The part of a flower is an interesting topic in the chapter “How do organisms Reproduce”. This chapter is from the class 10th biology section. All the parts of a flower are briefly explained in our article. A flower is a reproductive structure of flowering plants (or angiosperms) that typically consists of colorful petals, protective sepals, male part stamens, and female part pistils.
Flowers play a crucial role in plant reproduction by attracting pollinators, Helping pollen move between the male and female parts of the plant’s reproductive system, and later on, creating seeds that can grow into fresh new plants. The male part (Stamen) of the Flower consists of Anther and Filament, while the female part (Carpel or Pistil) of the flower comprises Stigma, Style, and Ovary.
Parts of a Flower Diagram
A flower diagram typically consists of several key parts. At the center of a flower is a pistil (female part of a flower), which includes the stigma, the style, and the ovary. Surrounding the pistil are the stamens (the male part of a flower), each comprises of an anther and a filament. The petals, often colorful, encircle the reproductive parts. Lastly, the sepals protect the developing flower bud. This combination of components plays a crucial role in the reproductive cycle of flowering plants.
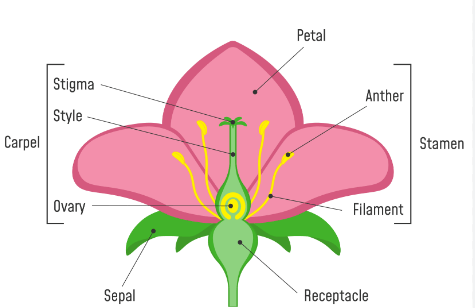
Parts of a Flower and Their Functions
There are a total of 5 main parts of a flower, which are the receptacles, sepals, petals, stamen, and carpel. Each part of a flower has a specific function that contributes to the reproduction process of a plant. These parts of a flower are divided into two parts: The vegetative part and the Reproductive part.
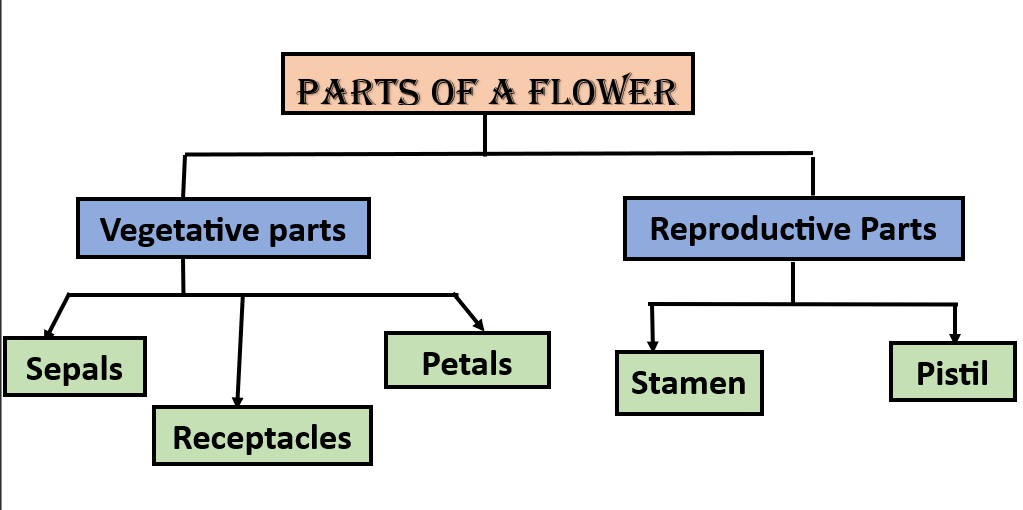
In a flower, the parts that aren’t involved in making seeds are called vegetative parts. These are things like receptacles, petals, and sepals. On the other hand, the parts that help make seeds are the reproductive parts, which include the stamen, pistil, or carpel. Along with the vegetative and reproductive parts, a flower also consists of four Whorls which are calyx, corolla, stamen, and carpel. Here discuss both the vegetative and reproductive parts of a flower. Firstly the main 9 parts of a flower are tabulated below:
| Parts of the Flower | |
| Name of the parts | Description |
| Receptacles | It is the base of the flower where all the floral organs (such as petals, sepals, and stamen) are attached. |
| Sepals | The leaf-like structures found at the base of a flower protect the flower during its budding stage and can be green or colored. |
| Petals | They are the most beautiful, colorful, and delicate parts of a flower. The petals surround the reproductive organs, they also help in attracting pollinators, which leads to the process of pollination. |
| Stamen | The stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower, consisting of filament and anther. The anther produces pollen, while the filament holds the anther in place. |
| Carpel | The carpel is a female reproductive structure of a flower, consisting of a stigma, style, and ovary. |
Vegetative Parts of a Flower
The vegetative parts of a flower are components that support and protect a flower’s reproductive structure. The vegetative parts involve the receptacles, sepals, and petals. All three vegetative parts of a flower combine and contribute to the functioning and success of both pollination and fertilization. Let’s discuss all the vegetative parts of a flower in brief.
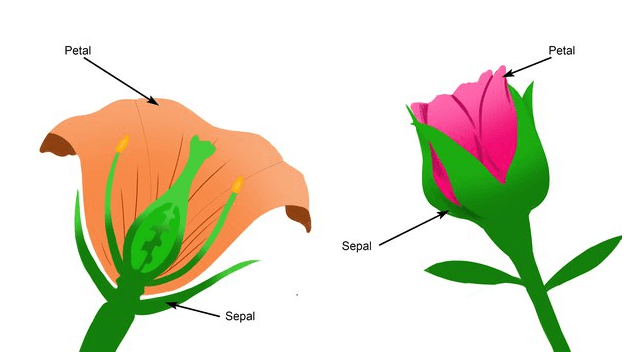
| Different Vegetative Parts of a Flower | |
| Vegetative parts | Description |
| Receptacles | Receptacles are flower base that supports the reproductive parts of a flower and develops into a fruit after fertilization. |
| Sepals | Sepals are the outermost part of the flower which protects the developing bud. |
| Petals | Petals are the brightly colored parts of a flower that help in Pollination by attracting pollinators. |
1. Receptacles
The bottom part of a flower called the receptacle, is where all the different flower parts are connected. It can be said that the receptacles serve as an attachment point for the sepals, petals, stamen, and pistils of the flower. All these parts are arranged around the receptacle in different patterns. The receptacle is an important part of the flower, as it provides support and connection for various reproductive components. The receptacle is not a reproductive part itself, but it gives a platform that supports the floral organs together.
Functions of Receptacles
The receptacle is like a flower’s base that holds and organizes its parts. It also helps carry nutrients and can even play a part in making fruit for certain plants. Although it’s not super specialized, the receptacle does many important jobs in a flower.
- Structural Support: The receptacle provides structural support for the entire flower and holds all the other floral organs which are the sepals, petals, stamen, and pistils. This support makes sure that these reproductive parts are positioned well for effective pollination and fertilization to happen.
- Organ Coordination: By keeping all the flower parts together, the receptacles enable smooth teamwork among the various reproductive organs.
- Nutrient Transport: The receptacles might contribute to moving nutrients around. All the parts of the flower are connected to the vascular system with the help of the receptacles.
- Adaptation and pollination: The receptacle’s size, shape, and features can be adapted to attract specific pollinators, ensuring effective pollination.
- Formation of Fruits: As the flower matures and gets fertilized, the receptacles often transform into parts of a fruit structure, providing a protective enclosure for the developing seeds.
2. Sepals
The sepals are leaf-like structures that form the outermost whorl of a flower, usually green in color. Collectively all the sepals are known as “Calyx”. The sepals or calyx play a great role in protecting the flower when it is in its initial stages or we can simply say when the flowers are in the bud form.
Functions of Sepals
The sepal plays several functions, and these functions can vary among different plant species and types of flowers. The functions of the sepals include the protection of the developing bud, and providing support to the petals, these petals also play a very important role in attracting pollinators and regulating the opening and closing of the flower. Some other important functions of a sepal are discussed below:
- Protection: Sepals enclose and protect the developing flower bud in its early stage, providing a shield against physical damage, pathogens, and harsh weather conditions.
- Determination of flower color: Sepals can influence the coloration of the flower, as their pigmentation can contribute to the overall appearance of the blooming flower.
- Regulation of Bud Opening: Sepals can control the opening of the flower bud, allowing it to open at the appropriate time for pollination and preventing premature blooming. They usually act as a barrier, which helps in preventing the flower from opening.
- Photosynthesis: In some plants, photosynthesis can be performed by the sepals, in the presence of sunlight which gives energy to the plant. However, this feature is less common.
- Sensory Role: Sepals can play a role in sensing and responding to environmental cues, such as changes in light, temperature, or humidity.
3. Petals
The petals refer to the colorful parts of a flower. The petals lie inside the sepals. Collectively all the petals are known as “Corolla”. The petals are usually scented and sticky which allows the flower’s reproductive process by enacting pollinators. The petal’s main function is to attract insects (for pollination) and to protect the reproductive organs which are at the center of the flower.
Functions of Petals
The petals play many important roles, one of them is that the petals help in the reproductive success of the flower by pollinators, protecting reproductive structures, and facilitating the pollination process. Some other important functions of the Petals are discussed below:
- Attraction: Petals are often brightly colored and scented to attract pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds, which leads to the process of fertilization.
- Protection: Petals can shield the reproductive parts of a flower, including the stamen and pistil, from harsh weather conditions and potential damage.
- Advertisement: The shape, color, and patterns of the petals can convey information to the pollinators about the flower’s nectar availability and suitable pollination.
- Landing Platform: Petals provide a stable platform for pollinators to land on, making it easier for them to access the flower’s nectar and pollen. This makes sure that the pollen grains are transferred for Fertilization.
- Environmental Sensing: Petals can respond to environmental changes such as temperature and light, influencing their opening and closing, which affects pollination
Reproductive Parts of a Flower
A flower consists of both male and female reproductive structures that enable the process of reproduction in plants. The male reproductive part of a flower is known as the Stamen which consists of a filament and anther. The anther consists of the plant’s male reproductive cells or sperms, and the female reproductive part of a flower is known as the Pistil which consists of the stigma, style, and ovary. All three parts of the pistil work together and help in the formation of seeds and fruits. We have discussed both Stamen and Pistil or Carpel below.
| Reproductive Parts of a Flower | |
| Reproductive Parts | Description |
| Stamen | The stamen is the male reproductive organ of a flower which consists of anther and filament. |
| Carpel or Pistil | The carpel is the female reproductive organ of a flower which includes stigma, style, and ovary. |
1. Stamen
The stamen is the little stalks with swollen tops just inside the ring of petals in a flower. The male reproductive organ of plants is known as Stamen. The stamen produces pollen grains. The stamen is a set of two parts other parts which are: the Filament and an Anther. The filament is the stalk of the stamen, while the anther is the swollen top of the stamen. The making and storing of the pollen grains is done by the anther of the stamen. The pollen grains appear as a yellow, powder-like substance.
The male gametes or male sex cells of the plant are present in the pollen grains. It is clear from the above discussion that the male gametes of a plant are made in the anther of the stamen. There are a very large number of stamens present in each flower.

Functions of the Stamen
The stamen has many different functions, one of them is the success of the reproduction process and genetic diversity of a flowering plant. The stamen is a set of two different parts: the filament and the anther. We have mentioned all the important functions of a stamen below.
- Pollen Production: The anther is responsible for producing pollens. These pollens contain the male reproductive cells called sperms, which are necessary for fertilization.
- Male Gamete Dispersal: The pollens are released into the environment with the help of the anther. These pollens can be carried by various pollinating agents like insects, birds, wind, or water to the other flower, which helps in the process of cross-pollination.
- Genetic Diversity: The stamen also helps in promoting genetic diversity within a plant population.
- Reproduction: The stamen and its pollen must coordinate with the Pistil (female reproductive parts) of other flowers for successful fertilization. This coordination makes sure that the pollens are transferred.
- Pollen Tube Formation: After pollination, the pollen tube formation occurs when the pollen grain lands on the stigma of the pistil. These pollen tubes grow down through the style, which delivers sperm cells to the ovules within the ovary for fertilization.
2. Carpel
The carpel is present at the center of a flower, which is a flask-shaped organ. The female reproductive organ of the flower is known as the Carpel. A carpel consists of three main parts: The stigma, style, and ovary. Where the topmost part of the carpel is known as Stigma. The Sigma is a sticky surface where pollens are received. The stigma helps in receiving the pollen grains from the anther of the stamen (at the time of pollination). The connecting link between the stigma and the ovary is known as style. There may be one or multiple carpels in each flower. All parts of the carpel or pistil work together for the proper functioning of the carpel.
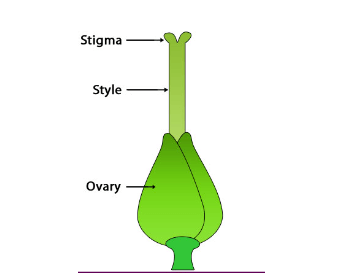
Functions of a Carpel or Pistil
The female reproductive structure found in a flower is the carpel or pistil. The main function of the Pistil or Carpel is to receive pollen, facilitate the fertilization process, and protect and nurture the developing seeds within the ovary. Other functions of the pistil are discussed here.
- Reproductive structure: The carpel is the female reproductive organ of a flower, responsible for producing and protecting the ovules.
- Ovule Enclosure: The carpel’s main function is to enclose and protect the developing ovules, which eventually develop into seeds after fertilization.
- Fertilization: Within the ovary, these pollens fertilize the ovule (egg-containing structures). This results in the formation of seeds.
- Seed Development: The ovules develop into seeds, after a successful fertilization. The protection and nourishment of these developing seeds is also provided by the pistil.
- Chemical Signaling: Specific chemicals and scents are released by these pistils or carpels that attract pollinators, and then these pollinators help in the transfer of pollens from one flower to the other.
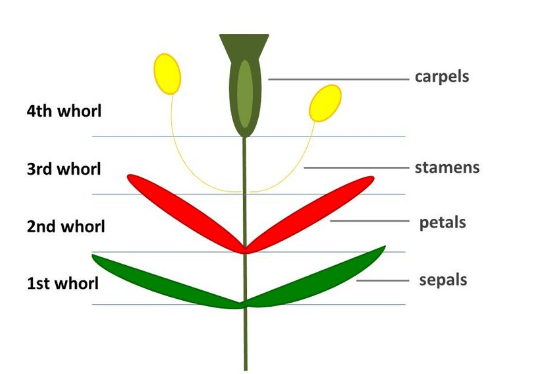
Whorls of a Flower
The whorls of a flower refer to the concentric rings of floral organs that are arranged around the central axis of a flower. A flower consists of a total of four whorls that are – the calyx, corolla, stamen, and carpel. Variations in the number, arrangement, and fusion of these whorls contribute to the diverse array of flower shapes and sizes observed in the natural world. All four types of Whorls of a flower are briefly discussed below.
| Different Whorls of a Flower | |
| Whorls | Description |
| Calyx | Calyx are the outermost whorls, made up of sepals. |
| Corolla | Corolla are the whorls present inside the calyx, composed of petals. |
| Stamen | Stamen is the male reproductive structure of a flower. |
| Carpel | The carpel is the female reproductive structure of a flower. |
Calyx
The outermost whorl of a flower is known as a Calyx, typically composed of individual leaf-like structures known as sepals. These sepals are generally green in colour, they encircle the base of the flower, and these sepals also play a great role in protecting the developing bud before it opens. The most important function of the calyx is to provide support and protection to the inner floral structure as it develops. When the flowers are fully opened, the sepals of the flower may remain small or change various shapes and colors, depending on the plant species.
Corolla
The second whorl of a flower is known as the Corolla, located just inside the calyx. One or more petals together are called corolla, these corollas are usually colorful and often play a role in attracting pollinators like insects, birds, or even bats. The petals are typically larger and more delicate than the sepals of the calyx. The corolla’s appearance, color, and shape can greatly vary across different plant species, reflecting adaptations to their specific pollination strategies.
Stamens
As we already discussed, the stamen is the male reproductive structure of a flower. Each stamen mainly consists of two parts: a filament and an anther. The pollens are produced by the anther, these pollens contain the male gametes which are necessary for fertilization.
Carpels
The carpels are known as the flower’s female reproductive structures. Every carpel has its own ovary, style, and stigma. The ovary contains the female gametes which are known as ovules. After fertilization, the ovaries develop into fruits. The other details about the carpel are discussed in the above paragraphs.
Also Read,


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













