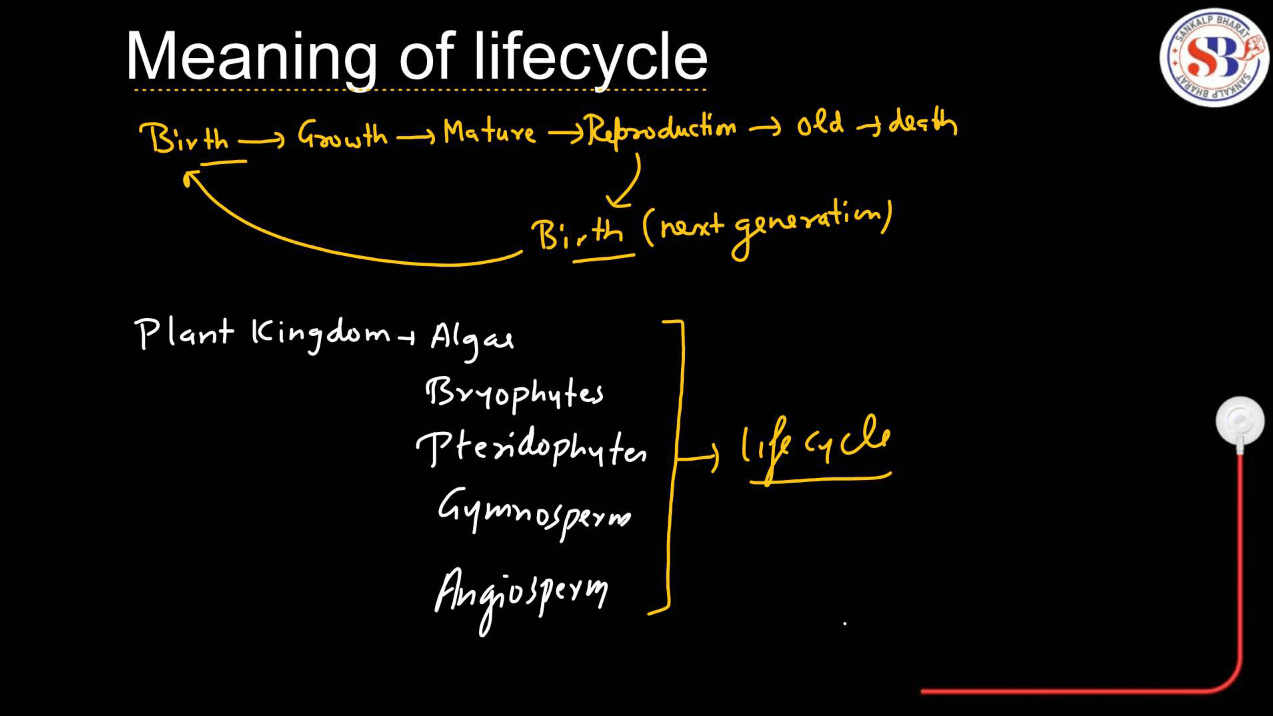
A life cycle is the series of stages a living thing goes through from birth to death. In plants, the life cycle typically begins with a seed. The seed germinates and grows into a seedling. As the seedling matures, it develops into a mature plant, producing flowers and fruits. These flowers are pollinated, leading to the formation of seeds, completing the cycle.
Each stage serves a purpose in the plant’s growth and Reproduction. For example, in the life cycle of a sunflower, the seed is planted in Soil, sprouts into a seedling, grows into a tall plant with leaves and a stem, produces bright yellow flowers, and eventually develops seeds within the flower head. These seeds can then be dispersed and germinate to start the cycle anew.
Process of Life Cycle of a Plant
The life cycle of a plant begins with germination, where a seed absorbs water and nutrients, initiating growth. As the seedling emerges, it develops Roots for anchorage and absorption and leaves for photosynthesis. Converting sunlight into energy. The plant undergoes vegetative growth, increasing in size and branching out, aided by water, nutrients, and sunlight. Eventually, it reaches maturity, characterized by flowering, reproduction, and seed production.
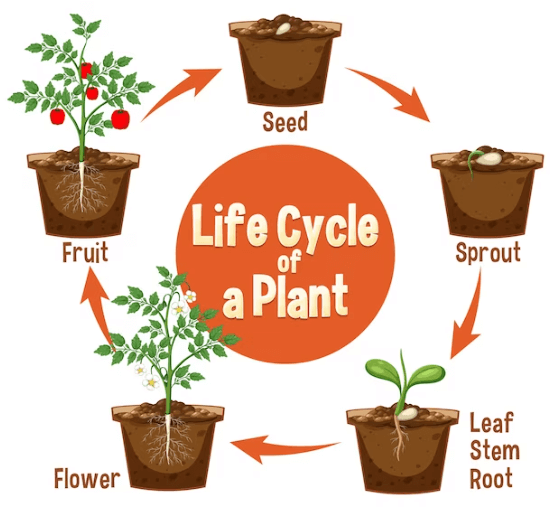
Pollination, either by wind, insects, or other animals, transfers pollen to the female reproductive organs, leading to fertilization. Fertilized eggs develop into seeds within fruits or pods. With favorable conditions, seeds disperse, either by wind, water, animals, or mechanical means, starting the cycle anew upon germination. Some plants may undergo dormancy during adverse conditions improve. This cyclic process ensures the continuation of plant species and adaptation to diverse environments.
Phases in the Life Cycle of Plants
Here are the well-defined phases in the life cycle of plants. This cycle repeats as seeds germinate, grow, reproduce, and produce new seeds, ensuring the survival and propagation of the plant species.
- Seed Germination:
- Seeds absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
- Germination begins with the emergence of the redicle (embryonic root) and then the shoot.
- The seedling develops roots for anchorage and absorption of water and nutrients.
- Vegetative Growth:
- The plant grows leaves, stems, and roots.
- It focuses on Photosynthesis to produce energy for growth.
- Vegetative growth continues until the plant reaches maturity.
- Reproductive Phase:
- Flowers develop on the plant, marking the beginning of the reproductive phase.
- Pollination occurs, transferring pollen from the male to the female reproductive phase.
- Fertilization takes place, resulting in the formation of seeds.
- Seed Formation and Dispersal:
- Fertilized flowers develop into fruits, containing seeds.
- Seeds mature within the fruit.
- Once mature, seeds are dispersed by various methods such as wind, water, animals, or gravity.
- Dormancy:
- Some seeds enter a period of dormancy, where metabolic activity slows down to survive adverse conditions.
- Dormancy may be broken by specific environmental cues like temperature, moisture, or light.
- Seed Germination (again):
- When conditions become favorable, dormant seeds germinate, restarting the life cycle.
Types of Life Cycles in Plants
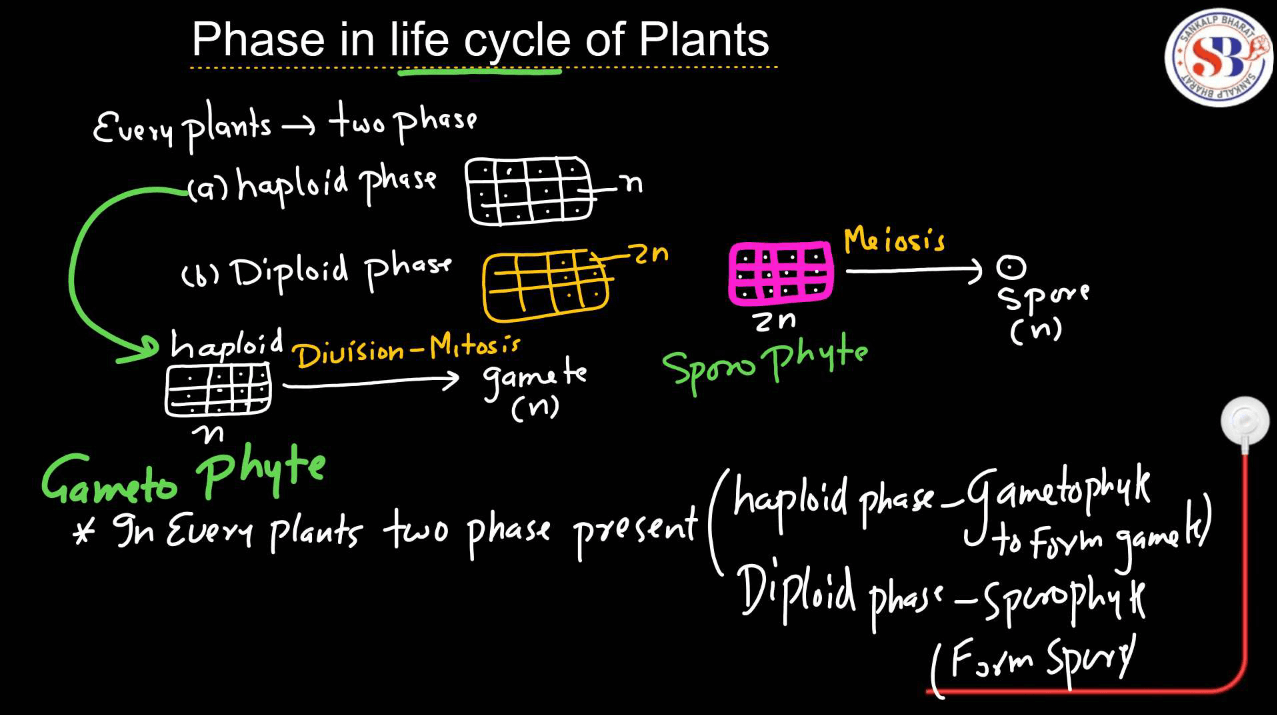
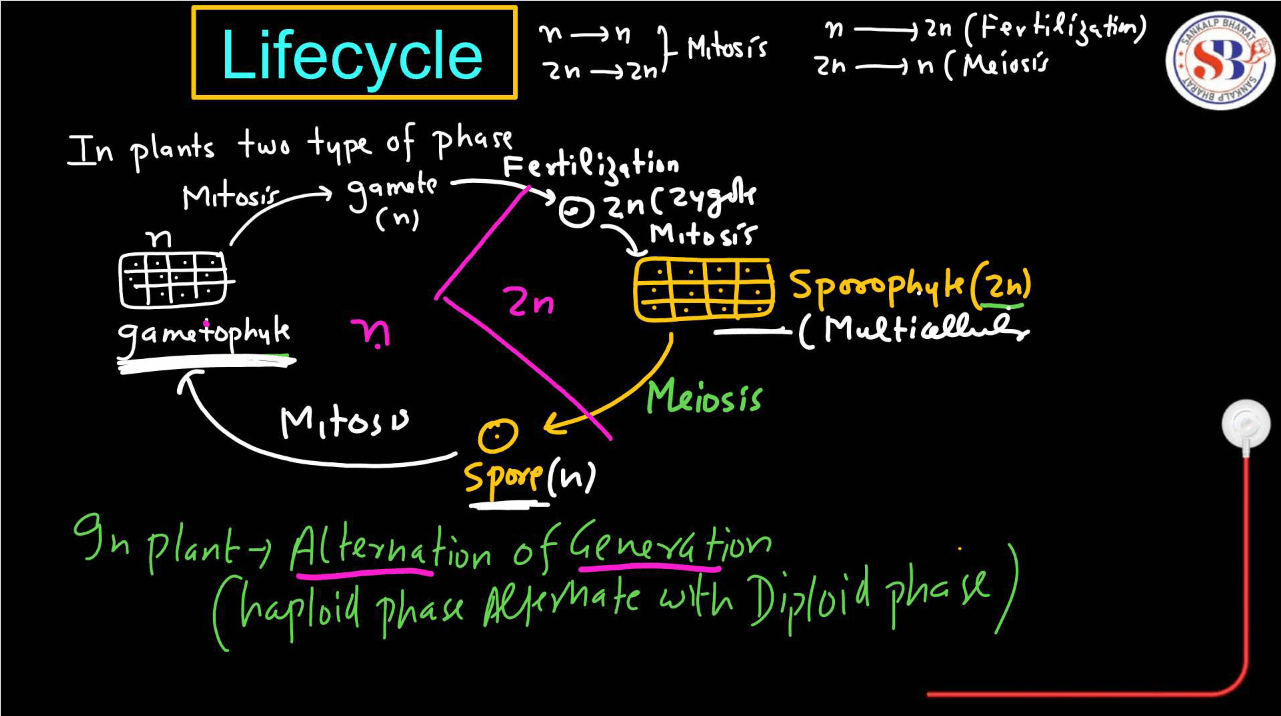
In plants, there are mainly three different types of life cycles in plants: Haplontic, Haplodiplontic, and Diplontic.
| Different Types of Plant Life Cycle | |
| Types | Description |
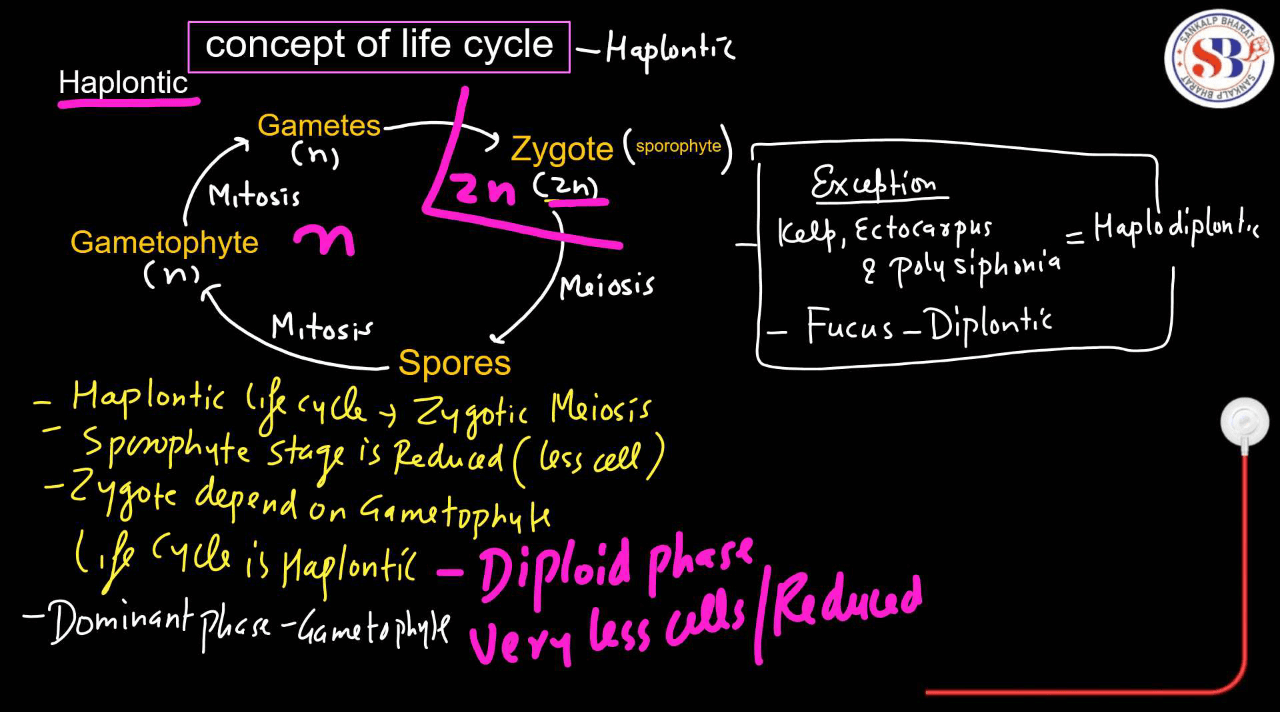
| Haplontic Life Cycle | The haplontic life cycle in plants involves a dominant haploid phase where gametes are produced, followed by a brief diploid phase after fertilization, primarily seen in lower plants like algae. |
| Diplontic Life Cycle | The diplontic life cycle in a plant features a dominant diploid phase where most of the organism’s life is spent, with meiosis occurring to produce haploid gametes for Reproduction. |
| Haplodiplontic Life Cycle | The haplodiplontic life cycle in plants includes alternating generations of haploid and diploid phases. Haploid gametophytes produce gametes, which fuse to form diploid sporophytes and vice versa. |
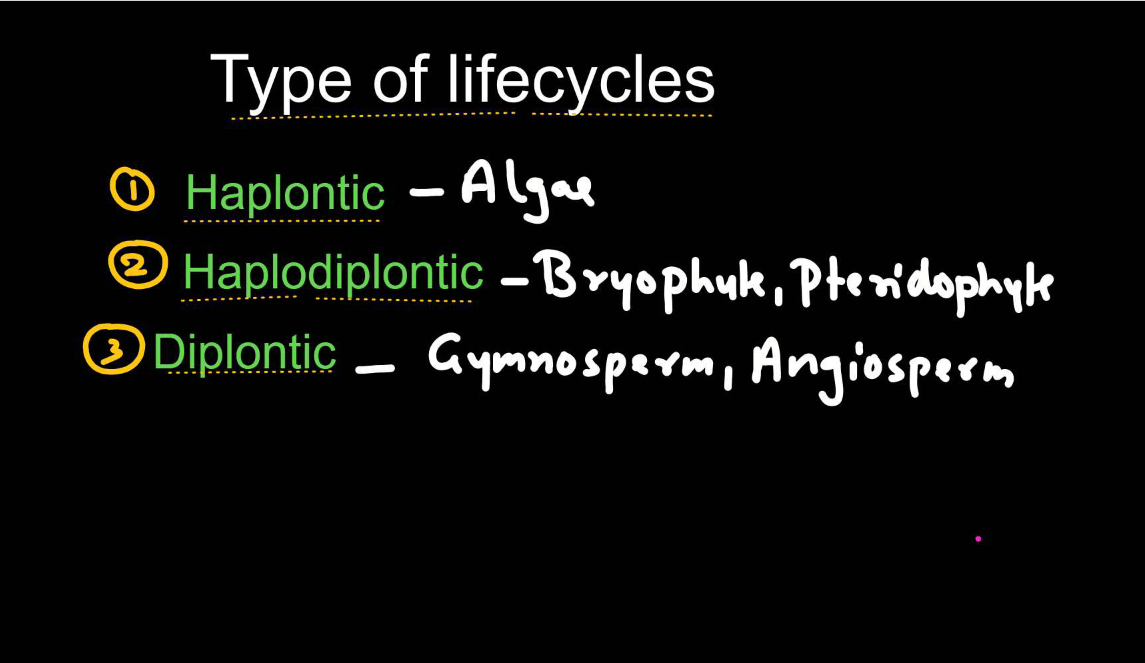
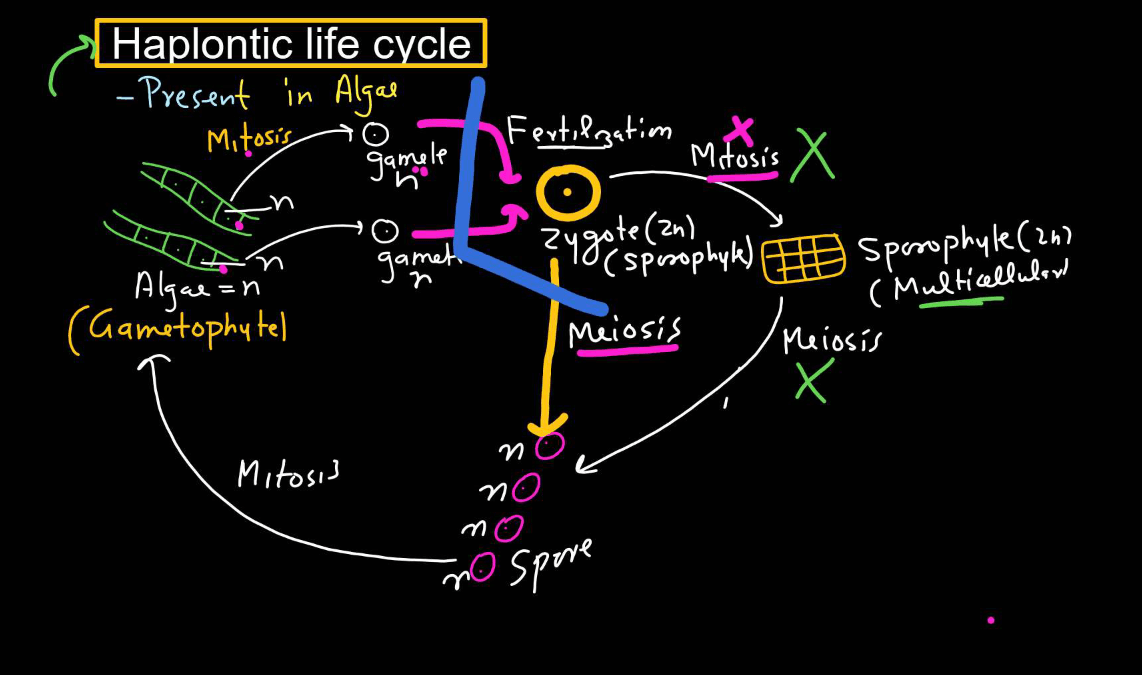
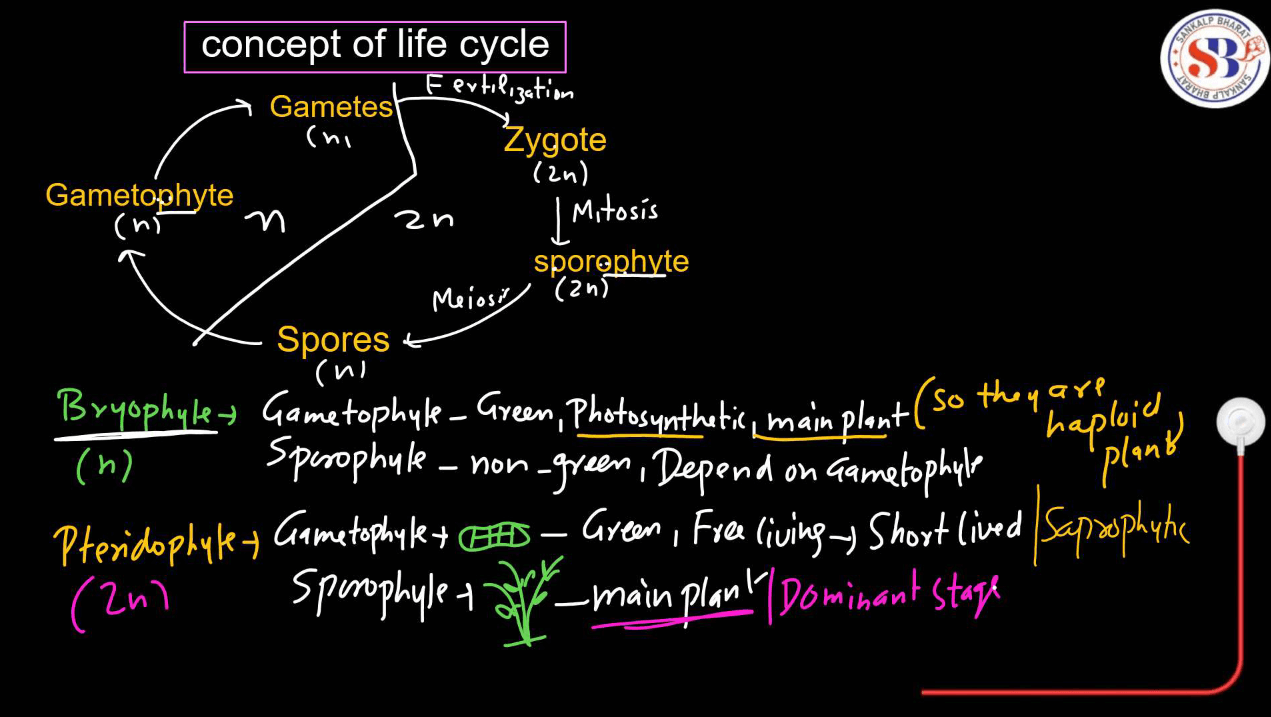
Haplontic Life Cycle
- The haplontic life cycle is a type of reproductive cycle found in certain organisms, like many types of algae and Fungi.
- It involves two main stages: The haploid stage and the diploid stage.
- In the haplontic life cycle, the dominant stage is haploid, meaning the organism primarily exists as a single set of chromosomes. This haploid stage produces gametes (reproductive cells) through mitosis.
- When these gametes fuse during fertilization, they form a diploid zygote, which undergoes meiosis to produce haploid cells again, restarting the cycle. The diploid stage is relatively short-lived compared to the haploid stage. This cycle allows for genetic diversity through the shuffling of genetic material during meiosis and fertilization.

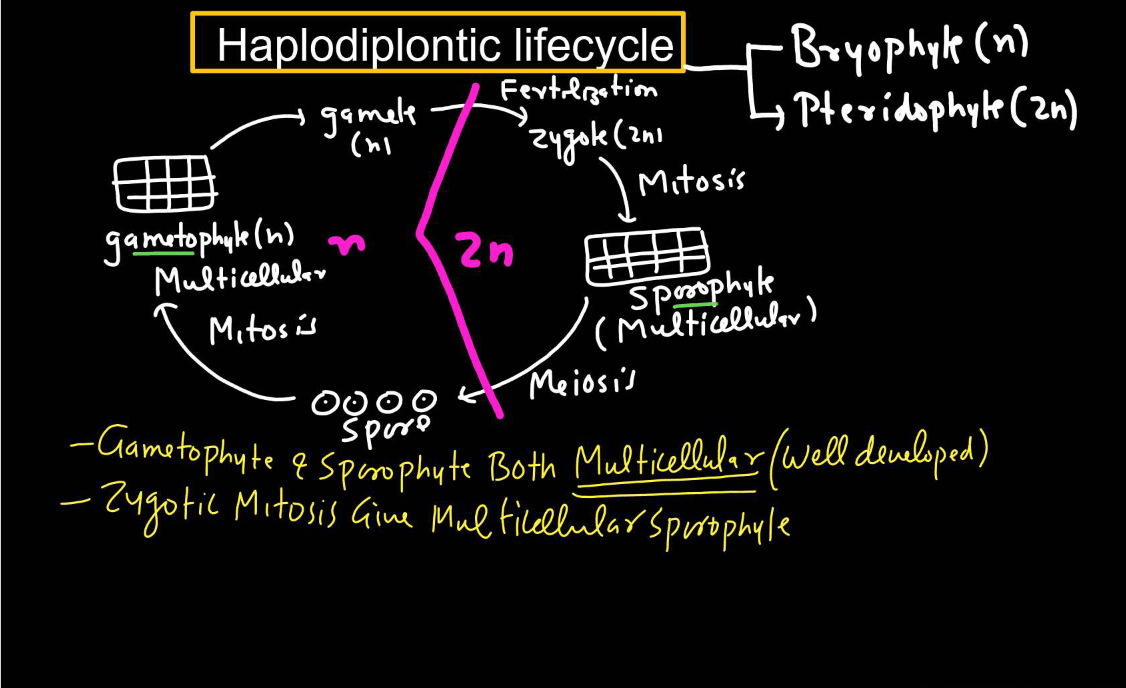
Haplodiplontic Life Cycle
- The Haplodiplontic life cycle, also known as the diplobiontic life cycle, is a reproductive strategy found in certain plants and algae, such as ferns and some algae species.
- It involves alternating between two multicellular stages: The haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte.
- In this life cycle, the haploid gametophyte produces gametes through mitosis.
- When these gametes fuse during fertilization, they form a diploid zygote, which develops into a diploid sporophyte through mitosis. The sporophyte produces haploid spores through meiosis
- These spores then germinate into haploid gametophytes, completing the cycle. This alternation of generations allows for genetic variation and adaptation to different environmental conditions.


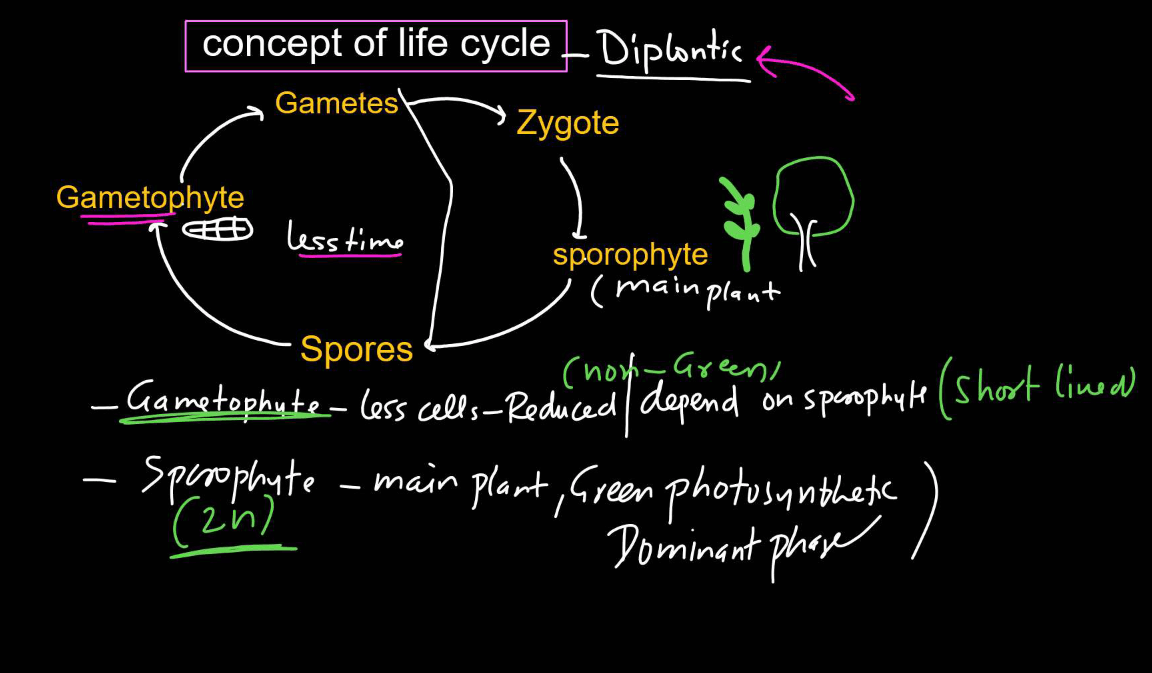
Diplontic Life Cycle
- In the complete diplontic life cycle of plants, the dominant stage is the diploid phase, where the plants exist as full organisms.
- It starts when haploid gametes, produced by a specialized structure called gametangia, fuse during fertilization to form a diploid zygote.
- This zygote then undergoes mitotic division to grow into a mature, multicellular diploid organism called the sporophyte. The sporophyte produces spores through meiosis, which are dispersed and eventually develop into haploid gametophytes.
- These gametophytes produce gametes through mitosis, completing the cycle.
- The gametes fuse again during fertilization, restarting the diploid phase. The life cycle is common in higher plants like ferns, gymnosperms, and flowering plants.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













