Both Excretion and Egestion are the two most important topics from Chapter: 01 “Life Processes” of class 10th Biology section. Certainly, Egestion and Excretion are two distinct biological processes in the body. Excretion focuses on the elimination of metabolic waste products, like urea, through the kidneys and urinary system. This helps maintain the body’s internal balance and prevents harmful waste buildup. On the other hand, Egestion pertains to the elimination of undigested and indigestible materials, such as fiber, from the digestive tract through the large intestine and anus. While excretion deals with waste generated by the body’s metabolic waste to keep the body’s internal environment stable.
Define Egestion and Excretion
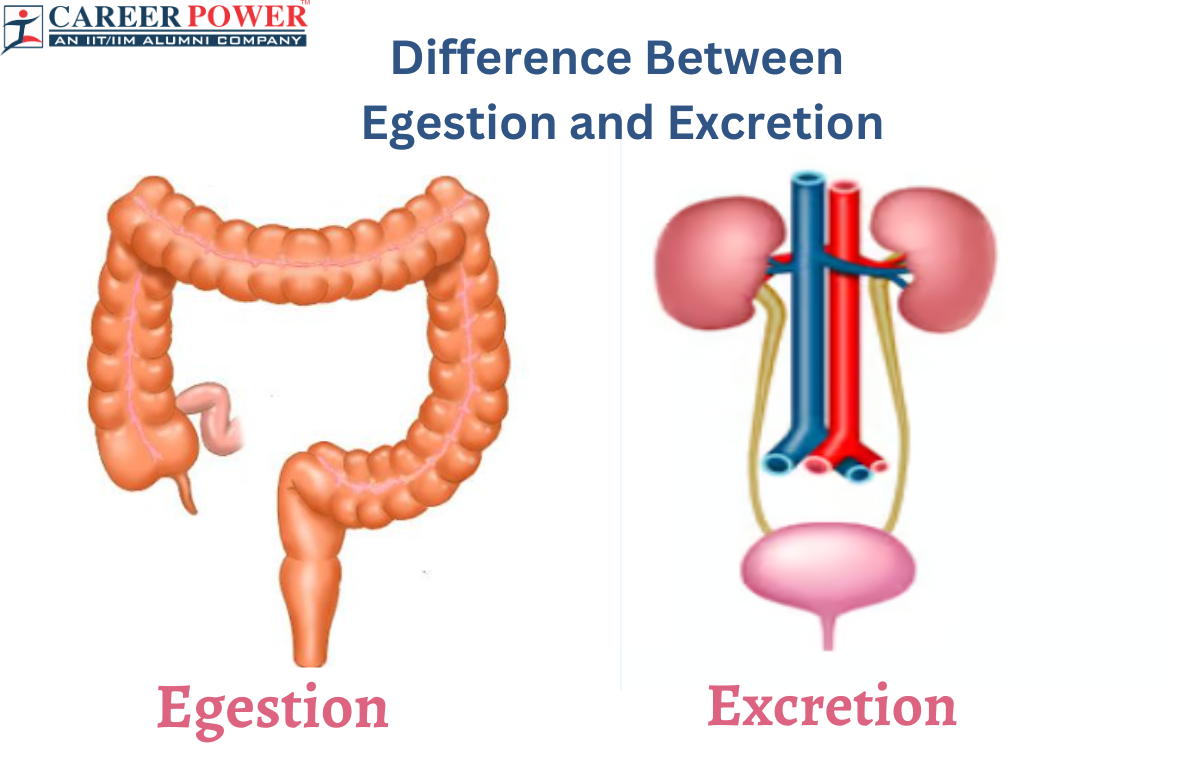
Excretion is a biological process by which waste products, such as metabolic byproducts and toxins, such as carbon dioxide, urea, excess salts, and other harmful substances, are removed from the body through various organs and systems such as lungs, kidneys, skin, and digestive system. The process of Excretion helps maintain a stable internal environment and supports the body’s overall health and balance.
Egestion, also known as defecation, is the final stage of the digestion process. It involves the expulsion of undigested food, indigestible fibers, and other waste products that have passed through the digestive system. The waste material accumulated in the rectum until it triggers the urge to defecate, and then it is expelled from the body through the anus. Egestion helps to rid the body of substances that cannot be utilized for energy or nutrients.
Difference Between Egestion and Excretion
Excretion and egestion are both processes involved in removing waste from the body, but they occur in different ways and involve different types of waste. As excretion involves the removal of metabolic waste products, such as carbon dioxide, urea, and excess salts, from the body; while egestion is specifically related to the elimination of indigestible or undigested material from the digestive system. Other differences between Excretion and Egestion on the basis of their nature, location, role they play in the process of digestion have been tabulated below:
| Difference Between Egestion and Excretion | ||
| Aspects | Excretion | Egestion |
| Definition | Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste products from the body. | Egestion is the elimination of undigested food materials from the body. |
| Process Location | Excretion mainly occurs in organs like kidneys, skin, liver, and lungs. | Egestion mainly occurs in the large intestine (colon) and rectum. |
| Mechanism | Excretion involves filtration, reabsorption, and secretion processes. | Egestion involves peristalsis, mechanical breakdown, and movement of materials. |
| Metabolic Regulation | Excretion helps in the maintenance of internal balance by regulating electrolytes. | Egestion is not involved in metabolic regulation; it only focuses on digestion. |
| Substances | Excretion involves the removal of metabolic waste, ions, etc. | Egestion involves the elimination of indigestible substances. |
| Nature of Waste | Excretion generally involves liquid or soluble waste. | Egestion typically involves solid or semisolid waste. |
| Role in Digestion | Excretion is not directly related to digestion. | Egestion is concluded as the process of digestion. |
| Frequency of process | Excretion is a continuous process that helps to prevent harmful waste accumulation. | Egestion occurs periodically after digestion to remove undigested or indigestible food. |
| Organs Involved | Kidneys, Lungs, Skin, and Liver are involved in the process of Excretion. | The intestines, Rectum, and Anus are involved in the process of Egestion. |
| Health Implication | Imbalances can lead to renal failure, toxicity, or disease. | Issues include constipation, diarrhea, and digestive disorders. |
Advantages of Egestion and Excretion
Both Egestion and Excretion are important processes for an organism to maintain its internal balance and eliminate waste. Excretion removes metabolic waste products, toxins, and excess substances, helping to prevent harmful buildup in the body. Egestion, on the other hand, eliminates undigested or indigestible materials from the digestive system, preventing obstruction and promoting efficient nutrient absorption. Both processes contribute to the overall health and proper functioning of an organism’s internal system.
Advantages of Excretion
Excretion serves several important functions in living organisms. Some of them are mentioned here.
- Waste Removal: Excretion eliminates metabolic waste products, such as urea and carbon dioxide, preventing their accumulation and potential toxicity.
- Maintaining Homeostasis: Excretion helps regulate the body’s internal environment by balancing electrolytes, water, and pH levels.
- Detoxification: It removes harmful substances and excess ions, such as ammonia, from the body, reducing the risk of cellular damage.
- Osmoregulation: Excretion helps organisms maintain proper water balance by eliminating excess water in dilute environments and conserving water in arid conditions.
- Cellular Function: Proper excretion supports the normal functioning of cells and tissues, contributing to overall health and well-being.
- Prevents Tissue Damage: Elimination of nitrogenous waste, such as urea, prevents its accumulation in tissues, which can cause damage.
Advantages of Egestion
As Egestion has its own essential advantages, it’s very important to maintain a balanced and healthy diet to support effective digestion and waste elimination. Some other advantages of egestion are discussed below.
- Waste Elimination: Egestion removes indigestible materials and waste products from the digestive system, preventing their accumulation and potential harm.
- Nutrient Absorption: Egestion ensures that only digested nutrients are absorbed by the body, preventing the uptake of harmful or unnecessary substances.
- Preventing Gut Bacteria Overgrowth: Proper egestion helps prevent the overgrowth of harmful bacteria in the digestive tract, which could lead to infections or imbalances.
- Regulation of Gut Motility: Egestion play a role in regulating the movement of material through the digestive system, supporting efficient digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Maintenance of Colon Health: Adequate egestion helps maintain the health of the large intestine and colon by preventing the accumulation of waste.
- Contributing to Overall Well-Being: Proper egestion contributes to overall bodily comfort, proper digestion, and a healthier gastrointestinal system.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













