Chlorophyll A and B work in concert to absorb light energy across a broader spectrum, maximizing the efficiency of photosynthesis. They help plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, providing energy for plant growth and sustaining various ecosystems. The distinct absorption spectra of these pigments contribute to the green color of plants, reflecting the wavelengths of light they do not absorb. Here we have discussed a little more information about chlorophyll A and chlorophyll B detail.
Chlorophyll A and Chlorophyll B
Chlorophyll A and Chlorophyll B are crucial pigments in photosynthesis, the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy. Chlorophyll A plays a central role in capturing light energy and initiating the photosynthetic process. Chlorophyll B complements A by capturing light at different wavelengths, expanding the range of light that can be utilized for photosynthesis.
Define Chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll A is a vital pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells, essential for Photosynthesis. Imagine it as the plant’s solar panel, capturing sunlight to convert into energy. Its green color absorbs light most efficiently in the red and blue parts of the electromagnetic spectrum while reflecting green light, giving plants their characteristic color.
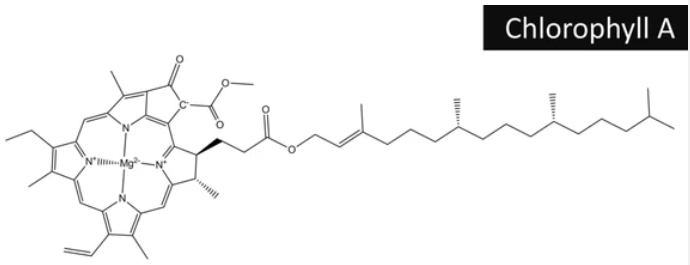
Chlorophyll A plays a key role in the first steps of photosynthesis, where it captures light energy and uses it to combine carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose, the plant’s food. This process releases oxygen as a byproduct, contributing to the air we breathe. Without chlorophyll A, plants wouldn’t be able to harness sunlight for energy, and the fundamental process sustaining plant life and much of Earth’s ecosystems would be compromised.
Define Chlorophyll B
Chlorophyll B is another essential pigment found in the chloroplasts of the Plant Cell, working alongside chlorophyll A in the process of photosynthesis. Think of it as a partner to Chlorophyll A, expanding the range of light that plants can absorb. While chlorophyll A absorbs light most efficiently in the red and blue regions of the spectrum, chlorophyll B complements this by absorbing light more effectively in the blue and red-orange parts.
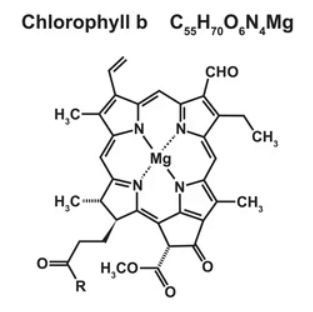
Together, chlorophyll A and B enhance the plant’s ability to capture a broader spectrum of sunlight, maximizing energy absorption for photosynthesis. This collaboration allows plants to thrive in various light conditions. Like chlorophyll A, chlorophyll B plays a crucial role in converting light energy into chemical energy, facilitating the synthesis of sugars that sustain plant growth. In essence, chlorophyll B is a crucial teammate in the intricate dance of photosynthesis, ensuring plants can efficiently utilize available light resources.
Difference Between Chlorophyll A and Chlorophyll B
Chlorophyll A absorbs light most effectively in the red and violet-blue parts of the spectrum, while chlorophyll B absorbs light in the blue and red-orange parts. The main difference lies in their specific absorption peaks, contributing to a broader range of light absorption in plants. Other differences are tabulated below:
| Difference Between Chlorophyll A and Chlorophyll B | ||
| Characteristics | Chlorophyll A | Chlorophyll B |
| Absorption Peaks | Chlorophyll A absorbs light most efficiently in the red and blue regions of the spectrum. | Chlorophyll B absorbs light more effectively in the blue and red-orange parts, complementing chlorophyll A. |
| Color | Chlorophyll A appears blue-green in color. | Chlorophyll B appears yellow-green in color. |
| Accessory Pigments | Chlorophyll A is the main pigment in photosynthesis. | Chlorophyll B acts as an accessory pigment, capturing additional light energy. |
| Specific Structures | Chlorophyll A present in all photosynthetic organisms. | Chlorophyll B is typically found in higher plants and green algae. |
| Wavelength Range | Chlorophyll A absorbs light with wavelengths of around 430 nm and 662-680 nm. | Chlorophyll B absorbs light with wavelengths of around 453-642 nm. |
| Functions | Chlorophyll A primary role in converting light energy to chemical energy during photosynthesis. | Chlorophyll B enhances light absorption, transferring captured energy to chlorophyll A |
| Evolutionary Origins | Chlorophyll A is present in the earliest photosynthetic organisms. | Chlorophyll B evolved later in green plants. |
| Concentration | Chlorophyll A generally higher in concentration compared to chlorophyll B. | Chlorophyll B is present in lower amounts but crucial for broadening the light absorption spectrum. |
| Structural Differences | Chlorophyll A is a methyl group in a specific position. | Chlorophyll B is an aldehyde group in the same position as the methyl group in chlorophyll A. |
| Adaptation to Light Conditions | Chlorophyll A is efficient in standard light conditions. | Chlorophyll B is adapted to low light conditions, extending the range of usable light for photosynthesis. |
Importance of Chlorophyll A and Chlorophyll B
Both Chlorophyll A and Chlorophyll B maximize the range of light absorption for photosynthesis. Facilitates the synthesis of carbohydrates for plant growth. Reflects green light, giving plants their characteristic color, and is vital for the sustainability of ecosystems by supporting the base of the Food Chain. Other importance of chlorophyll A and chlorophyll B are discussed below:
Importance of Chlorophyll A
Here we have discussed a few points that highlight the importance of Chlorophyll A.
- Chlorophyll A is a primary pigment in photosynthesis.
- It absorbs light energy in the blue and red regions of the spectrum.
- Chlorophyll A initiates the conservation of light energy to chemical energy.
- Chlorophyll A is essential for the production of Glucose in plants.
Importance of Chlorophyll B
Here we have discussed a few points that highlight the importance of Chlorophyll B.
- Chlorophyll B is the complementary pigment to Chlorophyll A.
- Broadens the absorption spectrum by capturing light in the blue and red-orange regions.
- Chlorophyll B enhances the overall efficiency of Photosynthesis.
- Chlorophyll B plays a role in transferring absorbed energy to Chlorophyll A.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













