Endomembrane System
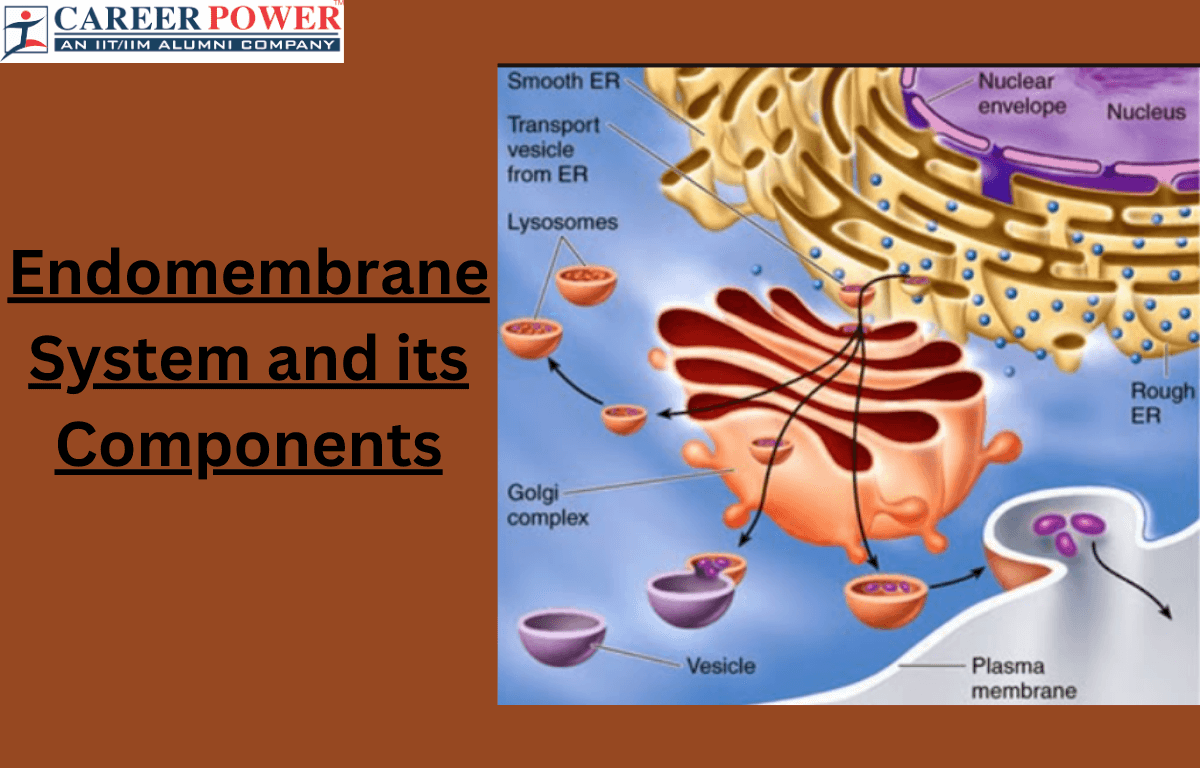
The endomembrane system is like a transportation and processing network within cells. It includes structures like the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi Apparatus, Vesicles, and Lysosomes. The ER is like a factory floor where proteins and lipids are made. These molecules then move to the Golgi Apparatus, which acts like a packaging and shipping center, modifying and sorting them for specific destinations inside or outside the cells. Vesicles are small sacs that transport these molecules between different parts of the endomembrane system or the cell surface. Lysosomes, on the other hand, are like recycling centers, breaking down waste materials. Overall, the endomembrane system plays a crucial role in maintaining cell structure, producing important molecules, and managing cellular waste.
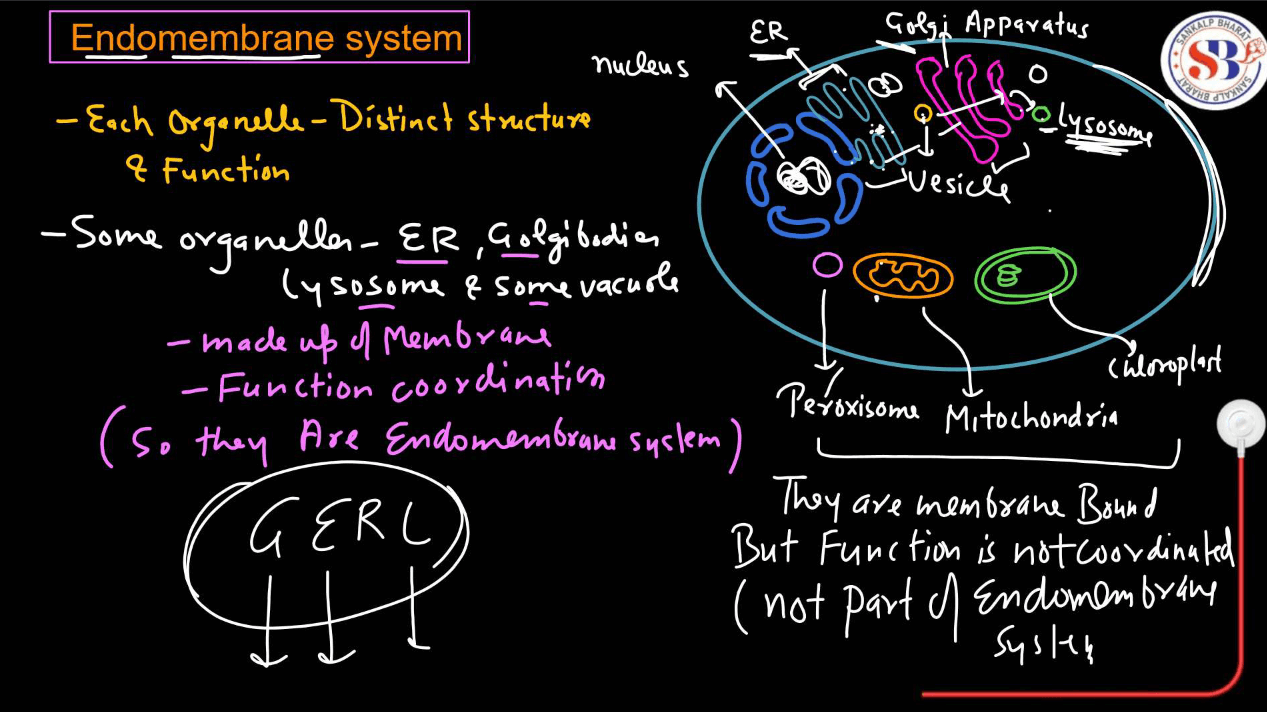

Different Components of Endomembrane System
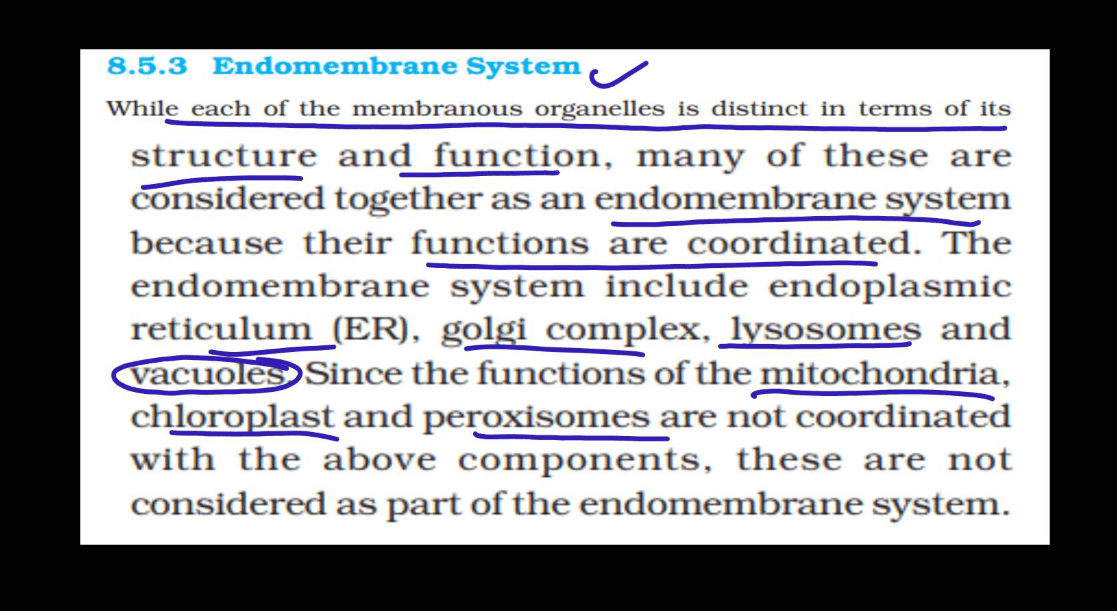
The endomembrane system is a network of membranes within a cell that work together to perform various functions related to protein synthesis, transport, and secretion. These components work together to ensure the proper synthesis, modification, sorting, and transport of proteins, lipids, and other molecules within the cell. Here are the main components of the endomembrane system:
| Different Components of Endomembrane System | |
| Nuclear Envelopes | The nuclear envelope is like a protective barrier around the nucleus of the cell. It helps regulate what goes in and out of the nucleus, keeping the cell’s genetic material safe. |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is like a transportation system inside a cell. It helps make and transport proteins and other molecules to where they are needed, like a busy highway in a city. |
| Golgi Apparatus | The Golgi apparatus is like a cell’s packaging and shipping center. It modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other molecules before sending them to different parts of the cell or outside. |
| Lysosomes | Lysosomes are like the recycling center of a cell. They contain enzymes that break down and recycle waste materials, old cell parts, and foreign substances to keep the cell clean and functional. |
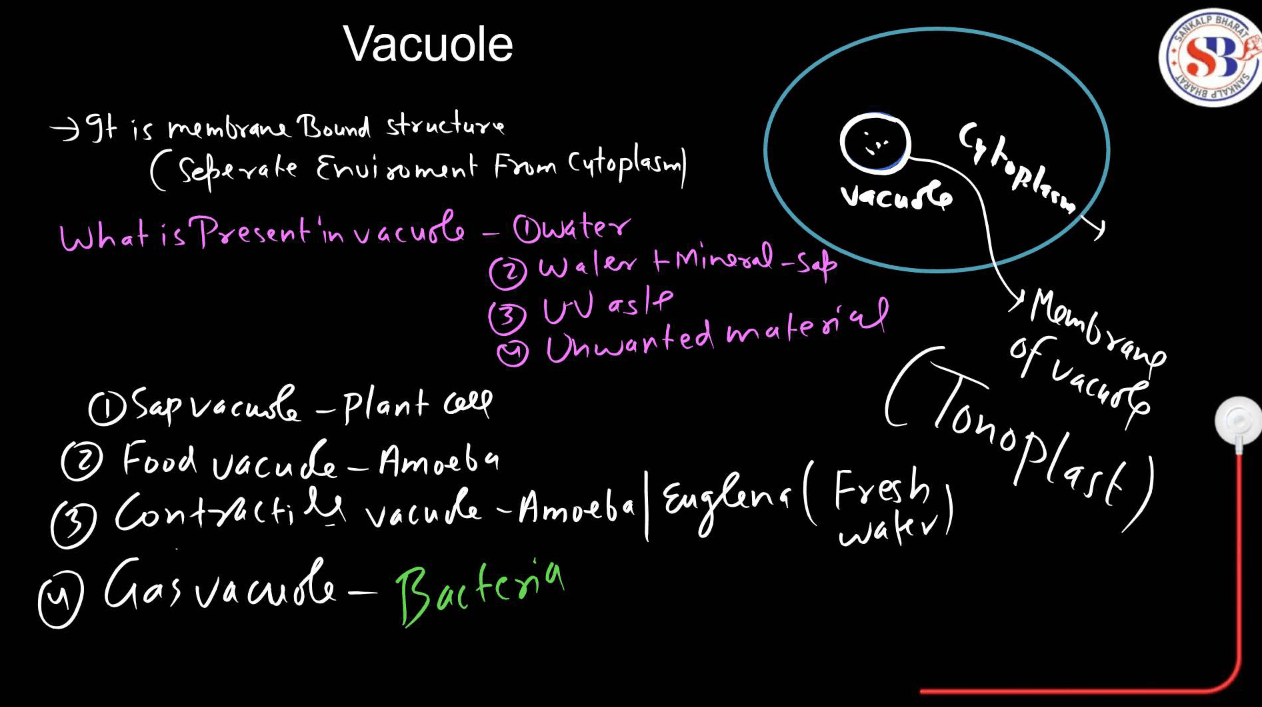
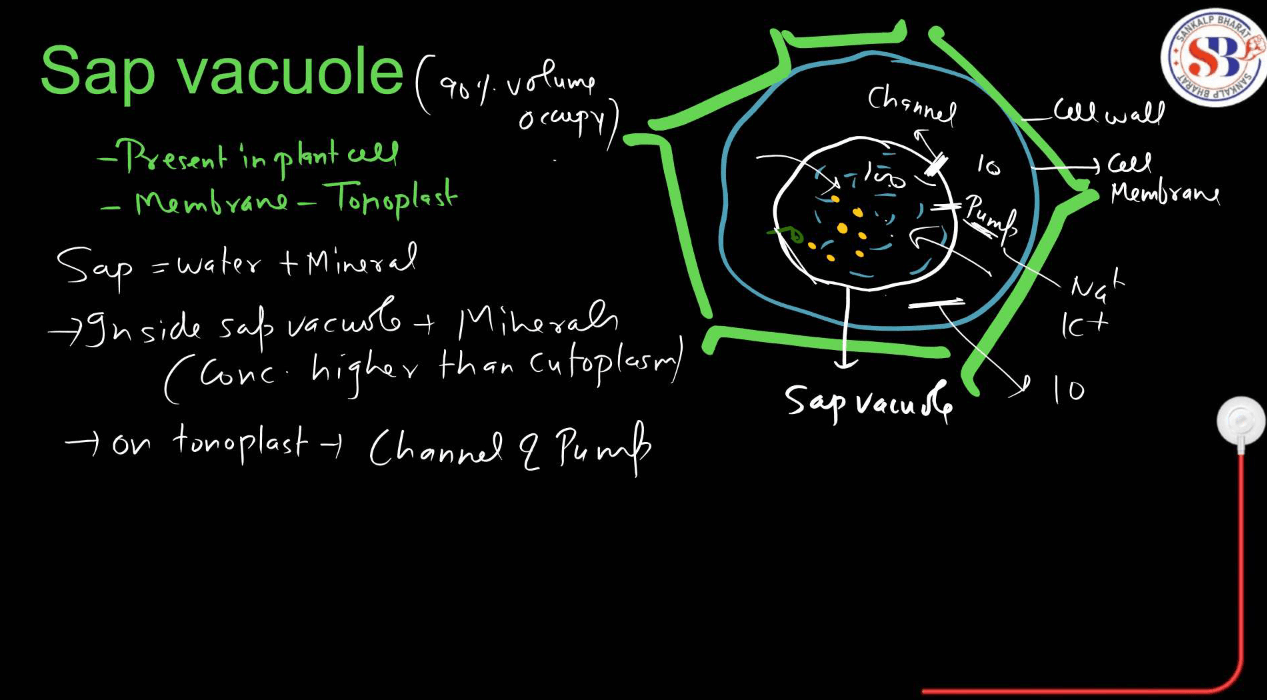
| Vacuoles | Vacuoles are like storage units in a cell. They store water, nutrients, and waste products. In plant cells, they also help maintain cell structure and support the plant’s growth. |
Nuclear Envelope
This is a double membrane that surrounds the nucleus and separates it from the cytoplasm. It contains pores that allow for the exchange of materials between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
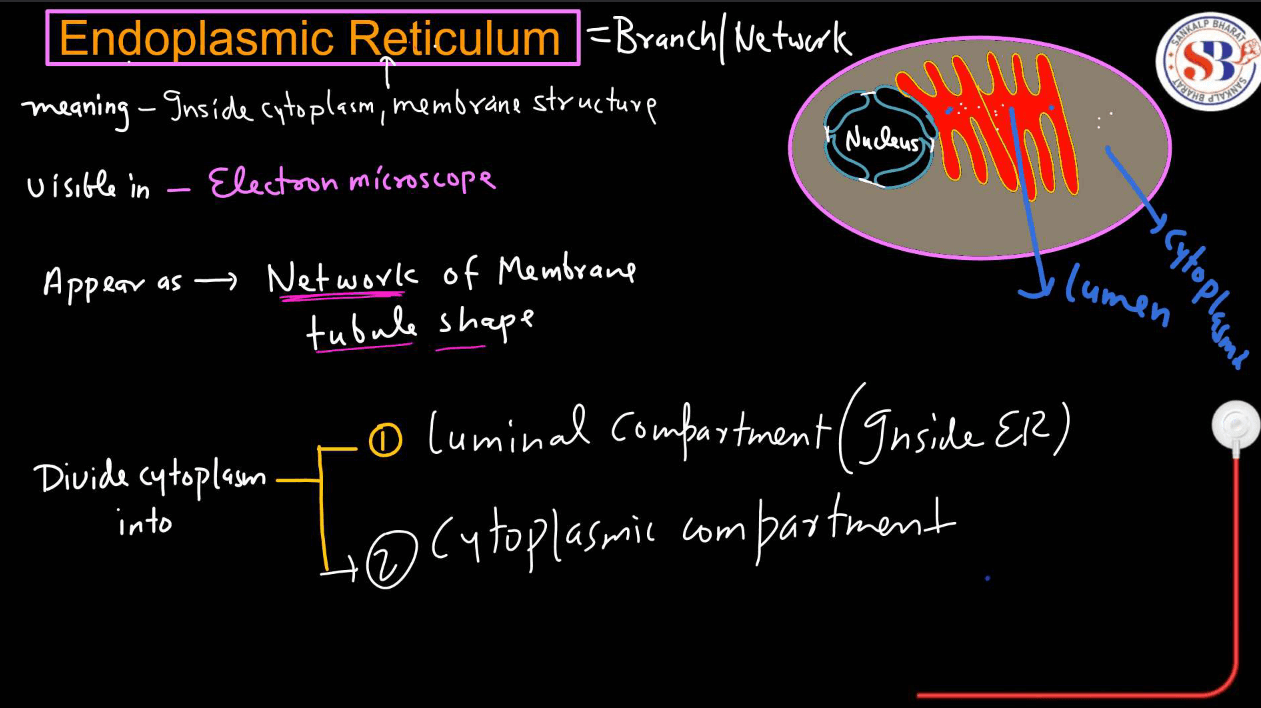
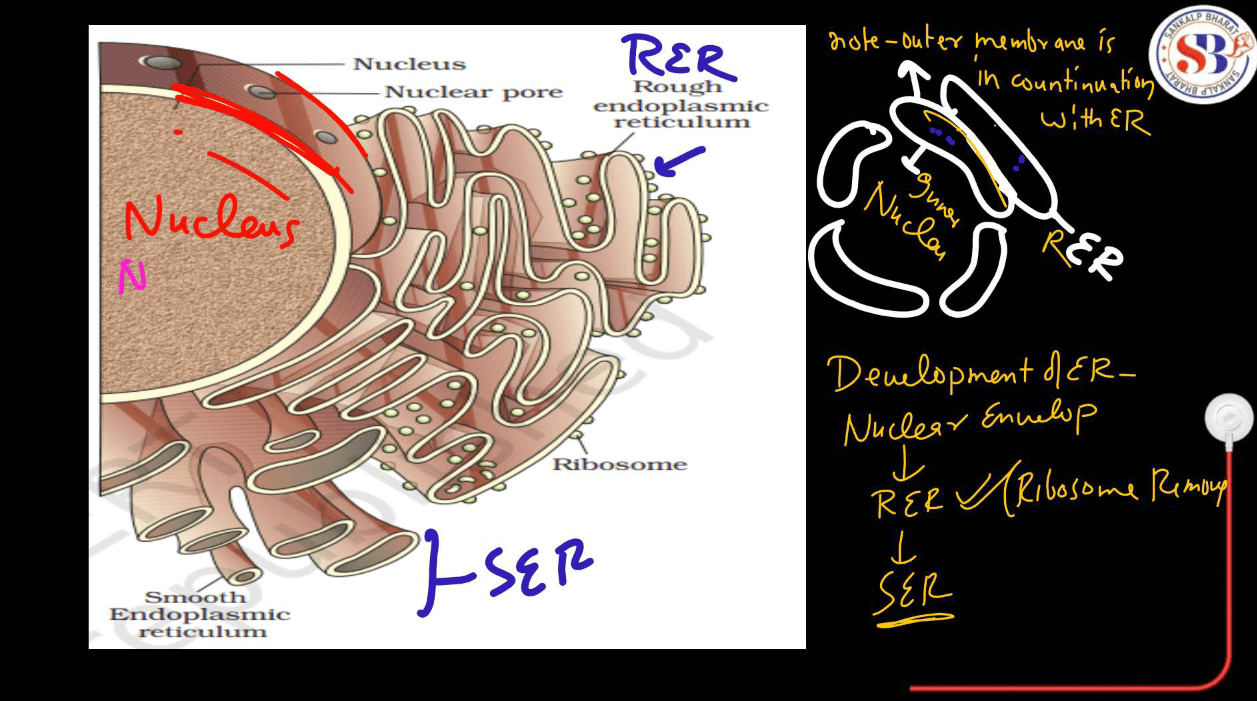
Endoplasmic Reticulum
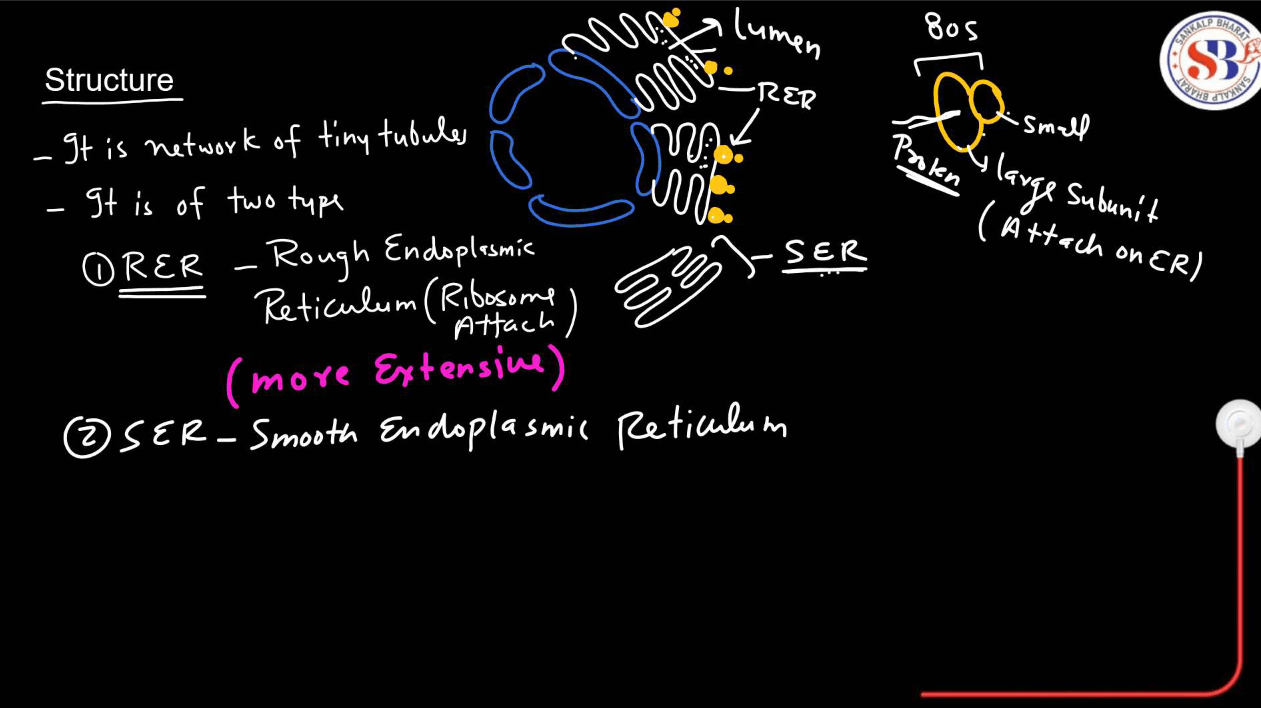
The endoplasmic reticulum is of two different types-
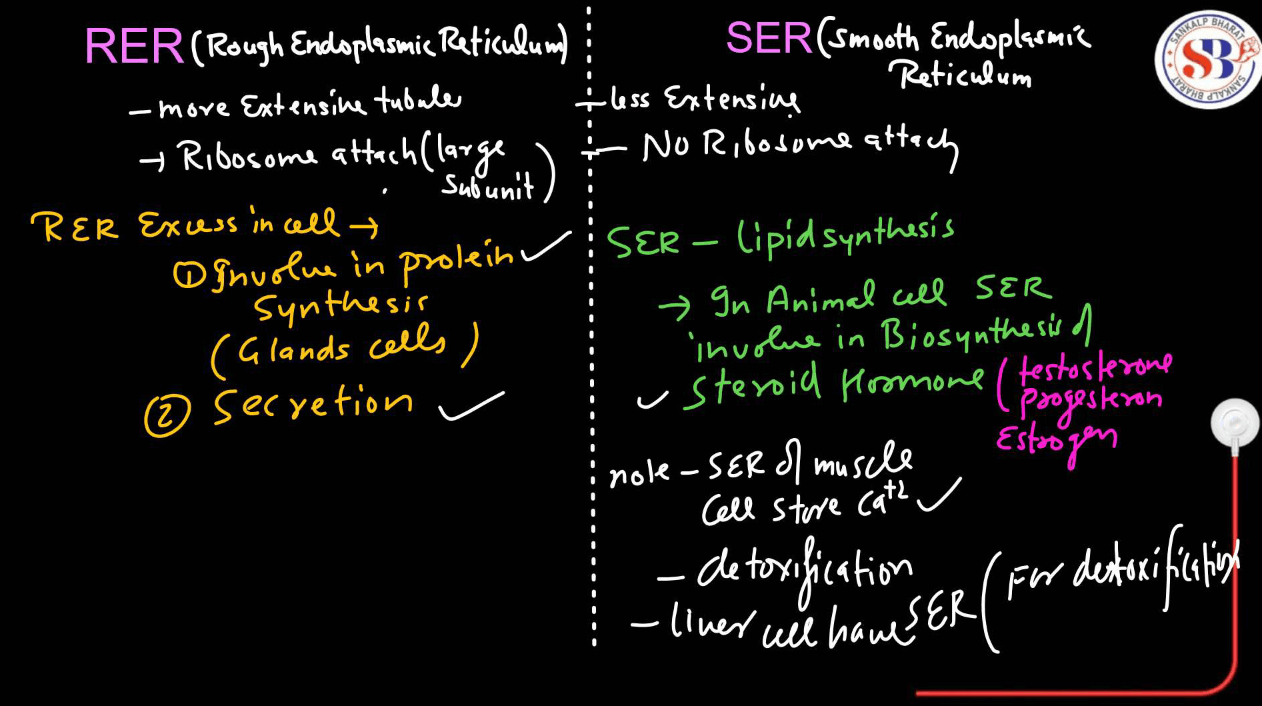
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: Studded with ribosomes on its surface, involved in protein synthesis and initial protein synthesis and initial protein folding.
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum: Lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium ion storage.
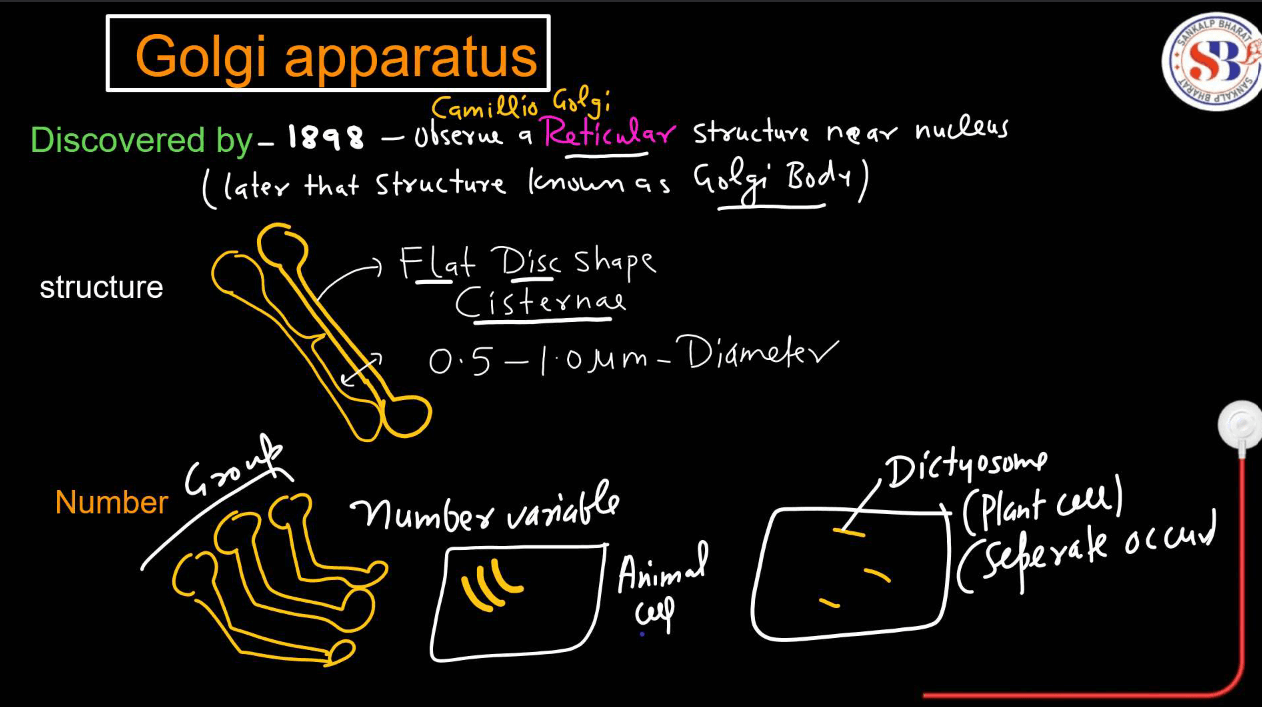
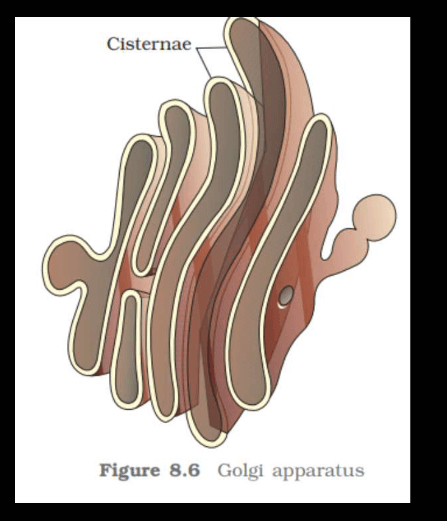
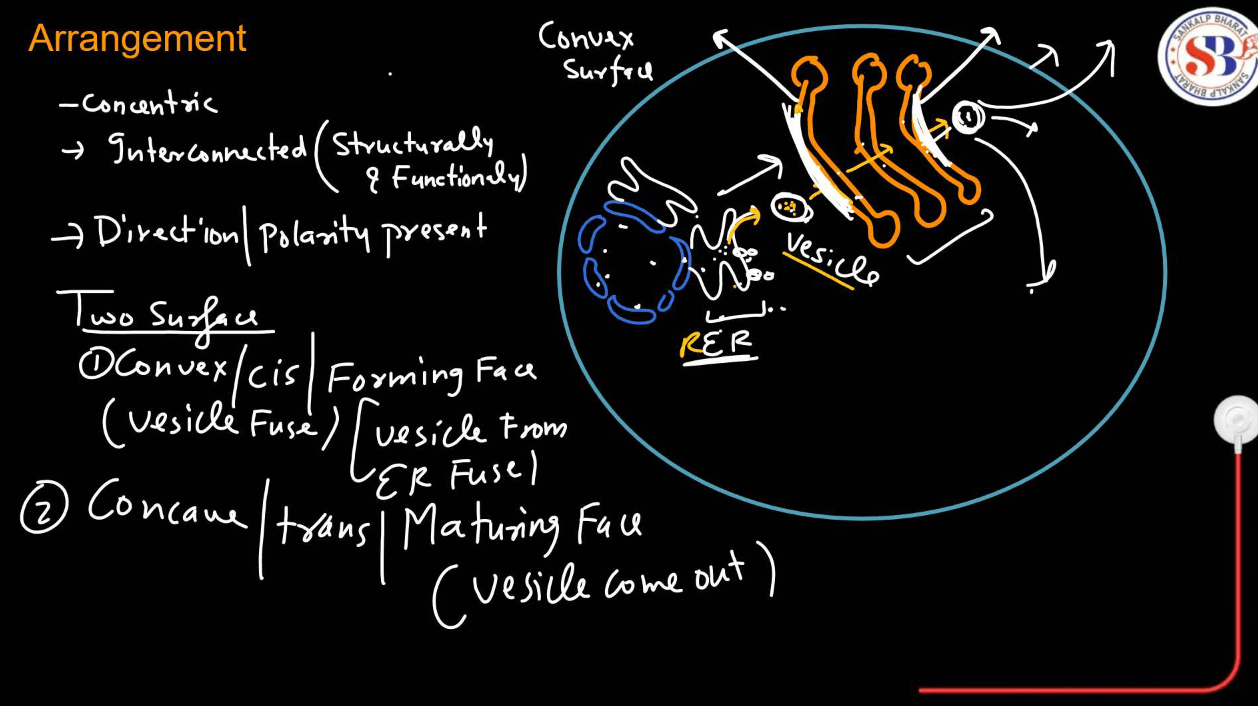
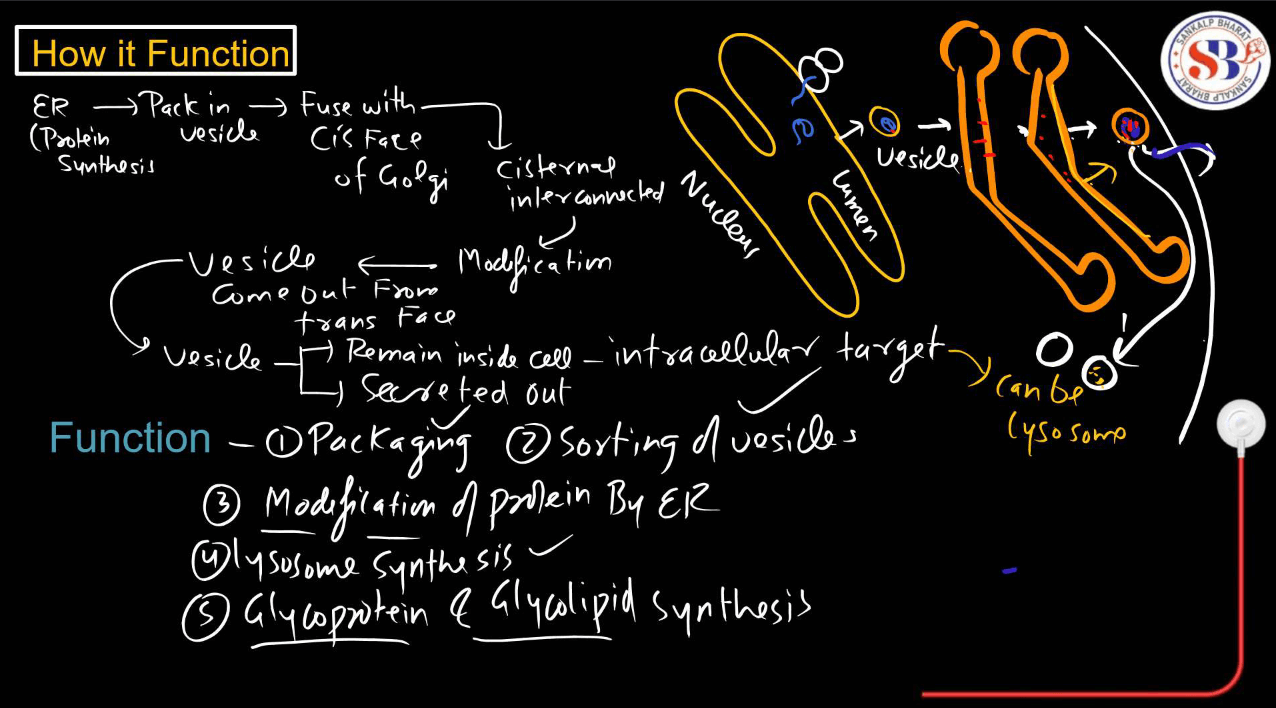
Golgi Apparatus
Consists of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae. It possesses, sorts, and modifies proteins and lipids received from the ER and packages them into vesicles for transport.
Vesicles and Vacuoles
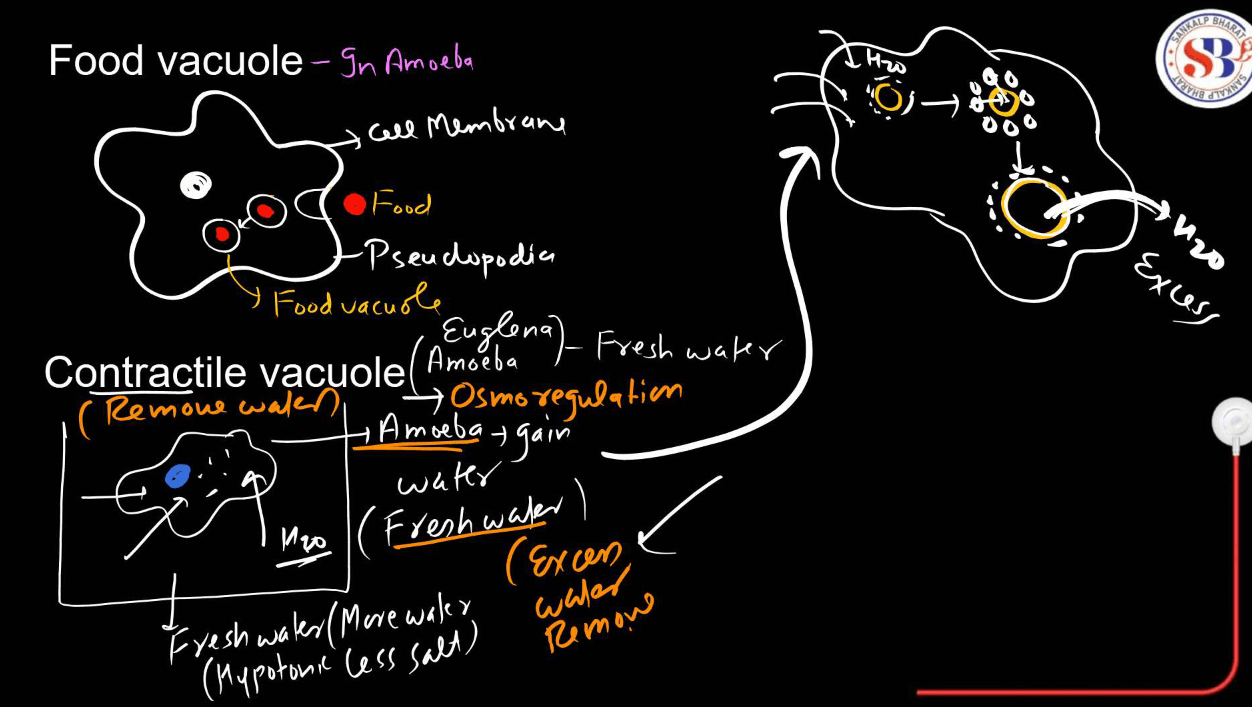
Small membrane-bound sacs are involved in various transport processes. Vesicles transport materials between organelles and to the cell membrane, while vacuoles are larger and can store substances like water, nutrients, or waste.
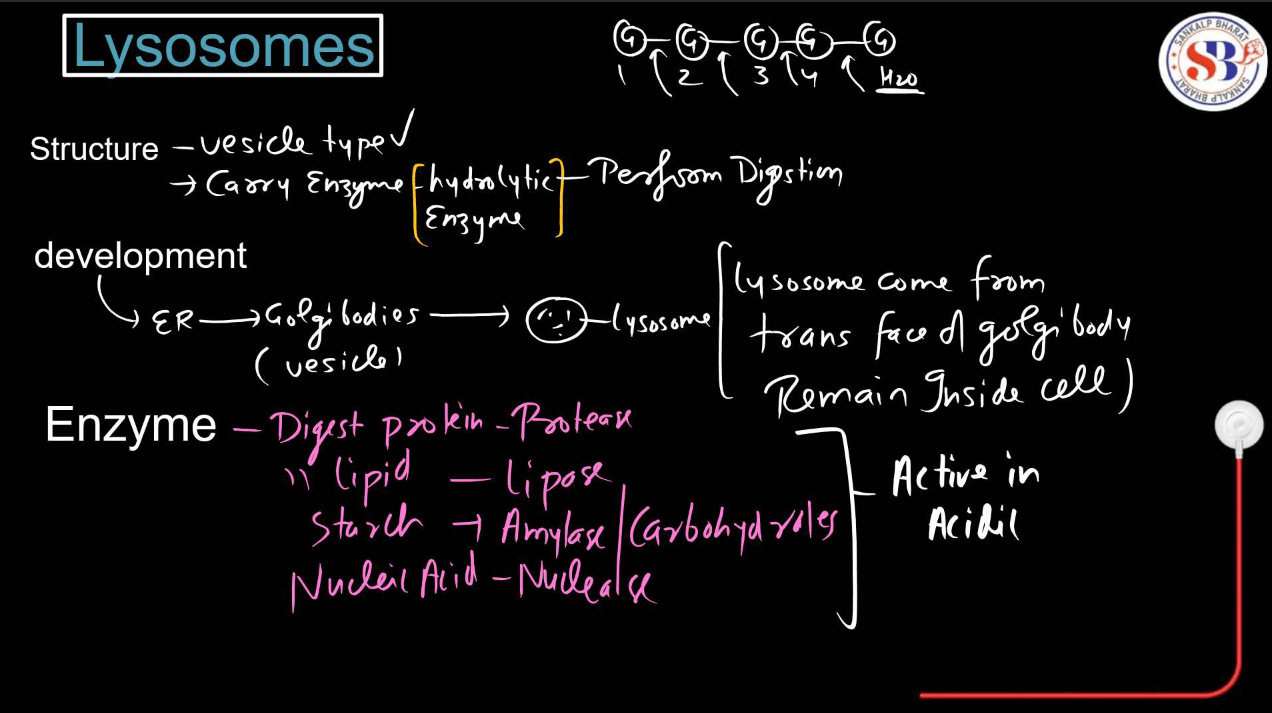
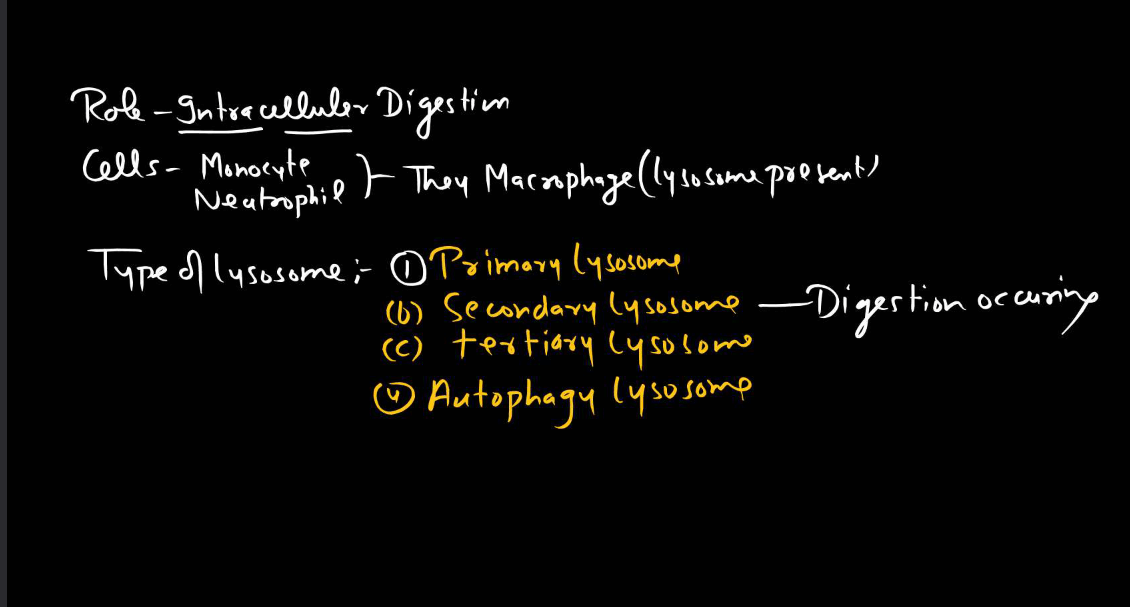
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles containing digestive enzymes. They break down macromolecules, old organelles, and foreign substances through a process called autophagy.
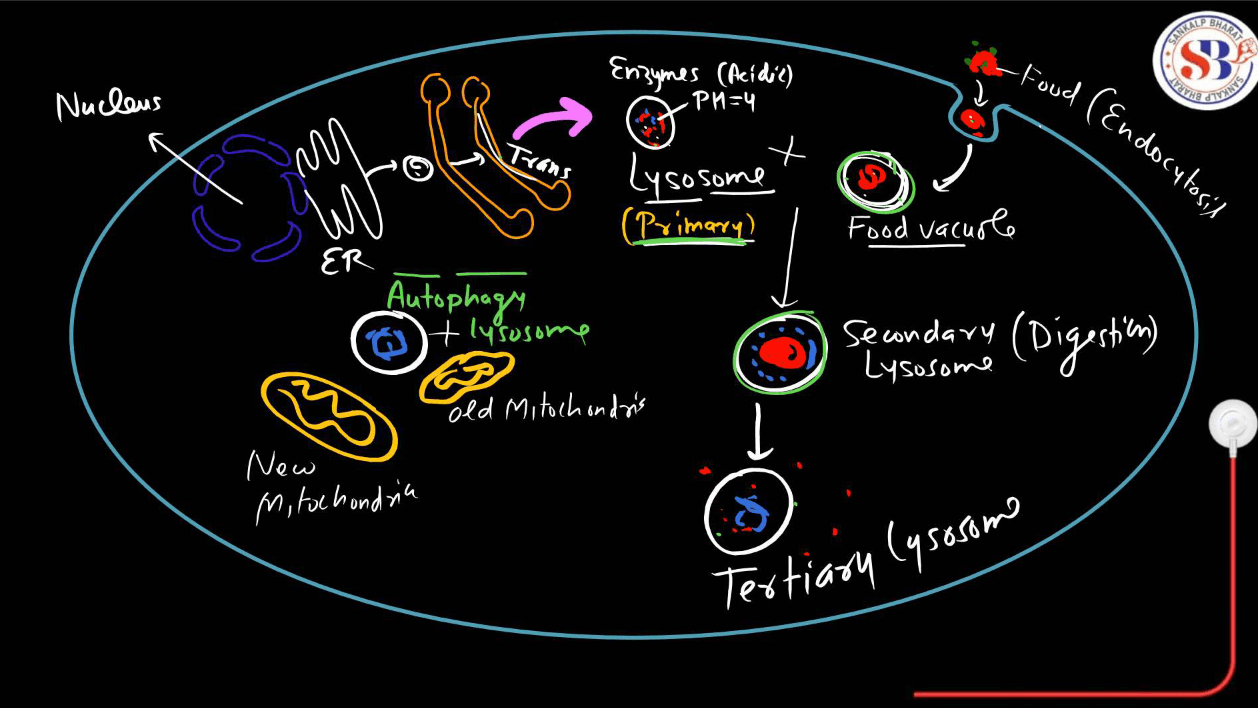

Endosomes
The Endosomes are membrane-bond vesicles that transport materials from the cell membrane, sorting them for recycling or degradation.
Peroxisomes
Peroxisomes are membrane-bound organelles that are involved in processes such as lipid metabolism, detoxification of harmful substances, and breaking down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
Plasma Membrane
While not part of the endomembrane system, it interacts with it extensively. The plasma membrane regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell, and vesicles are constantly exchanging materials with it.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













