The CBSE Class 12 Biology Additional Practice Questions Paper 2023-24 has been released by the Central Board of Secondary Education for all students of Class 12 who have chosen science as their major stream. The students can download the Class 12 Biology Additional Practice Questions Paper 2023-24 (CBSE) by visiting the official website of CBSE i.e., www.cbseacademic.nic.in. The students preparing to appear in the CBSE Class 12 Board exam 2024 are advised to go through the Class 12 Additional Practice Questions Papers 2023-24 and practice them thoroughly. As practicing these practice papers will help the students to understand and familiarize themselves with the newly upgraded CBSE paper pattern. All the students are informed that from this session onwards, there will be no term exams, in place a single examination will be conducted by the Central Board.
Class 12 Biology Additional Practice Paper Question 2023-23 (CBSE)
The newly released CBSE Class 12 Biology Additional Practice Paper 2023-24 is based on the entire syllabus. The students who are preparing for the CBSE Class 12 Biology examination 2023 can either download the biology sample paper from the official website of CBSE or check it in our article, as we have mentioned the complete CBSE Class 12 Biology Additional Practice paper with the solution below. Now let us discuss some important instructions that a student must know before attempting the exam.
The CBSE Class 12 Biology Additional Practice Paper 2023-24 consists of five sections and 33 questions. And all the 33 questions are compulsory. However, internal choices will be provided in a few questions, a student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions. The students will be given 3 hours to complete the examination.
- In Section A: There are 16 questions Carrying 01 mark each;
- In Section B: Consists of 05 questions of 02 marks each;
- In Section C: There are 07 questions of 03 marks each;
- In Section D: Contains 02 case-based questions of 04 marks each; and
- In Section E: Carries 03 questions of 05 marks each;
- Wherever necessary, the students are required to draw neat and properly labeled diagrams.
Biology Additional Practice Paper 2023-24 CBSE Class 12
The students can now download the CBSE Class 12 Biology Additional Practice Paper 2023-24 with their solutions and marking scheme. The students appearing in the CBSE Class 12th examination in the session 2023-24 must practice all the questions mentioned on the practice paper to familiarize themselves with the new updated format of the board exam.
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Class 12 Additional Practice Paper 2023-24 | |
| Additional Practice Paper Link | Solution Pdf Link |
| Biology Class 12 Additional Practice Paper | Solution Link |
CBSE Class 12 Biology Additional Practice Paper 2023-24
Here we have discussed all the questions of the Biology Additional Practice Paper 2023-24 with their solutions.
Section A – MCQs
Q1: During the pollen grain formation, the generative cell divides to give rise to
the two male gametes.
What is the ploidy of the generative cell?
(a) n
(b) 2n
(c) 3n
(d) 4
Ans: (a) n
Q2: Kiwi is a dioecious species. Which of the following methods can be Definitely ruled out as a possible mode of pollination in its case?
P) cleistogamous autogamy
Q) chasmogamous autogamy
R) geitonogamy
S) xenogamy
(a) Only P and R
(b) Only P and Q
(c) Only Q and S
(d) Only P, Q, and R
Ans: (d) only P, Q and R
Q3: Arun thinks that identifying the exact mRNA sequence from the protein sequence is difficult.
Is he correct and why?
(a) No, as the genetic code is universal.
(b) Yes, as the genetic code is degenerate.
(c) No, as the mRNA is translated into a protein sequence.
(d) Yes, as the mRNA contains introns which are non-coding sequences.
Ans: (b) Yes, as the genetic code is degenerate.
Q4: Crickets are insects that follow the XO type of sex determination. Which of the following statements is always true about this type of sex determination?
(a) Eggs that have an O chromosome will give rise to a male cricket.
(b) Eggs that have an X chromosome will give rise to a female cricket.
(c) Sperms that have an X chromosome will give rise to a male cricket.
(d) Sperms that have an O chromosome will give rise to a male cricket.
Ans: (d) Sperms that have an O chromosome will give rise to a male cricket.
Q5: Oysters are generally either dark or light in color. Dark oysters excel in dark environments, while light oysters thrive in bright environments. Intermediate-colored oysters are disadvantaged, lacking effective camouflage in either setting.
Which type of natural selection does this phenomenon exemplify?
(a) directional
(b) stabilizing
(c) disruptive
(d) (The phenomenon described does not exemplify natural selection.)
Ans: (c) disruptive
Q6. A team of archaeologists found a fossilized skeleton of a human-like creature with a brain capacity of more than 700cc. The structure and its associated findings also show evidence that this creature could use tools for hunting.
Which stage of human evolution is this creature NOT from?
(a) Homo erectus
(b) Homo habilis
(c) Neanderthal Man
(d) Australopithecines
Ans: (d) Australopithecines.
Q7. Which of the following is CORRECT about the movement of DNA on an agarose gel and the reason for it?

(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
Ans: (d) S
Q8. What is the MINIMUM possibility of a dominant trait being expressed in the offspring after a test cross?
(a) 25%
(b) 50%
(c) 75%
(d) 100%
Answer: (b) 50%
Q9. Which process is responsible for increasing the percentage of alcohol in whisky after fermentation?
(a) malting
(b) dilution
(c) distillation
(d) maturation
Ans: (c) distillation.
Q10. What does I in the restriction enzyme named ‘Hin S2 I’ indicate?
(a) It cuts after the first nucleotide in the restriction site.
(b) It is the first enzyme isolated from strain S2 of the bacterium.
(c) There is definitely more than one enzyme isolated from the same bacterium.
(d) There is only one enzyme that can be used to digest a plasmid from strain S2 for the bacterium.
Ans: (b) It is the first enzyme isolated from strain S2 of the bacterium.
Q11. Sumi and Nisha said the following about somatic hybridization in plants.
Sumi: Gametes are not required for hybridization.
Nisha: The resultant plant that grows after the fusion of the cells is genetically identical to the parent plants.
Who among them is/are CORRECT?
(a) only Sumi
(b) only Nisha
(c) Both Sumi and Nisha
(d) Neither Sumi nor Nisha
Ans: (a) Only Sumi.
Q12. Rupal says that in marine food chains where the pyramid of biomass is inverted, the 10% rule of energy transfer is not applicable.
Is she CORRECT and why?
(a) No, because every level still gets 10% of the energy from the lower level.
(b) Yes, because there are more consumers and so more energy is transferred.
(c) No, because the pyramid of biomass can never be inverted for any food chain.
(d) Yes, because there is a lower biomass of producers in these food chains so less energy is transferred.
Ans: (a) No, because every level still gets 10% of the energy from the lower level.
Question No. 13 to 16 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is true but R is false.
d) A is false but R is true
Q13. Assertion (A): The coconut endosperm is multinucleate throughout its development.
Reason (R): Some endosperms undergo free nuclear division without the formation of distinct cell boundaries.
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A.
Q14. Assertion (A): DNA ligase is not used in PCR.
Reason (R): Discontinuous fragments are not formed in the amplification of DNA by PCR.
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A.
Q15. Assertion (A): To promote sustainability while minimizing waste, it is recommended to reuse needles up to two times for the same person.
Reason (R): Sterilisation of needles eliminates all pathogens and ensures safety.
Ans: (d) A is false, but R is true.
Q16. Assertion (A): Nuclear DNA extracted from a cell is visible to the naked eye but unstained plasmid DNA running in an agarose gel is not.
Reason (R): Plasmid DNA is transparent but nuclear DNA is not.
Ans: (c) A is true, but R is false.
Section B
Q17. Kavya says that the placenta produces relaxin which plays a crucial role during pregnancy.
(a) Is she correct? Justify.
(b) Name TWO other hormones secreted by the placenta during pregnancy.
Ans: (a) 0.5 marks each for the following:
– No she is not correct.
– Relaxin is produced by the ovaries and not the placenta.
(b) 0.5 marks each for any two of the following:
– human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
– human placental lactogen (hPL)
– estrogens
– progestogens
Q18. Thalassemia is an autosomal recessive disorder that causes anaemic conditions in an individual. A blood smear from a heterozygous individual shows blood cells that are small, pale, and irregularly shaped along with normal RBCs.
(a) State the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of offspring born to a carrier mother and a thalassemic father.
(b) Does the allele for thalassemia exhibit codominance? Justify.
Ans: (a) 0.5 marks for each of the following:
– Genotypic ratio: 1:1 ratio of carriers: affected
– Phenotypic ratio: 50% will not show major symptoms while 50% will show the symptoms.
(b) 0.5 marks for each of the following:
– Yes
– Since both proteins are produced/both types of RBCs are visible, it is codominance.
[Accept any other valid answer.]
Q19. Explain any TWO reasons why the treatment of AIDS is only partially effective.
Ans: 1 mark each of any two of the following:
– HIV has a high mutation rate and genetic variability making it difficult to target.
– HIV can be latent for more extended periods of time, making it difficult to diagnose the disease.
– HIV replicates in immune cells of the human body and targeting them might pose a risk to the individual’s immune system and safety.
Q20. Rati wants to grow a variant of the lactobacillus spps. in a bioreactor. Lactobacillus is an anaerobic bacterium commonly used as a starter culture for dairy products. Shown below is a bioreactor she had in her laboratory.
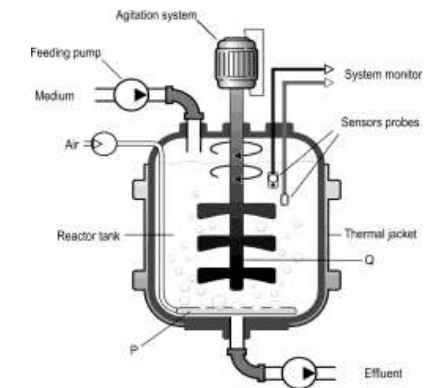
(a) Identify ONE component that should definitely NOT be present in the reactor to grow the lactobacillus spps. Justify.
(b) Explain TWO quantities that the sensors in the bioreactor should monitor.
Ans: (a) 0.5 marks each for the following:
– The air inlet/sparger should be absent.
– Since lactobacillus is anaerobic, it may not thrive well if oxygen is present.
(b) 0.5 marks each for any two quantities such as:
– A sensor should monitor temperature as bacteria are likely to die if the temperature fluctuates.
– Dissolved oxygen should be measured to ensure anaerobic conditions are maintained.
[Accept any other valid answer.]
Q21. Shown below is a food chain.

(a) Millipedes have a hard exoskeleton whose composition is different from that of the leaves. Considering all other conditions to remain the same, which step is likely to be slower between A to B and B to C, and why?
(b) What would be the direction of the flow of energy in this food chain?
Ans: (a) 0.5 marks for each of the following:
– B to C will be slower than A to B
– Since millipedes contain chitin, their decomposition will be slower than that of leaves that have cellulose.
(b) The flow of energy is A to B to C to D.
OR
Q21.(a) A coral reef can be regarded as an ecosystem. Mention any TWO reasons why.
(b) The net primary productivity (NPP) of a coral reef is approximately 2000 g C/m²/year and the gross primary productivity (GPP) is 4000 g C/m² /year.
Calculate the respiration losses (R) of this ecosystem.
Ans: a) 0.5 marks for any TWO of the following:
– A coral is a self-regulating and stable system.
– It has a variety of biotic (living) components, including corals, fish, invertebrates, algae, bacteria, plants, animals, and other organisms.
– It has a variety of abiotic (non-living) components, including water, sunlight, nutrients, and soil.
– The biotic and abiotic components interact with each other for life to sustain.
– Flow of energy and nutrients occurs in the system.
– It is a self-sustaining system as corals and other organisms that live on the reef produce their own food through photosynthesis, and the reef itself provides a stable habitat for the organisms that live there.
[Accept any other valid answers]
(b) GPP – R = NPP [0.5 marks]
4000 – R = 2000
R = 2000 g C/m²/year [0.5 marks]
Section C
Q22. A biologist sees the following cells in a cross-section of the seminiferous tubule and its surrounding tissues and counts the number of various kinds of cells.
Spermatozoa, Spermatid, Primary spermatocyte, Secondary spermatocyte, Leydig cells, Sertoli cells, Spermatogonium.
From these cells, identify the cells:
(a) that are diploid.
(b) that can produce hormones and their names.
Ans: (a) 0.5 marks for each type of cell:
– Leydig cells
– Sertoli cells
– Spermatogonium
– Primary spermatocyte
(b) 0.5 marks for each of the following:
– Leydig cells
– produces androgens
Q23. A couple is trying to conceive and start a family.
(a) If the woman’s period, which is regular, is scheduled to start on July 19, what was the estimated date of ovulation for the previous cycle?
(b) Name the four important reproductive hormones and state whether their levels will be high or low on the date identified in (a).
Ans: (a) 5th July
(b) 0.5 marks for each for the following:
Estrogen – The highest level
Progesterone – The lowest level
FSH – The highest level
LH – The highest level
[Do not award marks if the level is not mentioned.]
Q24. As part of assisted reproductive technologies (ART),
(a) What is the destination for blastomeres with a count of less than 8 cells and more than 8 cells?
(b) What could be the reason behind transferring to the destinations identified in (a)?
(c) What techniques are used to transfer the blastomeres to the destinations identified in (a)?
Ans: (a) 0.5 marks for each of the following:
– For less than 8 cells, blastomere is transferred to the fallopian tube.
– For more than 8 cells, blastomere is transferred to the uterus.
(b) Embryos with more than 8 cells are generally considered healthier and have a better chance of successful implantation and further development and hence are placed in the uterus and not the fallopian tube.
(c) 0.5 marks for each of the following:
– For less than 8 cells, zygote intra-fallopian transfer is done.
– For more than 8 cells, the intra-2 uterine transfer is done.
Q25. (a) State any FOUR phenomena in which the Hardy-Weinberg theorem may not hold true.
(b) A population of 100 individuals has a frequency of allele A of 0.3 and a frequency of allele a of 0.7. The frequency of the heterozygous genotype (Aa) is 0.49. Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? Justify.
Ans: (a) 0.5 marks for any FOUR of the following:
– gene migration
– genetic drift
– mutation
– genetic recombination
– natural selection
(b) For the population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the expected frequency of the heterozygous genotype (Aa) has to be
Since the frequency of the heterozygous genotype (Aa) is 49%, it deviates from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium/the population is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. [0.5 marks].
Q26. State whether each of these statements given below is/are true or false. Justify your answer.
(a) Flocs reduce the pollution in water by increasing its BOD.
(b) Mycorrhiza is a type of parasitic relationship in which only the plants benefit from fungi.
Ans: (a) – False [0.5 marks]
– Flocs reduce pollution by decomposing the organic matter present in water and decreasing its BOD. [1 mark]
(b) – False [0.5 marks]
– Mycorrhiza is a type of symbiotic relationship in which both plants benefit from fungi and vice versa. [1 mark]
Q27. Erythropoietin is a glycoprotein hormone that is otherwise naturally produced in the kidney when the body becomes anaemic. However, this does not happen in the case of chronic renal diseases where kidney function is lost. Epoetin alfa is a human erythropoietin produced in cell culture using recombinant DNA technology. The cell culture used is called Namalwa cells, a human cell culture. There are eight exons and seven introns in a single gene that encodes the hormone, whose sequence is known.
Explain the step-by-step process that should be followed for producing human erythropoietin in culture.
Ans: 0.5 marks each for the following:
– Use the sequence of exons to form a dsDNA molecule in vitro.
– Insert the dsDNA molecule into an appropriate vector.
– Introduce the recombinant vectors in bacterial hosts and select cells containing the recombinant vector with the gene of interest.
– Purify the vector and amplify it using PCR.
– Using a gene gun or any appropriate technique introduce the recombinant vector into host human cells/Namalwa cells.
– Grow these cells in bioprocessors and extract and purify the glycoprotein from the culture.
[Award marks if the answer is presented as a flowchart or diagram]
OR
Q27. Today, many genetic disorders can be detected using a single cell from an embryo. This helps in planning the child’s health care in advance, and in some cases even treating the disorder while the baby is still in the womb.
(a) Identify a biotechnological technique that can be used for this purpose. Give a reason to support your answer.
(b) Can the technique identified in (a) be used to detect the presence of RNA viruses? Justify.
Ans: (a) 1 mark each for the following:
– Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
– It can be used to detect very small quantities of nucleic acid sequences as would be the case with DNA from a single cell.
(b) 0.5 marks each for the following:
– Yes, it can be used.
– PCR can be used to amplify/detect any nucleotide sequence.
[Accept any other valid answer.]
Q28. In a study comparing two continents – Antarctica and Asia, the species-area relationship was investigated using the following data:
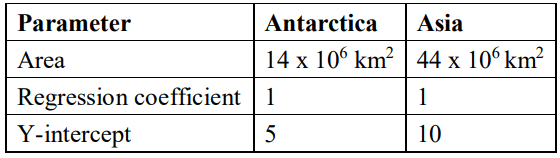
(a) Calculate the species richness value for each region.
(b) Based on (a), which continent will have greater biodiversity and why?
Ans: (a) 1 mark for the formula and 0.5 marks for the S value of each region:
S = CAz,
where
S = Species richness
A = Area
Z = Regression coefficient
C = Y-intercept
– For Antarctica, S = 5*(14*106 )(1) = 70*106
– For Asia, S = 10*(44*106 )(1) = 44*107
(b) 0.5 marks each for the following:
– Asia
– Since the species richness of Asia is more they have more species and so greater biodiversity than Antarctica.
Section D
Q29. Shown below is a cloning vector ‘Z’ that Kamla wants to use to create a recombinant vector with her gene of interest.
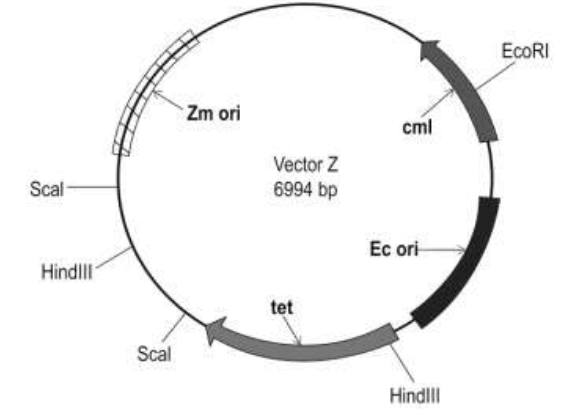
The vector consists of sites for three restriction enzymes – ScaI, HindIII, and EcoRI. Restriction sites for the same enzymes are also present in the gene of interest. There are two ‘ori’ sequences – one allows it to replicate in Escherichia coli and another allows replication in Zymomonas mobilis. Apart from this, the vector consists of two antibiotic resistance genes – one against tetracycline (tet) and another against chloramphenicol (CML).
(a) What is the advantage of having two ‘ori’ sequences in the same vector?
Give a situation in which this would be particularly useful.
OR
(a) If the vector was cut using HindIII, what would colonies growing on a medium containing tetracycline DEFINITELY contain?
(b) Suggest which of the three restriction enzymes would be suitable for insertion of the gene of interest. Give TWO advantages of using the enzyme chosen by you.
(c) State ONE disadvantage of using the other two restriction enzymes not chosen in (b).
Ans: (a) 0.5 marks each for the following:
– It helps the vector replicate in different hosts.
– When adding bacterial genes of interest into plant vectors, having ori’s that help the same plasmid replicate in both bacteria and plants would help simplify the process of gene cloning.
[Accept any other valid answer.]
OR
(a) The uncut vector without the gene of interest.[1 mark]
[Deduct 0.5 marks if a student writes the religated vector without a gene of interest].
(b) EcoRI would be ideal to use [1 mark]
0.5 marks each for any TWO advantages such as:
– It has a single restriction site, meaning that only two products will be obtained – either with the gene of interest or without it and will not give multiple products.
– The restriction site is within the chloramphenicol resistance gene, which on insertional inactivation will help select recombinant vectors.
[Accept any other valid answer.]
(c) Using ScaI and/or HindIII would lead to multiple end products/fragments being formed which would make selection of the
recombinant vector complicated.
Q30. Predator Y shown in the image below is a type of wild cat that inhabits the
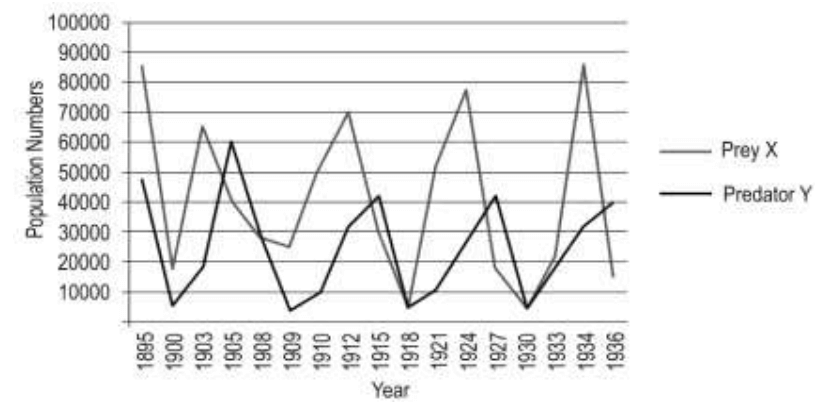
forests and preys primarily on prey X which are herbivores. Shown below is data on their respective populations over time.
(a) What is the likely cause for the pattern seen in the prey and predator populations through the years?
(b) Hypothetically, if all the predators of the forests become extinct, what will happen to the vegetation of the forest?
(c) Consider a situation where another similar species of predator immigrates to the forest. What is likely to happen over time and why?
Ans: (a) 0.5 marks each for the following:
– Since prey X is the primary food for prey Y, as the prey population increases, so does the predator population.
– More predators consume the prey causing the prey population to drop.
– As the prey population drops, predators do not have enough prey and so their population also drops.
– When this happens, the prey population increases again.
(b) The vegetation will also slowly disappear.
(c) 0.5 marks each for the following:
– The two species will compete for the same prey and the inferior one is likely to be eliminated over time.
– Since they both feed on the same prey, resources are limited causing the elimination of the inferior predator.
[Accept any other valid answer.]
OR
Q30. Juglone is a chemical produced naturally in most parts of the black walnut plant. This chemical leaches into the soil when the plant falls. This leads to the death of many plants that grow around the black walnut plant.
Identify the type of ecological interaction between the black walnut and other plants growing around it. Justify.
Ans: 0.5 marks each for the following:
– amensalism
– The black walnut is neither harmed nor benefitted while the plants surrounding it are harmed.
Section E
Q31. A Non-Government Organisation (NGO) aims to increase awareness against STDs.
(a) What could be the ideal target age group for the NGO?
(b) Mention any TWO potential long-term health-related complications of untreated STDs that the NGO should educate the target age group about.
(c) Mention ONE contraceptive method that provides protection against the STD. Justify.
(d) State TWO contraceptive methods that do not protect against STDs that they can educate the group about.
Ans: (a) 15-24 years
[Accept any other valid answer that includes a nearby age group]
(b) 1 mark each for the following:
– Chronic pain and discomfort in various body organs
– Infertility in some STDs
– Lower immunity levels and increased risk of other infections
– Higher risk of transmitting the diseases to others.
[Accept any other valid answer]
(c) 0.5 marks each for the following:
– condoms
– They act as a barrier preventing the mixing of body fluids.
(d) 0.5 marks each for any two of the following:
– Oral Contraceptive Pills
– Vasectomy or Tubectomy
– IUDs
OR
Q31. Amey and Lalita are expecting their first child, with Lalita being in her second month of pregnancy with no known complications. Amey’s family has a history of cystic fibrosis while Lalita’s family has a history of Down’s syndrome, leading to a concern that the baby may have one of these conditions.
(a) Suggest and explain a way of testing if their baby is at risk for any genetic disorders.
(b) In case of the presence of one or both of the abnormalities and posing a risk to the mother’s health, mention one possible option for them to consider.
(c) Is the process mentioned in (b) safe for Lalita at the current gestational age? Justify.
(d) Under what conditions is the process mentioned in (b) illegal?
Ans: (a) Amniocentesis – It involves taking a sample of the amniotic fluid and testing it for genetic abnormalities.
[0.5 marks each for suggesting the name of the method and explaining it]
(b) Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
(c) Yes, it is currently safe [1 mark]
This option should be considered before the completion of the first trimester, as it might be riskier after this period. [1 mark]
(d) MTP is illegal in cases involving determining the gender of the unborn child and female foeticide.
Q32. Shown below is a pedigree of an individual X who is suffering from ocular albinism which results in permanent vision loss. Use the pedigree to answer the questions that follow:
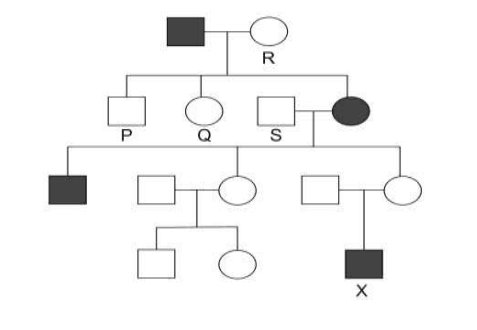
(a) Complete the following statement about this disease:
The trait for the disease is linked to ___________ (X-chromosome/Ychromosome/autosome) and is __________ (dominant/recessive).
(b) Give a reason to support your answer to (a).
(c) Identify the genotypes of individuals P, Q, R and S marked in the pedigree.
Ans: (a) 0.5 marks each for the following: 1.0
– X-chromosome
– recessive
(b) 1 mark each for the following:
– It is appearing in both males and females but more in males which need only one X chromosome for the trait to be expressed.
– The trait is being expressed in only in some children/small fraction and so is likely to be recessive.
[Accept any other valid answer.]
(c) 0.5 marks each for the following:
– P: XY
– Q: X0X
– R: X0X
– S: XY
OR
Q32. Shown below is a nucleotide sequence and the genetic code.
5′ – ATGCGTAGACTCGTA – 3′
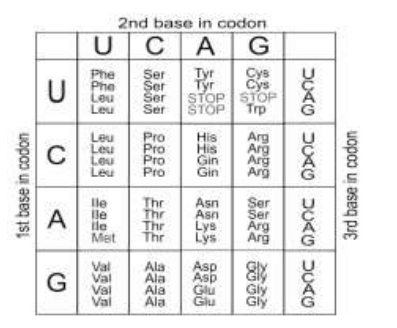
(a) Identify the protein sequence formed by this sequence.
(b) Draw the tRNA molecule for the third codon with its polarity labelled. Give a reason to support the polarity identified.
(b) The first guanine base in the nucleotide sequence changes to cytosine. Identify the type of mutation caused by this change.
(c) Will the mutated sequence form an mRNA and protein? Justify.
Ans: (a) TYR ALA SER GLU HIS [1 mark]
(b) Correct drawing with anticodon 3′ -AGA – 5′ [1 mark]
Reason: The mRNA sequence is translated in the 5′ to 3′ direction so the anticodon has to be in the 3′ to 5′ direction [1 mark].
(c) point mutation [0.5 marks].
(d) 0.5 marks each for the following:
– mRNA will be formed
– protein will not be formed
– The first codon is a stop codon due to which translation will not happen.
Q33. (a) Classify the following scenarios as active/passive immunity and justify your answer.
(i) A fetus receives antibodies from its mother through the placenta.
(ii) A person accidentally gets cut by a blade and later receives a tetanus shot.
(iii) A person receives a blood transfusion from a donor who has been vaccinated against a disease.
(b) Zoya is bitten by an infected Anopheles mosquito in the morning. In the evening, another non-infected Anopheles mosquito bites Zoya and then bites Zaheer immediately. How likely is Zaheer to get malaria? Justify your answer.
Ans: (a) 0.5 marks each for mentioning the type of immunity and 0.5 marks each for the reason:
(i) Passive immunity
Pre-formed antibodies are being transferred from the mother to the fetus as the fetus does not make its own antibodies.
(ii) Active immunity
A tetanus shot, which contains inactivated tetanus toxin, will stimulate the person’s immune system to produce his own specific antibodies against tetanus.
(iii) Passive immunity
The person receiving the blood transfusion is passively acquiring antibodies from the vaccinated donor that were made by the donor’s body and not the recipient’s body.
(b) – Zaheer is not likely/less likely get malaria. [1 mark]
– Since Zoya has been bitten by an infected mosquito and the process of infection of the liver cells and red blood cells takes more than 5 days, the non-infected second mosquito is not likely/ less likely to get infected by biting Zoya, and thus cannot/less likely to transfer the Plasmodium to Zaheer. [1 mark]
OR
Q33. A patient is suffering from fatigue, high fever, and weight loss, and has been observing an increasing number and size of lumps in various regions of her body over a very short time.
(a) What could she be suffering from?
(b) Mention FOUR ways in which the disease identified in (a) is caused and FOUR techniques that can be used to diagnose it.
Ans: (a) Malignant tumour/ Cancer
(b) 0.5 marks each for any four causes such as:
– genetic factors/family history
– carcinogens
– high energy ionising radiations (e.g. X-rays, gamma rays, etc.)
– non-ionizing radiations (e.g., UV)
– infection by oncogenic viruses.
0.5 marks each for any four diagnosis techniques such as:
– X-rays
– CT scans
– MRI scans
– Blood tests
– Biopsies
[Accept any other valid answer]



 CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Additional Pract...
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Additional Pract...
 CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Sample Qu...
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Sample Qu...
 CBSE Class 12 Physics Model Paper 2024-2...
CBSE Class 12 Physics Model Paper 2024-2...













