Cell organelles are specialized structures within a cell that have specific functions. Some of the cell organelles are Ribosomes, Cell membranes, Cytoplasm, Vacuoles, Golgi Apparatus, Mitochondria, Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), nucleus, and many more. The Golgi apparatus is one of the cell organelles that is responsible for packaging, modifying, and distributing proteins and lipids to various parts of the cell. It acts like a post office of the cell, ensuring that cellular products reach their intended destinations. Here is a brief description of the Golgi apparatus below in the article.
Definition of Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi Apparatus is a cellular organelle found in Eukaryotic cells. It plays a key role in processing and packaging proteins and lipids synthesized by the cells. The Golgi apparatus modifies these molecules and sorts them for transport to their final destination, either within the cell or outside of it. It consists of a series of flattened sacs or cisternae and is an essential part of the endomembrane system in cells.
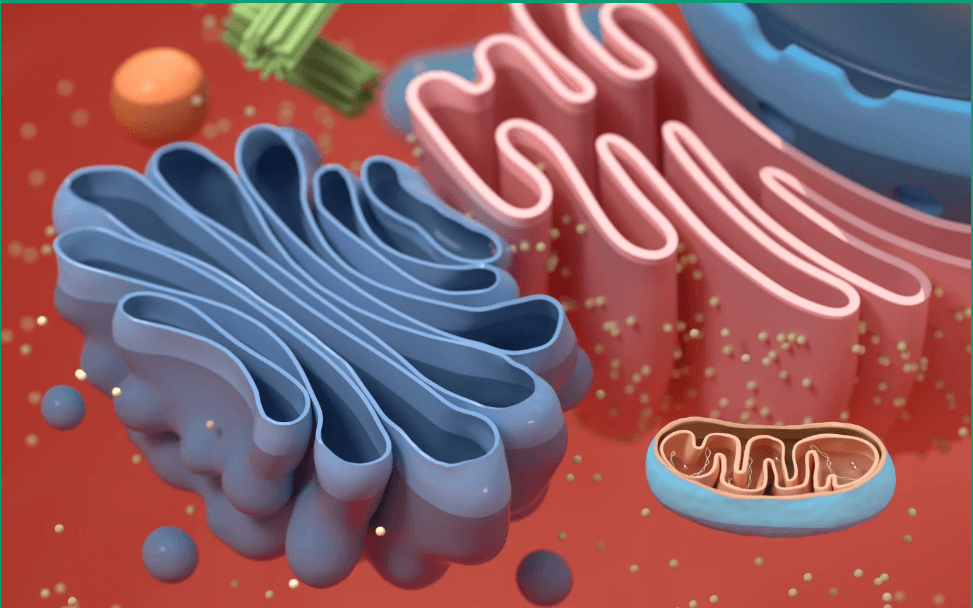
In addition to its role in processing and packaging proteins and lipids, the Golgi apparatus also helps in the glycosylation of proteins, where sugar molecules are added to proteins to form glycoproteins. This process is crucial for the proper functioning of many proteins. The Golgi apparatus has a cis face, which receives materials from the endoplasmic reticulum, and a trans face, which dispatches the modified molecules to their final destinations. It also plays a role in the synthesis of certain macromolecules, such as polysaccharides.
Overall, the Golgi apparatus is vital for cellular transportation and secretion, ensuring that newly synthesized molecules are properly modified, sorted, and sent to the appropriate places within and outside the cell.
Discovery of Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus was discovered by an Italian scientist named Camillo Golgi in the late 19th century. He observed this cellular organelle in 1898 and later described its structure and function, which involves packaging, modifying, and transporting proteins within the cell. His discovery significantly contributed to the understanding of cell Biology.
Golgi Apparatus – Diagram
The diagram of the Golgi apparatus typically shows a series of flattened, membranous sacs or vesicles. These sacs are arranged in stacks called cisternae. The Golgi apparatus is involved in modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids that are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum. It plays a key role in the transportation of these molecules to their final destinations within the cell or outside of the cell. The diagram often illustrates the process of synthesis and transport within cells.
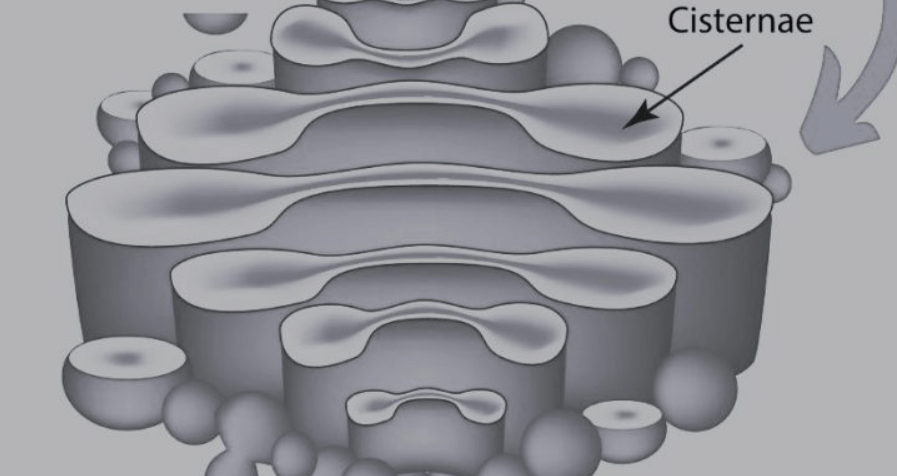
Structure of Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus has a distinctive structure consisting of flattened, membrane-bound sacs called cisternae. These cisternae are stacked on top of each other, resembling a stack of pancakes. The Golgi apparatus is often divided into three main regions based on its structure and function:
| Different Regions of Golgi Apparatus | |
| Golgi Apparatus Region | Function |
| Cis-Golgi Network (CGN) | Receives vesicles containing proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| Medial Golgi | Modifies proteins and lipids through processes like glycosylation and sulfation. |
| Trans-Golgi Network (TGN) | Trans-Golgi network packages modified molecules into vesicles for transport to their final destinations within or outside the cell. |
- Cis-Golgi Network (CGN): This is the entry face of the Golgi apparatus, where it receives vesicles containing proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum for further processing.
- Medial Golgi: The proteins and lipids received from the CGN pass through the media Golgi, where they undergo various modifications, including glycosylation and sulfation. These modifications are essential for the proper structure and function of the molecules.
- Trans-Golgi Network (TGN): This is the exit face of the Golgi apparatus. Modified and processed proteins and lipids are packaged into vesicles at the TGN for transport to their final destinations, either within the cell or outside of it.
Through these regions, the Golgi apparatus also contains enzymes that facilitate the modification and sorting processes. Additionally, the Golgi apparatus is connected to the endoplasmic reticulum, allowing for the exchange of lipids and other materials between these organelles. This structural organization allows the Golgi apparatus to play a central role in the modification, sorting, and packaging of molecules, ensuring their proper functioning within the cell.
Functions of Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi Apparatus has several important functions within the cell. These functions make the Golgi apparatus a central hub for processing, modifying, and transporting various molecules, ensuring the proper functioning of the cell.
- Post-Translational Modification: It modifies proteins and lipids, for example, by glycosylation (adding sugar molecules) and sulfation. These modifications are crucial for the proper structure and function of these molecules.
- Sorting and Packaging: The Golgi apparatus sorts and packages modified proteins and lipids into vesicles. These vesicles are then transported to various cellular locations, both inside and outside the cell.
- Protein Trafficking: It is involved in directing the newly synthesized proteins to their correct locations within the cell. This ensures that proteins end up where they are needed to carry out specific functions.
- Secretion: The Golgi apparatus is vital for the secretion of certain substances outside the cell. For example, in specialized cells, it plays a role in secreting enzymes, hormones, and other molecules.
- Lysosome Formation: The Golgi apparatus is involved in the formation of lysosomes, which are cellular organelles containing enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris.
- Membrane Renewal: It plays a role in the renewal and maintenance of the cell’s plasma membrane by incorporating newly synthesized lipids and proteins into the membrane structure.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













