Curious about the process of Photosynthesis? No need to worry, we have got you covered! As we know among all living organisms, only green plants and some other organisms like Algae and Cyanobacteria are Autotrophs or Phototrophs i.e., they make their own food by the process of Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose, a type of sugar. It takes place in the chloroplast of the plant cell.
What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process in which a plant uses sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugar. Photosynthesis can be influenced by a variety of environmental factors, including temperature and light intensity. In the process of Photosynthesis green plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O) for preparing food. During Photosynthesis, plants take Carbon dioxide (CO2) and release Oxygen (O2) and chemical energy stored in the form of Glucose. Photosynthesis is of two different types: Oxygenic Photosynthesis and Anoxygenic Photosynthesis.

Process of Photosynthesis
It’s a vital biological process that supports life on Earth by creating glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen through the utilization of carbon dioxide, water, and chlorophyll. Glucose produced at the time of photosynthesis serves as a primary source of energy for plants and is used in various cellular processes. The oxygen produced during photosynthesis is used by living organisms in the process of cellular respiration.
This process takes place in a unique structure called Chloroplast which is found mainly on the leaves. The chloroplast contains a green pigment called chlorophyll. This chlorophyll helps in capturing light energy. Photosynthesis is very important for Terrestrial and Aquatic ecosystems, as it helps in the growth and development of plants and algae.
Carbon dioxide + Water + Sunlight → Glucose + Oxygen
Stages of Photosynthesis
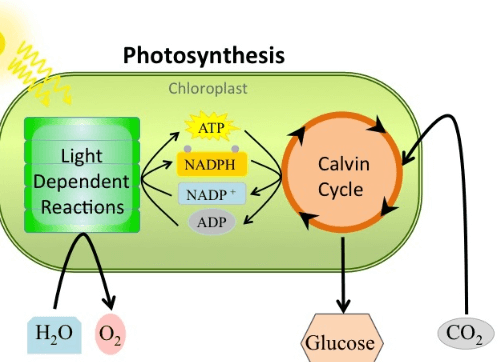
Photosynthesis happens in two main stages. First, in the light-dependent stage, plants use sunlight to make energy and release oxygen. This occurs in a part of the plant cell called the chloroplast. Then, in the light-independent stage, also called the Calvin Cycle, plants use the energy from the first step to change carbon dioxide from the air into food like sugar. This step doesn’t need sunlight and happens in another area of the chloroplast. Together, these stages allow plants to make their own food and oxygen using sunlight, air, and water.
- Light-Dependent Reaction
- Light- Independent Reaction
| Stages of Photosynthesis | |
| Stages | Description |
| Light-Dependent Reaction | Plants convert light energy into chemical energy, forming glucose and oxygen, in light-dependent reactions. |
| Light-Independent Reaction | Carbon dioxide combines with stored energy to create glucose in a light-independent reaction. It is also known as the Calvin Cycle. |
Light Dependent Reaction
This reaction takes place in the Thylakoid membrane (an internal system of interconnected membranes, that carry out the light reaction) of the chloroplast. The chlorophyll absorbs the light energy which is used to break water molecules into Oxygen and Protons then this Oxygen is released into the atmosphere while the protons are used to form energy-rich molecules like ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate).
Light Independent Reaction
The light-dependent reaction is also known as the Calvin Cycle. The cycle is named after Melvin Calvin who gave its mechanism in the 20th century. The light-dependent reaction takes place in the Stroma (a fluid-filled internal space of the chloroplast, it contains the DNA of the chloroplast, starch, ribosomes, and all the enzymes needed in the Calvin cycle) of the chloroplast. Through numerous chemical reactions, ATP’s energy and NADPH’s reducing power play a crucial role in converting carbon dioxide into glucose.
Photosynthesis Equation and Formula
Photosynthesis is the fundamental biological process that helps to maintain a balance of energy and carbon in our biosphere. The chemical equation for photosynthesis is an overall sum-up of the process. Photosynthesis can be simply described by the equation. Photosynthesis Equation can be written as
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Where,
- 6CO2 means that there are six molecules of carbon dioxide.
- 6H2O means that there are six molecules of water.
- Light energy is used to make the reaction faster.
- C6H12O6 means that there is only one molecule of glucose and it is the primary product of photosynthesis.
- 6O2 means that there are six oxygen molecules formed in the reaction. The Oxygen is released as a byproduct of photosynthesis.
This is the simplest representation of Photosynthesis, as it is a complex reaction that involves multiple numbers of intermediate steps and various enzymes.
Types of Photosynthesis
There are mainly two types of photosynthesis and both play a crucial role in the maintenance of an environment in their own ways. One of them gives oxygen as a by-product while the other does not give oxygen as a by-product. The two types of photosynthesis are mentioned below:
- Oxygenic Photosynthesis
- Anoxygenic photosynthesis
Now let us discuss both types of Photosynthesis in a tabulated form.
| Types of Photosynthesis | |
| Types | Description |
| Oxygenic Photosynthesis | Oxygenic photosynthesis is the process by which plants and cyanobacteria convert light into energy, producing oxygen. |
| Anoxygenic Photosynthesis | Anoxygenic photosynthesis is a light-driven process in certain bacteria that don’t produce oxygen as a byproduct. |
Oxygenic Photosynthesis
Oxygenic photosynthesis is the most common form of photosynthesis on Earth and it is very crucial for the production of oxygen. It is the process in which certain organisms such as plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Oxygenic photosynthesis is a complex process that takes place in the chloroplast of plants, blue-green algae, and cyanobacteria.
Oxygenic photosynthesis plays a great role in the maintenance of the ecosystem, as it provides the basis for food chains and energy flow in the biosphere. Oxygenic Photosynthesis increases the level of oxygen in the atmosphere, which allows the development of complex, oxygen-dependent life forms.
Anoxygenic Photosynthesis
Anoxygenic photosynthesis is a type of photosynthesis that occurs in certain bacteria including purple bacteria, and green sulfur bacteria, and does not give oxygen as a byproduct. These bacteria have a specialized light-absorbing pigment called Bacteriochlorophyll that helps to capture light energy. Anoxygenic photosynthesis uses electron donors such as hydrogen sulfide, ferrous iron, or organic compounds like succinate other than water.
This process is different from oxygenic photosynthesis. Anoxygenic photosynthesis plays a very crucial role in the carbon cycle. Anoxygenic photosynthesis is typically found in environments with low energy levels such as anaerobic mud, and aquatic sediments, and certain extreme environments like hot springs.
Factors Influencing the Process of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is affected by sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Plants need enough light to make energy and oxygen. They also need water from the soil and carbon dioxide from the air. If any of these factors are limited, the process won’t work as well, so plants need a good balance of all three to stay healthy.
- Light Intensity: The amount of light available affects the rate of photosynthesis. More light increases the rate up to a certain point.
- Carbon Dioxide Concentration: Higher levels of carbon dioxide can enhance the rate of photosynthesis.
- Temperature: The rate of photosynthesis increases with temperature up to an optimum point, beyond which it decreases due to enzyme denaturation.
- Water Availability: Water is a raw material in photosynthesis, so its availability can affect the process.
- Chlorophyll Concentration: Chlorophyll is essential for capturing light energy. More chlorophyll can increase the rate of photosynthesis.
- Nutrient Availability: Essential nutrients like nitrogen, magnesium, and iron are necessary for the synthesis of chlorophyll and other components of the photosynthetic machinery.
- Leaf Structure: The size, thickness, and arrangement of leaves can influence the absorption of light and the diffusion of gases.
- Environmental Conditions: Factors like wind and humidity can impact the rate of photosynthesis by affecting water and gas exchange.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process of preparing food in the presence of sunlight, water, carbon dioxide, and chlorophyll as mentioned above. Photosynthesis is very important as it is the fundamental process that helps to sustain life on Earth. Photosynthesis plays a very important role in the existence of all living organisms on earth, maintains the plant’s ecological balance, and provides food and energy for all living organisms. Without photosynthesis, life will be not possible on the Earth, and the ecosystem of the Earth will drastically change.
Now let us discuss the importance of photosynthesis:
- Photosynthesis helps plants prepare their food, and then these plants are consumed by almost all living organisms.
- During the process of Photosynthesis, plants use Carbon dioxide and release Oxygen which is essential for all living organisms. Photosynthesis also maintains the level of Oxygen (O2) and Carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Through photosynthesis green plants, algae, and cyanobacteria convert solar energy to chemical energy in the form of Glucose.
- Photosynthesis also forms the basis of the Food Chain and Food Webs within the ecosystem, as it provides energy to producers (plants) which are then consumed by the consumers in various ecosystems.
- The organic matter produced at the time of Photosynthesis gets buried over a million years, which leads to the formation of fossil fuels.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













