024 is based on the entire syllabus and they also include 50 percent of competency questions. The Class 10 SST Model Paper 2024 provides an overview of the board pattern, including the number of questions, types of questions (objective, short answer, long answer), time duration, and the overall structure of the actual question paper. The Class 10 Social Science paper is divided into six sections – A, B, C, D, E, and F. There are a total of 37 questions in the question paper. All the questions are compulsory.
- Section A: Starts from question number 1 to 20 which are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B: Q 21 to 24 are Very short answer-type questions of two marks each. The answers to these questions should not exceed 40 words.
- Section C: Q 25 to 29 are short answer-type questions of three marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 60 words.
- Section D: Q 30 to 33 which are long answer-type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E: Q 34 to 36 are case study-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each. The answers to these questions should be given in 100 words.
- Section F: Q 37 is a map-based question that carries 5 marks with two parts, 37 (a) from History (2 marks), and 37 (b) from Geography (3 marks).
Class 10 Social Science Model Paper 2024 PDF
These CBSE Class 10 SST Practice Questions will provide an overview of the actual board exam pattern, including the number of sections, types of questions (objective, short answer questions, and long answer questions), and the overall structure of the question paper. Download the CBSE Class 10 Social Science Model Paper 2024 PDF along with the solutions and marking scheme. Practice these Class 10 SST Model Paper 2024 to understand the pattern and type of questions that can be asked in board exams.
| CBSE Class 10 SST Model Paper 2024 PDF | |
| Additional Sample Paper PDF | Solution PDF |
| Class 10 SST Practice Question Paper | Solution Link |
Check :- CBSE Class 10 Result 2025
CBSE Class 10 2024 SST Sample Questions and Solutions
We have discussed the CBSE Class 10 SST Model Paper 2024 with all its solutions below.
Section A – MCQs
Q1: How was the Rowlatt Act of 1919 perceived in terms of fundamental rights and civil liberties by Indians?
(a) It was viewed as regressive legislation in favor of the majority of Indians.
(b) It was considered as severely curtailing the right to personal liberty.
(c) It was seen as a necessary measure to prevent communal tensions.
(d) It was regarded as a safeguard for protecting British soldiers.
Ans: (b) It was considered as severely curtailing the right to personal liberty.
Q2: Ankur, a resident from Rajasthan, decided to install a submersible water pump in his house, capable of extracting groundwater from depths of 250-300 m. This practice of installing similar pumps is becoming increasingly popular across the state.
Which of the following will this growing practice most likely lead to in the near future?
(a) decline in the groundwater quality
(b) reduced monsoon water resources
(c) increased number of waterborne diseases
(d) Water scarcity resulting from excessive utilization
Ans: (d) Water scarcity resulting from excessive utilization
Q3: Observe the map given below showing the distribution of thermal and nuclear power plants across India.
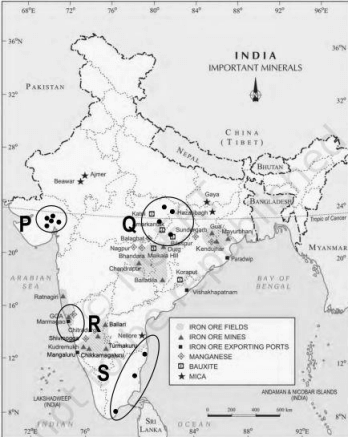
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is used to measure real-time air pollution levels. A high AQI represents poor air quality.
Accordingly, which of the following regions marked on the map is LIKELY to experience comparatively better AQI?
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
Ans: (c) R
Q3: Which method of energy production is environmentally friendly and practical for powering homes across regions in India?
(a) coal-fired power plants
(b) nuclear power plants
(c) solar power panels
(d) diesel generators
Ans: (c) solar power panels.
Q4: Rina, a 28-year-old woman from a marginalized community, is uneducated but adept at making traditional handicrafts. Her family toils hard to afford two square meals every day.
Accordingly, which development objective would be the MOST crucial for improving Rina’s and her kin’s well-being?
(a) increasing access to clean energy in Rina’s community
(b) reducing the impact of climate change on Rina’s community
(c) creating more training opportunities for Rina and other artisans
(d) ensuring that Rina has the same rights and opportunities as men in her community
Ans: (c) Creating more training opportunities for Rina and other artisans.
Q5: ‘India’s green energy goals have a serious problem – the Great Indian Bustard’ A Wildlife Institute of India (WII) survey covering 80 km of power lines across the Thar desert found 4 bustard (critically endangered species) deaths during a single year due to high-transmission wires, including some connected to wind turbines. Source: The Print
Should the installation of such power lines be reconsidered in areas where such species are found?
(a) Yes, alternative methods of power generation should be explored to minimize this risk.
(b) Yes, the goal of protecting biodiversity is the only goal that should be prioritized.
(c) No, the benefits of power lines outweigh the negative impact on the species.
(d) No, the species is not yet extinct, and currently, no action needs to be taken.
Ans: (a) Yes, alternative methods of power generation should be explored to minimize this risk.
Q6: There are two statements given below, marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option. Assertion (A): Power sharing can help to prevent conflict in society. Reasoning (R): Power sharing ensures that different social groups are included in decision-making processes, reducing marginalization and fostering inclusivity.
(a) A is true but R is false.
(b) A is false but R is true.
(c) Both A and R are true and R explains A.
(d) Both A and R are true but R does not explain A.
Ans: (c) Both A and R are true and R explains A.
Q7: In an Indian state, communities X and Y have been engaged in a long-standing conflict over issues of co-existence and resource sharing. The tensions have intensified, leading to a demand from both communities for self-administration.
What is the BEST resolution to this conflict?
(a) collapsing the present government due to its inefficiency in governing the state
(b) delaying the demands of self-administration and maintaining the current power structure
(c) imposing strict regulations to control the movements and interactions of both communities
(d) establishing a power-sharing arrangement where both communities have a role in decision-making
Ans: (d) establishing a power-sharing arrangement where both communities have a role in decision-making.
Q8: Which of the following is a definite indicator of the successful implementation of democratic governance?
(a) free economy dictated by market forces
(b) provision of basic amenities to the citizens
(c) establishment of central financial institutions
(d) establishment of institutions to protect people’s rights
Ans: (d) establishment of institutions to protect people’s rights
Q9: There are two statements given below, marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): Self-help groups are instrumental in promoting economic democracy.
Reasoning (R): They contribute to a more equitable distribution of economic power and opportunities.
(a) A is true but R is false.
(b) A is false but R is true.
(c) Both A and R are true and R explains A.
(d) Both A and R are true but R does not explain A.
Ans: (c) Both A and R are true and R explains A.
Q10: The principle of subsidiarity emphasizes that decisions should be made by the people who are most affected by them, promoting decentralization, efficiency, and citizen participation in governance, with higher levels of authority intervening only when lower-level authorities are unable to address certain issues effectively.
Which of the following constitutional principles/legislations is in close alignment with the principle stated above?
(a) separation of power between the executive, legislature, and judiciary
(b) division of power between the central, state, and local government
(c) right of individuals to form and join political parties of their choice
(d) reservation for women in the highest law-making bodies
Ans: (b) division of power between the central, state, and local government
Q11: Globalisation is the increasing interconnectedness of the world through the flow of goods, services, capital, ideas, and people. Which of the following examples represents globalization?
(a) an online advertising portal for goods sold by local vendors run by the Indian government
(b) an IKEA store in Bengaluru selling products manufactured in China
(c) a traditional Vietnamese market selling handicrafts in Hanoi
(d) a Sunday market selling groceries produced locally
Ans: (b) an IKEA store in Bengaluru selling products manufactured in China
Q12: The Indian masses willingly participated in the Civil Disobedience Movement, despite the challenges faced during the Non-Cooperation Movement. Accordingly, which of the following quotes BEST reflects the outlook of the masses?
(a) ‘The greatest glory in living lies not in never falling, but in rising every time we fall’
(b) ‘An eye for an eye only ends up making the whole world blind’
(c) ‘Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere
(d) ‘Obedience is the key to a peaceful society
Ans: (a) ‘The greatest glory in living lies not in never falling, but in rising every time we fall’.
Q13: Given below is the painting ‘Imperial Federation – Map of the World showing the extent of the British Empire in 1886’. Observe the painting and answer the question that follows.

Source: https://exhibits.stanford.edu
Which of the following elements depicted in the painting seem conflicting when presented together?
(a) The British soldiers and British colonies spread in both East and West
(b) The variety of animals and costumed figures depicting countries and their people
(c) Britannia, the personification of Britain, seated on top of the world and the words federation written at the top of the image
(d) the words ‘freedom’ and ‘fraternity’ written at the top and Atlas, depicting human labor, holding the world upon his shoulders
Ans: (d) The words ‘freedom’ and ‘fraternity’ are written at the top and Atlas, depicting human labor, holding the world upon his shoulders.
Note: The following question is for Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of Q. No. 13
Q13: Read the information given below about the painting – ‘A map celebrating the British Empire’.
The painting has a map that commemorates the British Empire, symbolizing its territorial holdings and influence across various regions of the world.
Given below are a few elements that have been depicted in the painting. Identify the ones that are conflicting when presented together.
(a) the idea of freedom and imperialism
(b) the colonial nations and the colonies
(c) the occupations of a farmer and a soldier
(d) the British and people from different backgrounds together
Ans: (a) the idea of freedom and imperialism.
Q14: There are two statements given below about the Print Revolution, marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): The distribution, application, and preservation of knowledge were fundamentally altered with the invention of printing.
Reason (R): Printing enabled intellectuals to produce, comment on, and evaluate texts that spread as ideas across Europe.
(a) A is true but R is false.
(b) A is false but R is true.
(c) Both A and R are true and R explains A.
(d) Both A and R are true but R does not explain A.
Ans: (c) Both A and R are true and R explains A.
Q15. Which of the following is the primary factor that contributed to the emergence of multiple political parties at the same level in India?
(a) a federal political system
(b) varied economic conditions
(c) linguistic and regional diversity
(d) Low levels of literacy and political awareness
Ans: (c) Linguistic and regional diversity
Q16: Which of the following policy decisions by the central government could potentially serve as a trade barrier?
(a) strengthening export subsidies
(b) simplifying customs procedures
(c) implementing higher tariffs on imports
(d) promoting fairer trade practices globally
Ans: (c) Implementing higher tariffs on imports
Q17: Given below is a cartoon created by Neelabh Banerjee, the renowned Indian cartoonist, illustrator, and comics artist.
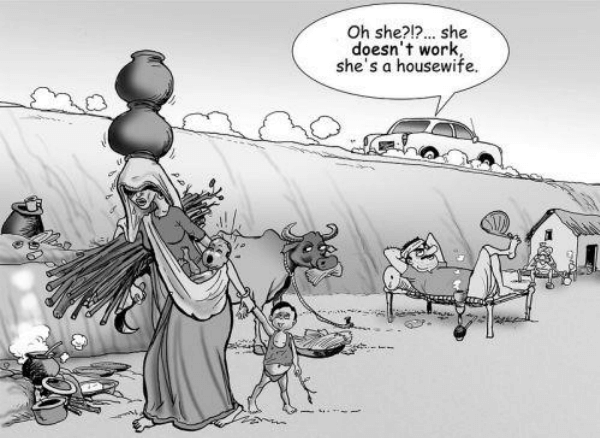

Source: asiapacific.unwomen.org
What is the cartoon trying to depict?
(a) the sexual division of labour in India
(b) natural and unchangeable gender divisions
(c) income-generating activities done by women in rural India
(d) the ability of men to contribute equally to domestic work as women
Ans: (a) the sexual division of labour in India
Note: The following question is for Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of Q. No. 17
Q17: In a cartoon created by Neelabh Banerjee, the renowned Indian cartoonist, illustrator, and comics artist, a woman is depicted in a rural setting, carrying water pots on her head and a bundle of sticks in her hands. She is also holding her child’s hand. Meanwhile, a man, presumably her husband, is seen lying on a cot. The husband is heard saying, “Oh, she? She doesn’t work. She’s just a housewife.”
What is the cartoon trying to depict?
(a) the sexual division of labour in India
(b) natural and unchangeable gender divisions
(c) income-generating activities done by women in rural India
(d) the ability of men to contribute equally to domestic work as women
Ans: (a) the sexual division of labour in India
Q18: The table given below highlights the percentage of workers in the three sectors of the economy in India. The data for the year 2023 has actual figures while the data for 2040 is hypothetical based on the published figures of the year 2023.
Any of the three hypothetical scenarios could be possible in the year 2040. Study the table carefully and answer the questions that follow.
| Year | Primary | Secondary | Tertiary |
| 2023
(Source: Statista) |
44% | 25% | 31% |
| 2024
(Hypothetical Scenario: 1) |
20% | 45% | 35% |
| 2023
Hypothetical Scenario: 2) |
60% | 20% | 20% |
| 2040
Hypothetical Scenario: 3 |
15% | 40% | 45% |
With all other factors remaining the same, which of the following scenarios would have the biggest impact on India’s global leadership in the future?
(a) Only Hypothetical Scenario 1
(b) Only Hypothetical Scenario 2
(c) either Hypothetical Scenario 1 or 2
(d) either Hypothetical Scenario 1 or 3
Ans: (d) Either Hypothetical Scenario 1 or 3
Q19: Based on the information given in the table, which of the following statements is LIKELY to be correct?
(a) In scenarios 1 and 2, the secondary sector will need the least workers.
(b) In scenario 2, India will become a major services-based economy.
(c) The primary sector in scenario 2 will be the highest contributor to the GDP of the country.
(d) In scenarios 1 and 3, maximum employment opportunities will be created in the secondary sector.
Ans: (d) In scenarios 1 and 3, maximum employment opportunities will be created in the secondary sector.
Q20: In a representative democracy, which of the following best describes the role of elected representatives?
(a) They have absolute power and authority to make decisions without consulting the public.
(b) They are accountable to the public and make decisions on behalf of their constituents.
(c) They act as mere figureheads with no real power or influence in the government.
(d) They serve lifetime appointments and cannot be removed from office.
Ans: (b) They are accountable to the public and make decisions on behalf of their constituents.
Section B – Very Short Answer Questions
Q21: ‘Consumer Affairs raids Malda markets to check malpractices; Complaints were received that soft drinks were being sold at a higher price…’
Source (edited): Millennium Post
(i) Which consumer right was being violated in the above instance of soft drinks being sold at a higher price?
(ii) Which consumer right was LIKELY invoked in response to the complaints?
Ans 21: (i) Right to be informed
(ii) right to seek redressal
Q22: Shruti performed a web search for ‘Teacher’ and found that 80% of the images had women, while a search for ‘Pilot’ mainly showed men.
Discuss how these web search results reflect societal perceptions and the sexual division of labour. Explain with an example.
Ans 22: – The over-representation of women as teachers and men as pilots reinforces traditional notions of job roles. The role of teaching is considered a caregiving job suitable for women while the role of pilot is regarded as a physically and mentally demanding job ideal for men.
– Similarly, the job of a nurse is associated more with women, and the job of an engineer is associated with men. These trends represent social perceptions and perpetuate the sexual division of labour.
(to be assessed as a whole)
Q23: Examine the possible consequences on the basic rights of party members within political organizations that lack internal democracy.
Ans 23: – Freedom of Speech and Expression – Party workers may face restrictions on voicing their opinions, ideas, or concerns within the party structure.
– Right to Equality of Opportunity – Not everyone would get an equal chance to climb up the success ladder.
– any other relevant point
(any two to be evaluated for two marks)
OR
Q23: In a hypothetical democratic nation with a population that is religiously homogenous, should there still be multiple political parties? Justify your sentence in about 40 words.
Ans 23: Yes, because despite a religiously homogenous population, having multiple political parties –
– helps represent diverse political perspectives
– helps in policy formation – helps avoid authoritarianism
– provides an alternative to the voters
– any other relevant point
Q24: Assess the reasons for the concentration of the woolen textile industries in the sub-tropical region in India vs. their absence in the southern part of India.
Ans 24: – Climatic conditions – Southern India has a climate that is not favorable for wool production.
– Lack of raw material – Sheep rearing is not widespread in southern India.
– Low demand – The demand for wooden textiles is very low in southern India due to hot and humid temperatures.
– any other relevant point
All these requirements are met in the sub-tropical region of India hence the woollen textile industry is concentrated in this region of India.
(to be assessed as a whole)
Section C – Short Answer Type Questions
Q 25: ‘A drought-induced water shortage can have far-reaching consequences, affecting agricultural productivity, the availability of food resources, industrial activities, and livelihoods, thereby significantly impacting human well-being.’
i) What does the above statement represent about the relationship between different resources?
ii) How does such a situation represent a lack of resource planning?
Ans25: -It represents the interconnectedness and interdependence between resources.
-Availability of food resources depends on water and a negative impact on agriculture would affect livelihoods impacting human resources.
(to be evaluated as a whole)
-The situation represents a lack of water management and over reliance onmonsoons.
(to be evaluated as a whole)
Q 26: Discuss the MOST LIKELY impact if India operated without a federal system.
Build the answer around these points:
– regional autonomy
– Effectiveness in governance
– decision-making process
Ans26: 1. Regional autonomy: Regional governments would have little or no decision-making power. Regional aspirations might get suppressed.
2. Effectiveness of Governance: Local issues might not receive due attention, leading to a disconnect between grassroots reality and governance.
3. Decision-making processes: The decision-making process might become undemocratic and less inclusive. It is likely to neglect regional aspirations.
(Award one mark for each point)
Q27: Read the statements given below regarding Indian Railways.
Statement 1 (S1): Indian Railways has largely been a Public Sector Enterprise.
Statement 2 (S2): Private players are making an entry into the Indian Railway market.
Explain what trend these statements – S1 and S2 – reflect in the railways sector in India.
Ans27: -It represents a growing trend of public-private partnership in the Indian market.
-With private trains running, the service quality and the customer experience would be enhanced.
-It would lead to diversification of choices for the Indian masses.
-It would also lead to an investment in the public infrastructure.
– But it could also lead to railways becoming unaffordable for the common masses.
-It would also result in revenue loss for the government
(to be assessed as a whole)
Q28: Which sector, organized or unorganized, is preferable for employment? Explain.
Ans28: It is a preference that might depend on a variety of factors –
People might prefer to work in the organized sector because of –
– job security
– social security benefits
– regular income
People might prefer to work in the unorganized sector because of –
– flexibility
– escaping paperwork
– quick employment opportunity
(Award marks for whichever sector the students chose. To be assessed as a whole)
Q29: Discuss the role of newspapers in shaping public opinion and the democratisation of information during the modern period.
Ans29: -It led to the dissemination of information.
-It served as a platform for shaping public discourse.
-It led to increased awareness about social, political, and economic issues.
-any other relevant point
(any three to be assessed)
Section D – Long Answer Question
Q30: Examine the significance and key milestones of the Civil Disobedience Movement that took place in India during the struggle for independence.
Ans30: Key milestones
Dandi March: Gandhi’s 240-mile march to Dandi to produce salt became a powerful symbol of resistance and gained international attention.
Repression and Imprisonment: British authorities responded with repression and arrests, fueling public outrage and strengthening the movement.
Negotiations and Outcomes: The movement led to negotiations between Congress and the British government but fell short of full independence.
Significance
Mass Participation: The movement witnessed widespread involvement from diverse segments of society, showcasing unity and determination.
Boycott of British Goods: Indians boycotted British products to promote self reliance and protest colonial economic policies.
Spread of Nationalist Ideas: The movement raised awareness, inspired active participation, and fostered national unity among the masses.
Legacy and Inspiration: The movement’s legacy as a symbol of non-violent resistance inspired future freedom fighters worldwide.
(to be assessed as a whole)
OR
Q30: Read the following excerpt about the Right to Protest in India and answer
the question that follows.
The Constitution of India guarantees the fundamental right to protest, which is derived from the broader rights of freedom of speech and expression, and freedom to assemble peacefully. However, this right is subject to reasonable restrictions in the interest of India’s sovereignty. Violent actions during protests are in violation of citizens’ fundamental duties, emphasizing that the right to protest encompasses only peaceful demonstrations.
Source: Legal Service India
Examine the elements of Satyagraha employed during the 20th-century Indian freedom struggle in light of their alignment with the Right to Protest granted by the Indian constitution as mentioned in the passage.
Ans30: – The elements of Satyagraha that align with the right to protest of present times include non-violence, peaceful protests, respect for human rights, and emphasis on dialogue and negotiation.
– These aspects promote democratic values, freedom of speech, and the right to dissent.
– However, there are certain elements of satyagraha that may go against the Indian constitution.
– For example, acts of civil disobedience that involve breaking laws or disrupting public order can be seen as conflicting with the principle of upholding the rule of law.
– Additionally, satyagraha techniques that obstruct essential services or hinder the functioning of government machinery may be deemed unconstitutional.
(to be assessed as a whole)
Q31: A think tank has been given the task to design an outline to measure how successful has democracy been in any country. Discuss the key indicators that the think tank should consider while designing this outline and explain why these factors are crucial in assessing the outcomes of democracy.
Ans31: – Free and fair elections: This represents a healthy democratic process in place
– Citizen’s right to information: This is important since only after having the right information can the citizens hold the government accountable
– Protection of minority rights: This represents a strong commitment to democratic principles as this would enable the minority community to participate in the decision-making processes
– Poverty: reduction in poverty over the years would indicate the successful implementation of democracy
– Rule of law: The presence of institutions like an independent judiciary helps uphold the law and ensures fairness, justice, and equal treatment to citizens
– any other relevant point
(any five to be evaluated)
OR
Q31: Free and fair media is one of the most important outcomes of democracy. Comment.
Ans31: -A democratic government needs to be an accountable, responsive and legitimate government.
-It needs to ensure that it has enabled its citizens to participate in the decision-making processes.
-It has to make sure that its citizens are informed and making informed choices.
-It needs to make sure that it is accommodating varied perspectives.
-Media as a fourth pillar helps fulfill all these objectives of a democratic government and hence it is one of the most important outcomes of democracy.
(to be assessed as a whole)
Q32: Describe circumstances that drive individuals to seek loans from informal sources of credit.
Ans32: – Immediate financial requirement
– the absence of collateral
– unavailability of documents
– informal economy and irregular income
– limited/restricted access to formal sources of credit
– any other relevant point
(any five to be assessed)
OR
Q32: State the potential negative economic implications that would arise in an economy in the absence of the concept of credit.
Ans32: – Limited access to funds for starting businesses or making investments.
– limited capacity of savings.
– limited ability to finance education and skill development.
– limited ability to purchase very high-worth items like cars, houses, etc.
– limited financial flexibility and convenience.
-any other relevant point.
(any five to be evaluated for five marks)
Q33: Read the information given below regarding the Delhi-Dehradun Expressway and answer the question that follows.
The Delhi-Dehradun Expressway is all set to open to the public by the end of 2023. It would reduce the travel time between the two cities from 6 to 2 hours. The 210 km long expressway will start from North East Delhi and pass through Baghpat, Shamli, Muzaffarnagar, Saharanpur and Dehradun. The last 20km stretch will pass through the eco-sensitive zone of Raja Ji National Park where Asia’s longest elevated wildlife corridor of six lanes and 12 km will be constructed that includes the 340 m DatKaali tunnel. The 340-meter-long tunnel near DatKaali temple, Dehradun will help reduce the impact on wildlife, and multiple animal passes have been provided in the Ganeshpur-Dehradun section for avoiding animal-vehicle collisions.
Source (edited): Livemint
Analyze the development of the Delhi-Dehradun Expressway in terms of its impact – negative and/or positive – on economic growth, the environment, and the goal of sustainable development.
Ans33: Economic Growth
-Reduced travel time will boost trade and tourism
-Can lead to greater investment in the valley
-The construction itself is leading to the generation of employment opportunities
Environment
-Passing through an eco-sensitive zone will lead to loss of flora and fauna
-Increased vehicular emissions will lead to increased pollution
Sustainable Development
– Environmental concerns have been taken into account and wildlife corridors have been built.
-Green construction methods could solve the problem of carbon emissions
(to be evaluated as a whole)
OR
Q33: As per Britannica Dictionary, when the world is seen as a community in which people are connected by computers, television, etc., and all depend on one another, the world becomes a ‘global village’.
Accordingly, they elaborate on the role of air transport in making the world a ‘global village’.
Ans33: Accessibility: Air transport has significantly improved accessibility to distant locations, making it a convenient mode of travel in cases where other means of transportation are impractical.
– Facilitating International Trade: Supply chains have been revolutionized by the quick movement of cargo by air, enabling companies to easily access international markets. Now, time-sensitive shipments, high-value commodities and perishable goods can all be delivered quickly, which has boosted global trade.
– Boosting Tourism: People from different countries can now explore new destinations, experience diverse cultures, and build connections with individuals from around the world. This exposure has led to a better understanding of various traditions and customs, promoting cross-cultural appreciation.
– Advancing Business and Diplomacy: Face-to-face meetings, conferences, and negotiations between individuals and representatives from different nations are now more feasible, fostering collaboration and cooperation. This has been crucial in promoting international business ventures and resolving global issues.
– Humanitarian Aid and Crisis Response: During emergencies, natural disasters, or humanitarian crises, air transport enables the swift delivery of relief supplies, medical assistance, and rescue teams to affected areas. This quick response saves numerous lives and provides vital support during times of distress.
– any other relevant point
(Assess any five points for one mark each)
Section E: Case-Based Questions
Q34: Read the information about climate-smart agriculture and answer the question that follows.
Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) is an approach that helps guide actions to transform agri-food systems toward green and climate-resilient practices. CSA supports reaching internationally agreed goals such as the Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Agreement on climate change. CSA supports the Food and Agriculture Organisation Strategic Framework 2022-2031 based on the Four Betters: better production, better nutrition, a better environment, and a better life for all, leaving no one behind.
Source (edited): Food and Agriculture Organisation
(i) A CSA expert suggested increased production and consumption of millets in India. Justify their stance.
(ii) What is the necessity to think of CSA in India?
(iii) Suggest two methods through which India can shift towards CSA.
Ans34: (i) -Millets have high nutritional value.
-They are rainfed, hardly need any irrigation facilities, and hence can be grown in arid and semi-arid regions.
– Millets do not require a lot of investment to flourish which can help them be great commercial grain substitutes in poorer nations.
(any one point to be evaluated)
(ii) It is important to start planning for CSA in India because of the changing climate due to global warming.
(to be evaluated as a whole)
-use of genetically modified seeds resistant to insect damage for cropping
-shift towards organic and natural farming methods
-any other relevant point
(any two to be evaluated)
Q35: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Population trends and dynamics can have an enormous effect on prospects for poverty reduction and sustainable development. Poverty is influenced by – and influences – population dynamics, including population growth, age structure, and rural-urban distribution. All of this has a critical impact on a country’s development prospects and prospects for raising living standards for the poor. Investments in better health, including reproductive health, are essential for individual security and for reducing mortality and morbidity (the condition of suffering from a disease or medical condition), which in turn improve a country’s productivity and development prospects.
Source: UNFPA
(i) How does investing in improved healthcare infrastructure contribute to the reduction of preventable diseases and chronic conditions?
(ii) Explain the relationship between population trends and poverty reduction.
(iii) ‘Poverty is influenced by – and influences – population dynamics, including population growth, age structure, and rural-urban distribution.’
Analyze the statement and highlight the mutual relationship between poverty and population.
Ans35: (i) Investments in better healthcare provide people with access to essential healthcare services, such as vaccinations, prenatal care, and treatment for common diseases.
– This can help to reduce the number of people who die from preventable diseases (mortality) and who suffer from chronic conditions (morbidity).
(ii) An expanding population can exert pressure on a country’s resources, including food, water, and land, which can consequently result in heightened poverty levels as individuals may face insufficient access to nourishment and adequate housing.
(to be assessed as a whole)
(iii) Population growth can strain resources and infrastructure, potentially increasing poverty.
– The age structure of a population affects labour markets and social support systems, which can impact poverty levels.
– Rural-urban distribution determines access to essential services and economic opportunities, further influencing poverty rates.
– Poverty can contribute to specific population dynamics, such as high fertility rates and limited access to healthcare, perpetuating the cycle of poverty.
– any other relevant point
(two points to be assessed for two marks)
Q36: Read the following lines from Gandhiji’s addressal at the A.I.C.C. (All India Congress Committee) in Bombay on 8-8-42 outlining his plan of action, in Hindustani, and answer the questions that follow:
“You may take it from me that I am not going to strike a bargain with the Viceroy for ministries and the like. I am not going to be satisfied with anything short of complete freedom. Maybe, he will propose the abolition of the salt tax, the drink evil, etc. But I will say, “Nothing less than freedom.” Here is a mantra, a short one, that I give you. You may imprint it on your hearts and let every breath of yours give expression to it. The mantra is: ‘Do or Die’. We shall either free India or die in the attempt; we shall not live to see the perpetuation of our slavery. Every true Congressman or woman will join the struggle with an inflexible determination not to remain alive to see the country in bondage and slavery. Let that be your pledge. Keep jails out of your consideration.”
Source: Smithsonian Magazine
(i) Explain any one key impact that Gandhiji’s rejection of “striking a bargain with the Viceroy for ministries and the like” had on the people participating in the freedom struggle.
(ii) How did this mantra differ from earlier strategies employed in the struggle for independence?
(iii) Discuss the economic context and political climate that led to the adoption of the ‘Do or Die’ mantra.
Ans36: (i) People joined the freedom struggle with stronger determination and pledged not to live to see the perpetuation of India’s slavery.
– any other relevant point
(any one point to be assessed for one mark)
(ii) The movement aimed at achieving complete independence without accepting any concessions or partial freedoms from the British government. Earlier strategies, such as non-violent civil disobedience and negotiation, focused on pressing the British government to grant incremental reforms and concessions. The ‘Do or Die’ approach, in contrast, signaled a departure
from the quest for piecemeal changes and instead demanded immediate and complete freedom for India.
(to be assessed as a whole)
(iii) During the freedom struggle, the failure of the British government to fulfill promises of granting dominion status to India after World War II left Indian leaders were disillusioned with incremental reforms.
– The movement was triggered by discontent among Indians due to the harsh impacts of the war on the economy and living conditions.
– The political climate in India was tense, with growing impatience for complete independence.
– Mahatma Gandhi, advocating non-violent civil disobedience, sought a more decisive strategy to break the stalemate in negotiations with the British.
(Assess for any two points, one each for political and economic context)
Section F – Map Skill Based Question
Q37: (a) Two places A and B have been marked on the given outline map of India. Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them.
i. The place where the Jallianwala Bagh massacre took place
ii. The 1927 Indian National Congress session was held at this place
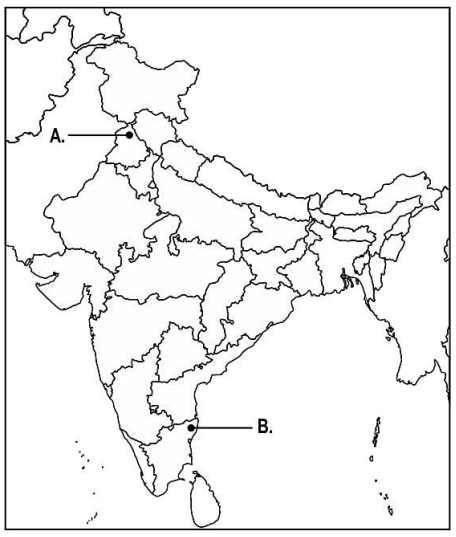
37 b. On the same map of India, locate and label any three of the following with suitable symbols.
i) a dam built on the river Sutlej.
ii) a software technology park in Northern India.
iii) the southernmost port on the east coast of India.
iv) a nuclear power plant in the state of Maharashtra.
Note: The following question is for Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of Question 37 part (a) and part (b).
(a)
i. Name the place where the Jallianwala Bagh massacre took place.
ii. Name the place where the Indian National Congress session was held in
1927.
(b)
The following question is for Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of Q. No. 37 (b)
Answer any three of the following.
i) Name the dam built on the river Sutlej.
ii) Name the place in northern India where an important software technology park is present.
iii) Name the southernmost port on the east coast of India.
iv) Name the nuclear power plant present in the state of Maharashtra.
Ans37: (i) Amritsar, Punjab
(ii) Madras
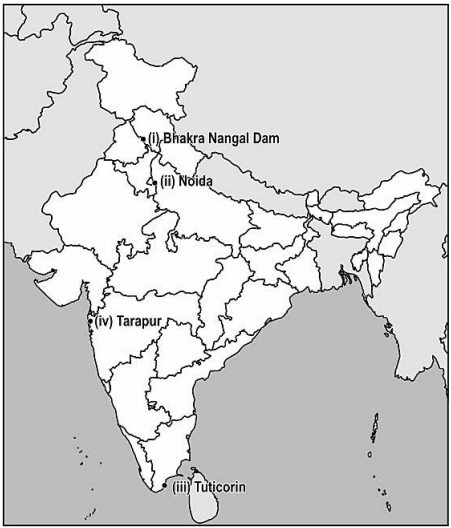
Note: The following question is for Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of Question 37 part (a) and part (b).
(a)
i. Name the place where the Jallianwala Bagh massacre took place.
ii. Name the place where the Indian National Congress session was
held in 1927.
(b)
The following question is for Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of Q. No. 37 (b)
Answer any three of the following.
i) Bhakra Nangal Dam
ii) Noida
iii) Tuticorin
iv) Tarapur Atomic Power Plant
(Award one mark each for any three correct locations)
CBSE Class 10th Social Science Exam 2024: Preparation Tips
All the CBSE Class 10th students are advised that they must remember, that a balanced approach to studying and understanding concepts is key.
- Understand the Syllabus: Familiarize yourself with the CBSE Class 10th Social Science Syllabus to know the topics you need to cover.
- Make a Schedule: Plan a study schedule that allocates sufficient time for each topic. Balance your study sessions to cover all subjects regularly.
- Use NCERT Books: CBSE recommends NCERT textbooks. Read them thoroughly, as they provide the foundation for the exam.
- Take Notes: Summarize important points while studying. This aids in quick revision and helps reinforce concepts.
- Practice with Previous Papers: Solve previous year’s question papers to understand the exam pattern and time management.
- Create Mind Maps: Use visual aids like mind maps to connect concepts. This enhances memory and understanding.



 CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Additional Pract...
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Additional Pract...
 CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Sample Qu...
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Sample Qu...
 CBSE Class 12 Physics Model Paper 2024-2...
CBSE Class 12 Physics Model Paper 2024-2...













