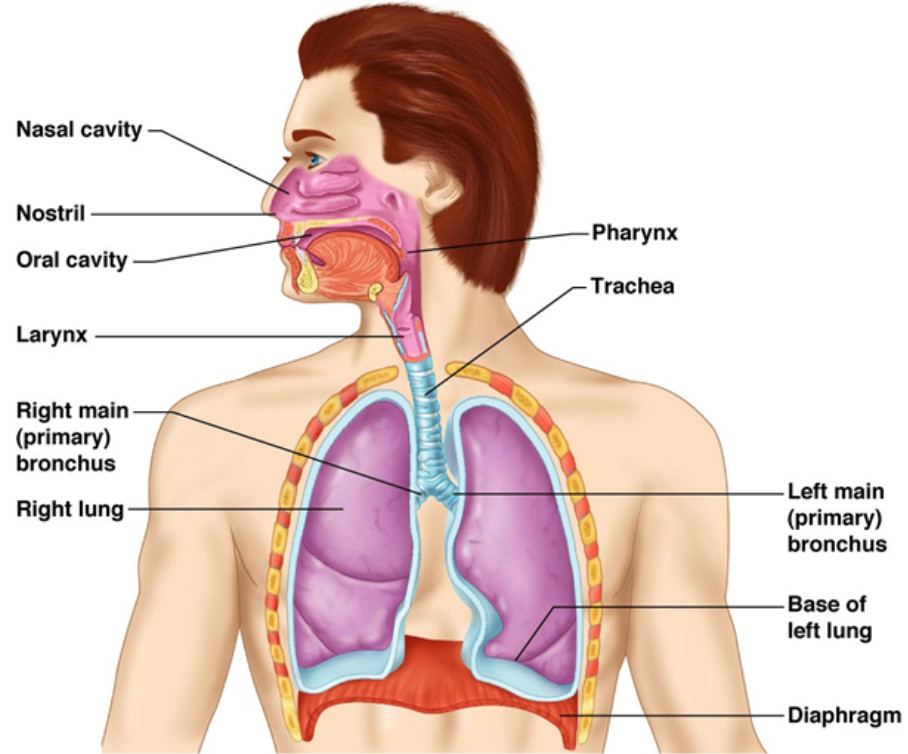
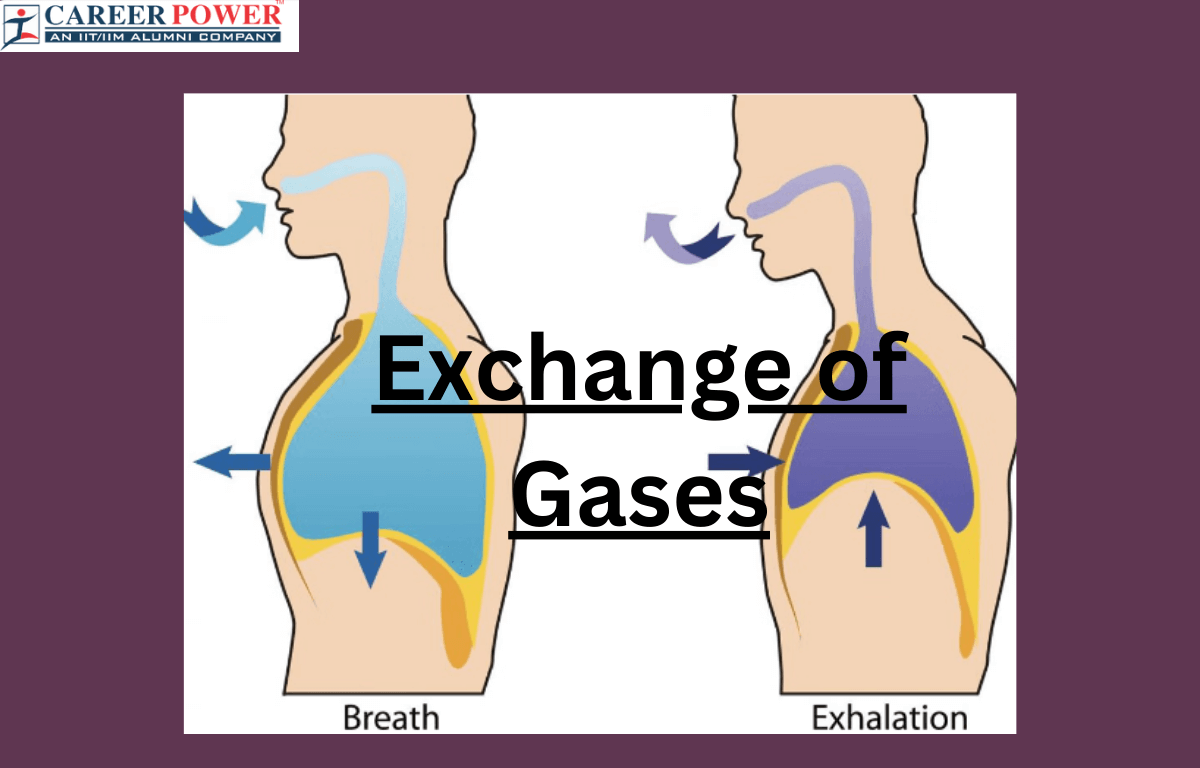
Breathing is a vital process that keeps us alive. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen from the air and exhale carbon dioxide. Our lungs play a crucial role in this exchange. As we breathe in, the diaphragm, a muscle beneath the lungs, contracts, creating space for the lungs to expand. This allows fresh air to flow in and fill tiny air sacs called alveoli. Oxygen then enters our bloodstream, providing energy to our body’s cells. On the exhale, the diaphragm relaxes, pushing out the used air. It’s an automatic process controlled by the Brain to ensure our bodies get the oxygen they need for various activities and functions.
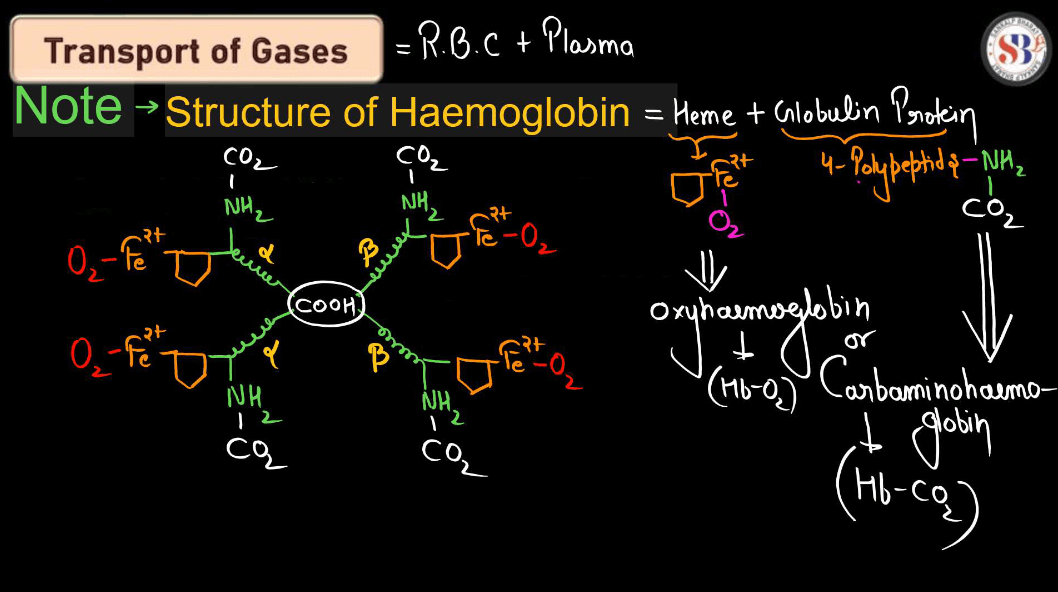
Transport of Gases
During Respiration, the transportation of gases involves the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide in and out of our bodies. When we breathe in, our Lungs take in oxygen from the air, which then binds to red blood cells in our bloodstream. These oxygen-loaded blood cells travel through arteries to reach various tissues and organs, providing them with the oxygen they need for energy production. Simultaneously, carbon dioxide, a waste product generated by our Cells, binds to red blood cells and is transported back to the lungs through veins. Upon exhaling, we release this carbon dioxide into the air. This continuous exchange of gases is essential for sustaining life, ensuring our cells receive oxygen for energy and expelling carbon dioxide to maintain a balanced Respiratory System.
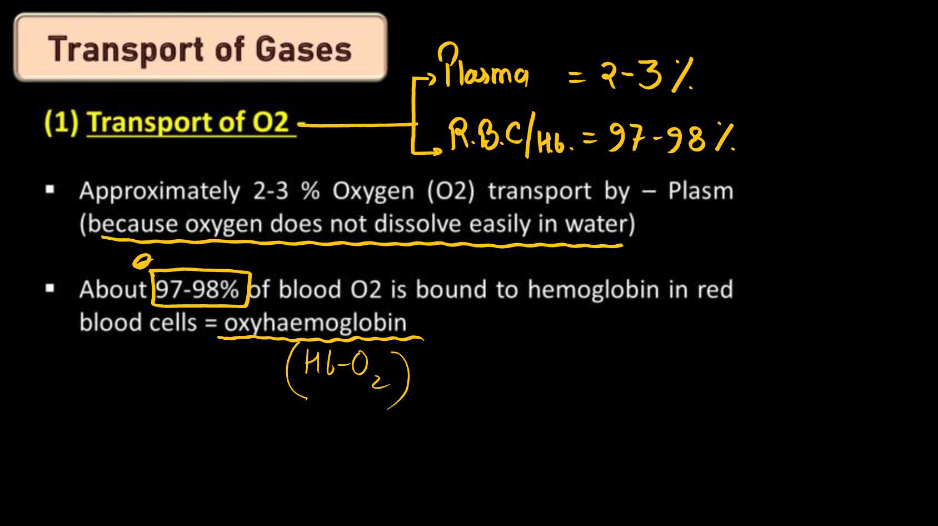
Transportation of Oxygen During Respiration
During Respiration, oxygen transportation occurs in two main steps. First, when we breathe in, oxygen enters our lungs and binds with hemoglobin. Second, Blood rich in oxyhemoglobin travels through arteries to various body tissues. As cells undergo cellular respiration, they release carbon dioxide. Hemoglobin then picks up this carbon dioxide and transports it back to the lungs. Breathing out expels the carbon dioxide from our bodies. So, respiration involves inhaling oxygen, binding it to hemoglobin, delivering it to cells, picking up carbon dioxide, and exhaling it. This process ensures our cells receive oxygen for energy production while efficiently removing waste carbon dioxide.
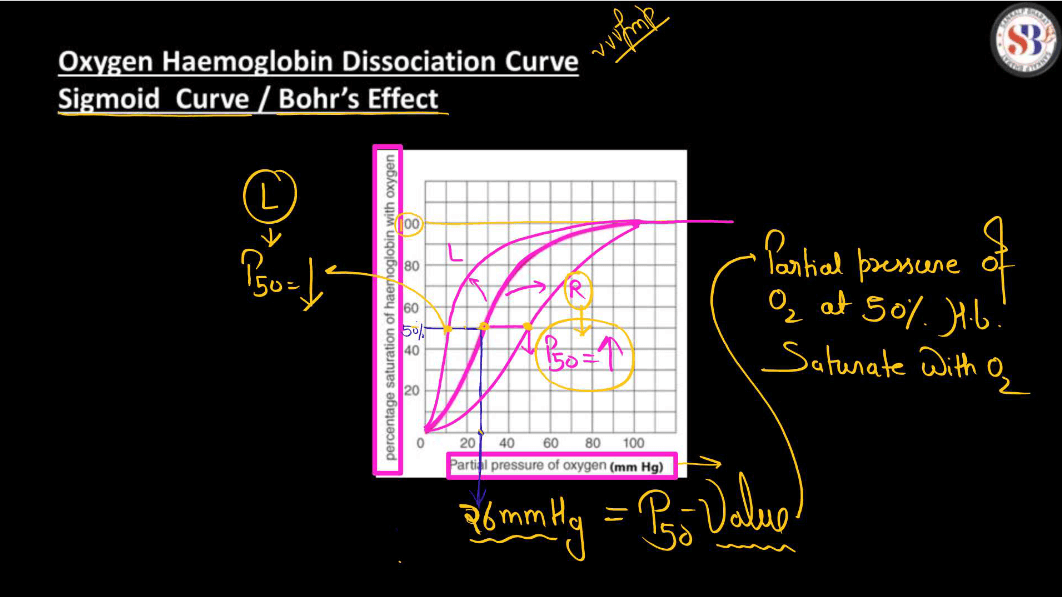
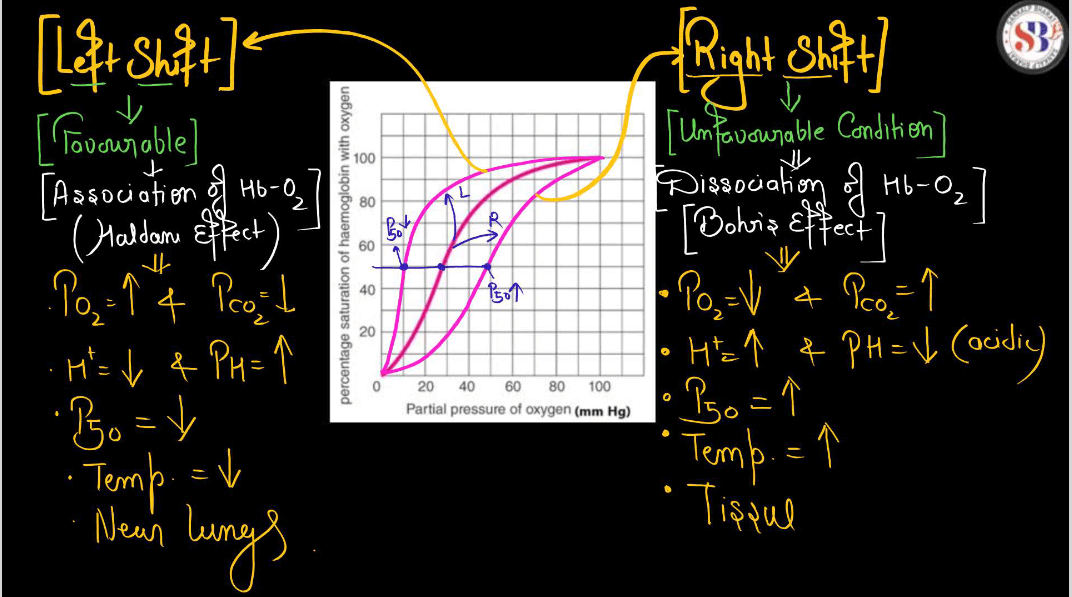
Oxygen Hemoglobin Dissociation Curve
The oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve illustrates how hemoglobin, the protein in Red Blood Cells (RBCs), binds and releases oxygen. In simple terms, think of hemoglobin as a delivery truck and oxygen as its cargo. When the truck is in the lungs (high oxygen environment), it loads up with oxygen easily. As the truck travels through the body (lover oxygen environment), it releases oxygen to tissues. The curve shows this relationship. At high oxygen levels, hemoglobin holds onto oxygen tightly, ensuring efficient loading in the lungs. In areas with lower oxygen, like tissues, the curve allows easy unloading. This adaptability ensures oxygen is delivered where needed most.
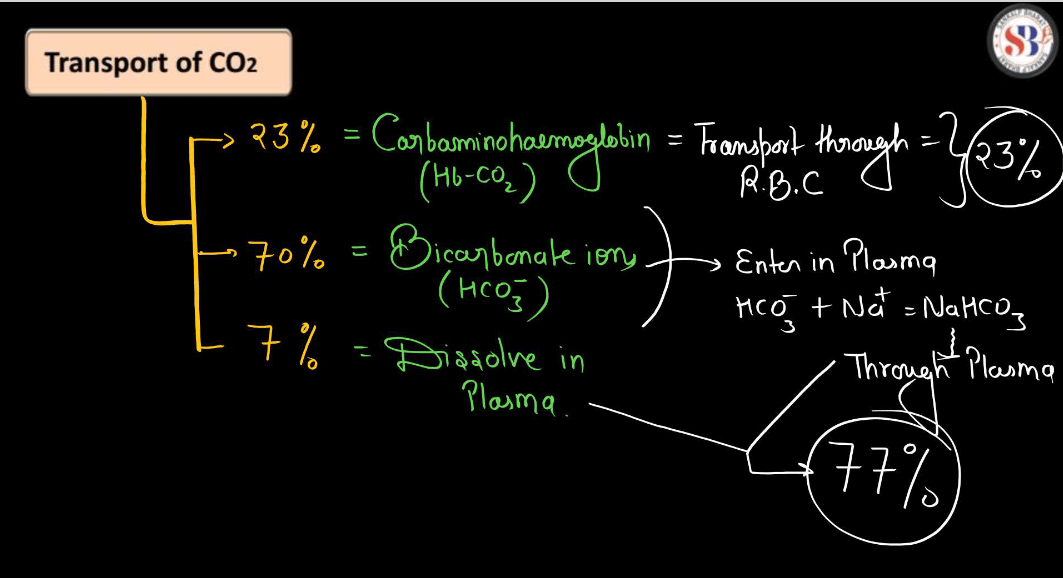
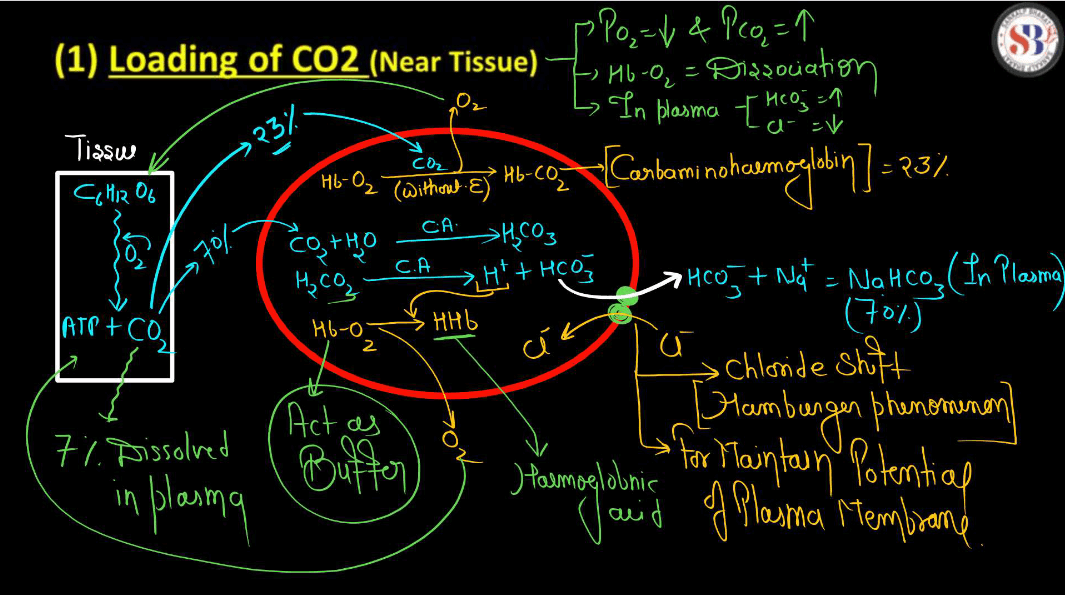
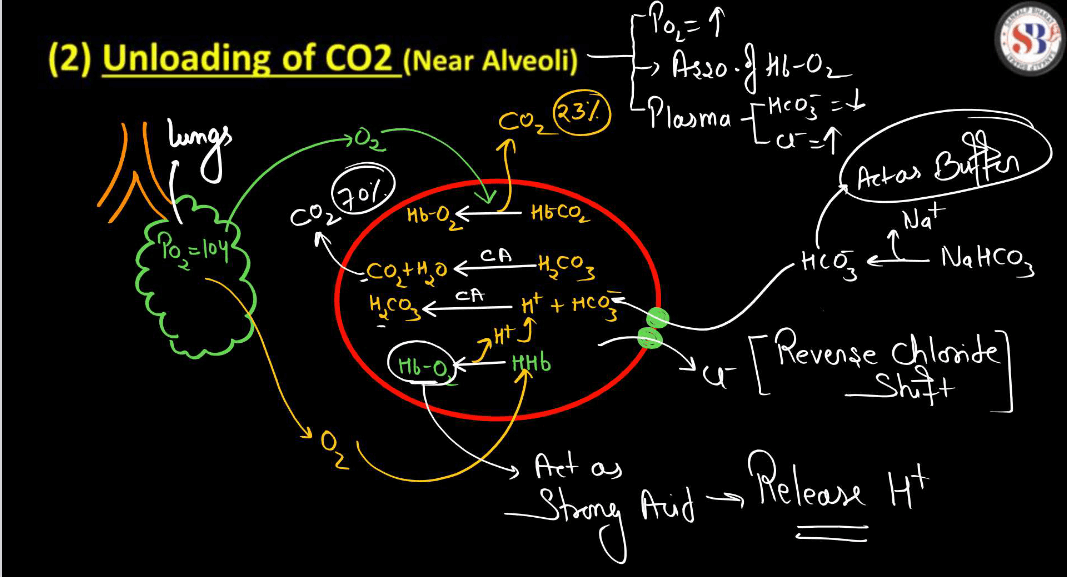
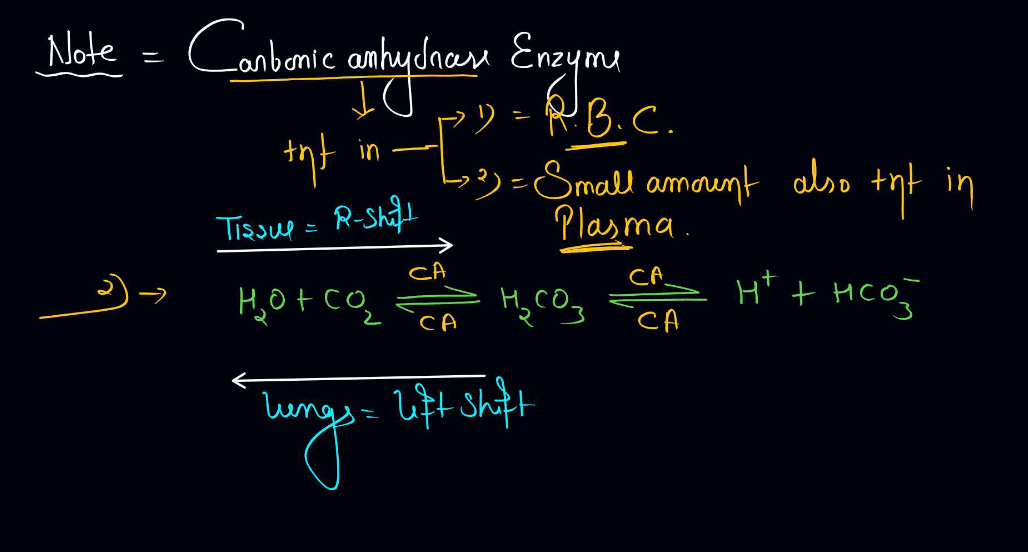
Transportation of Carbon Dioxide During Respiration
During Respiration, cells produce carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste product. This Carbon Dioxide needs to be transported out of the cells to maintain a balance. It mainly travels in the blood, binding with hemoglobin or dissolving in plasma. The bloodstream carries CO2 to the lungs, where it is expelled when we exhale. Hemoglobin helps in forming a compound with CO2 called carbaminohemoglobin. Additionally, some CO2 dissolves directly in the plasma. This transportation process ensures that cells don’t accumulate excess CO2, preventing a buildup that could be harmful. Overall, it’s like a continuous shuttle service in our body, with the bloodstream acting as the route for carbon dioxide to exit cells and reach the lungs for efficient removal during the breathing process.
Disorders of the Respiratory System
Some of the respiratory disorders have been discussed below:
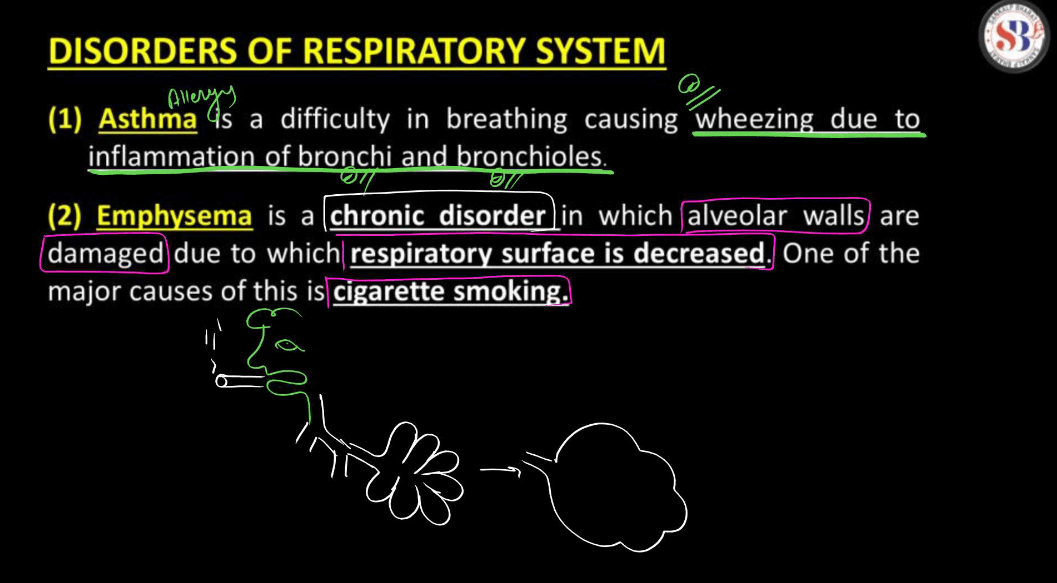
- Asthma: It is a condition where the airways narrow, causing difficulty in breathing, It often involves wheezing and shortness of breath.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): This term includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It’s a progressive lung disease that makes it hard to breathe due to damaged airways.
- Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, often resulting in coughing and production of mucus.
- Pneumonia: An Infection in the lungs causing inflammation. Symptoms include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.
- Lung Cancer: Uncontrolled cell growth in the lungs, often caused by smoking. It can interfere with normal lung function.
- Pulmonary Embolism: A blood clot in the lungs, which can be life-threatening by blocking blood flow.
- Sleep Apnea: Brief interruptions in breathing during sleep, affecting the quality of sleep and causing fatigue.
- Cystic Fibrosis: A genetic disorder causing thick, sticky mucus buildup in the lungs, leading to respiratory and digestive issues.
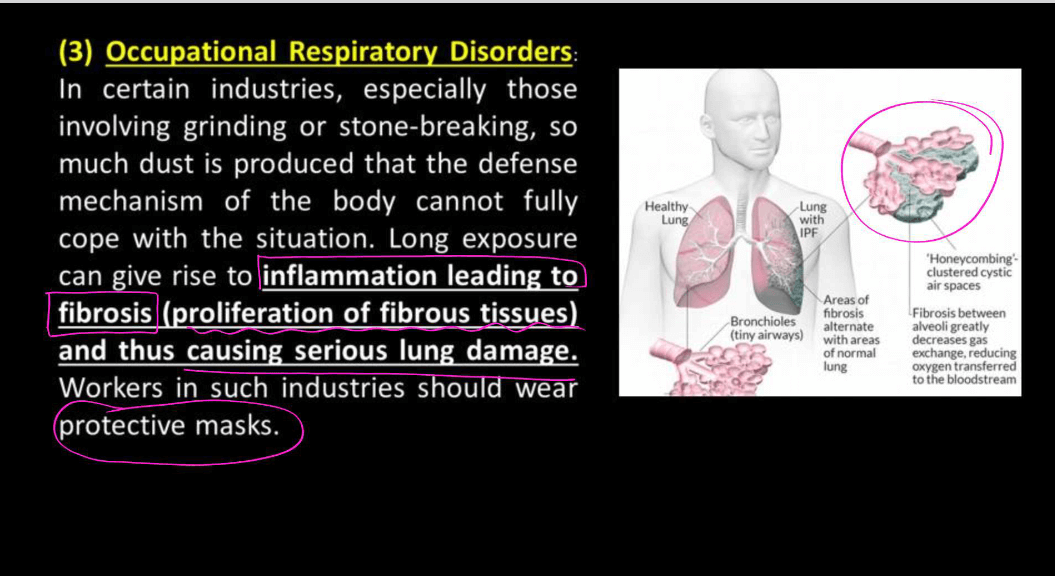
- Interstitial Lung Disorder: Various conditions causing scarring of lung tissues, making it harder for the lungs to expand.
- Tuberculosis (TB): An infectious disease affecting the lungs, causing persistent cough, fever, and weight loss.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













