Organ systems are a group of organs that work together to perform specific functions in the body. The endocrine system regulates bodily functions by releasing hormones into the bloodstream, which act as chemical messengers to target organs. These hormones help control processes like metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Examples of organs in the endocrine system include the thyroid gland, pancreas, and adrenal glands. On the other hand, the exocrine system uses ducts to release substances such as sweat, saliva, and digestive enzymes directly to specific locations. Unlike hormones of the endocrine system, exocrine secretions usually act locally rather than throughout the body. Below we have discussed more about the Human endocrine system.
What is Human Endocrine System
The human endocrine system is like a messaging system in the body. It is made up of glands that produce and release hormones, which are chemicals that regulate various functions like growth, metabolism, mood, and Reproduction. Think of hormones as tiny messengers that travel through the bloodstream to different organs and tissues, telling them what to do.
The main glands in the endocrine system include the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, and reproductive glands. Each gland produces specific hormones that target certain parts of the body. For example, the thyroid gland releases hormones that control metabolism, while the adrenal glands produce hormones that help manage stress.
When everything is working smoothly, the endocrine system helps maintain balance and keep our bodies functioning properly. But if there’s an imbalance or a gland isn’t working right, it can lead to health problems like diabetes, thyroid disorders, or hormonal imbalances.
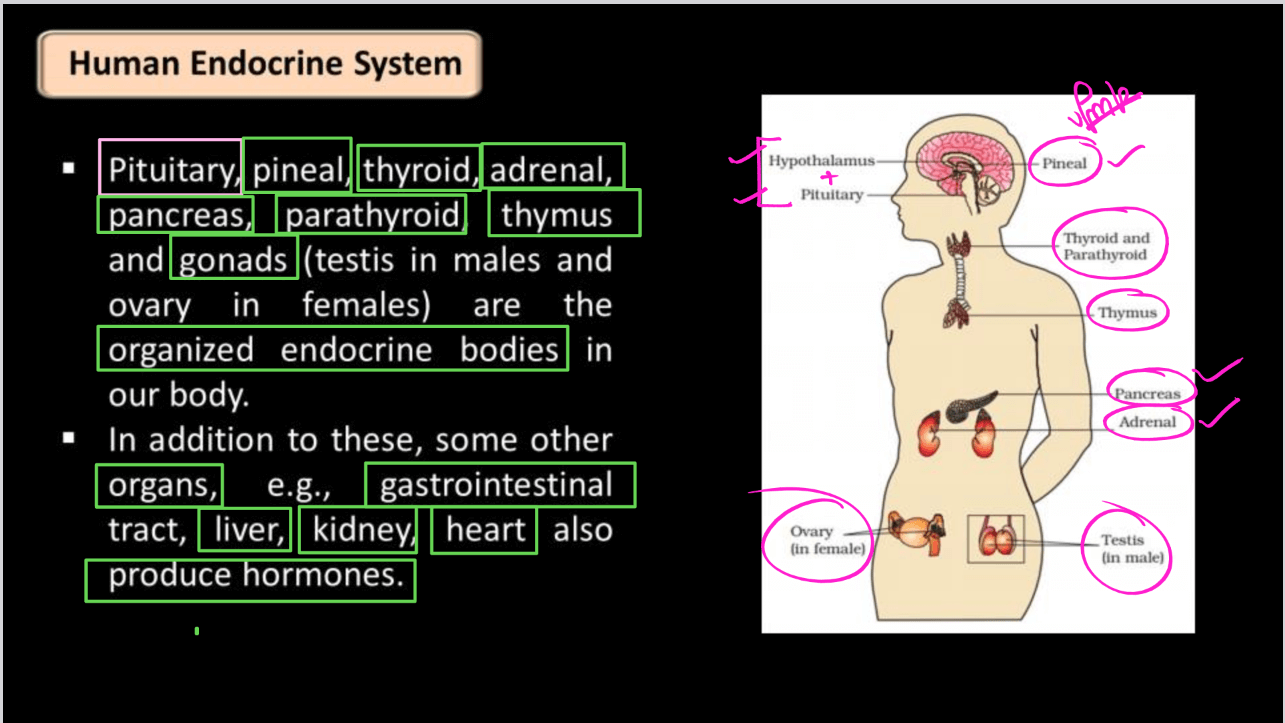
Endocrine Glands
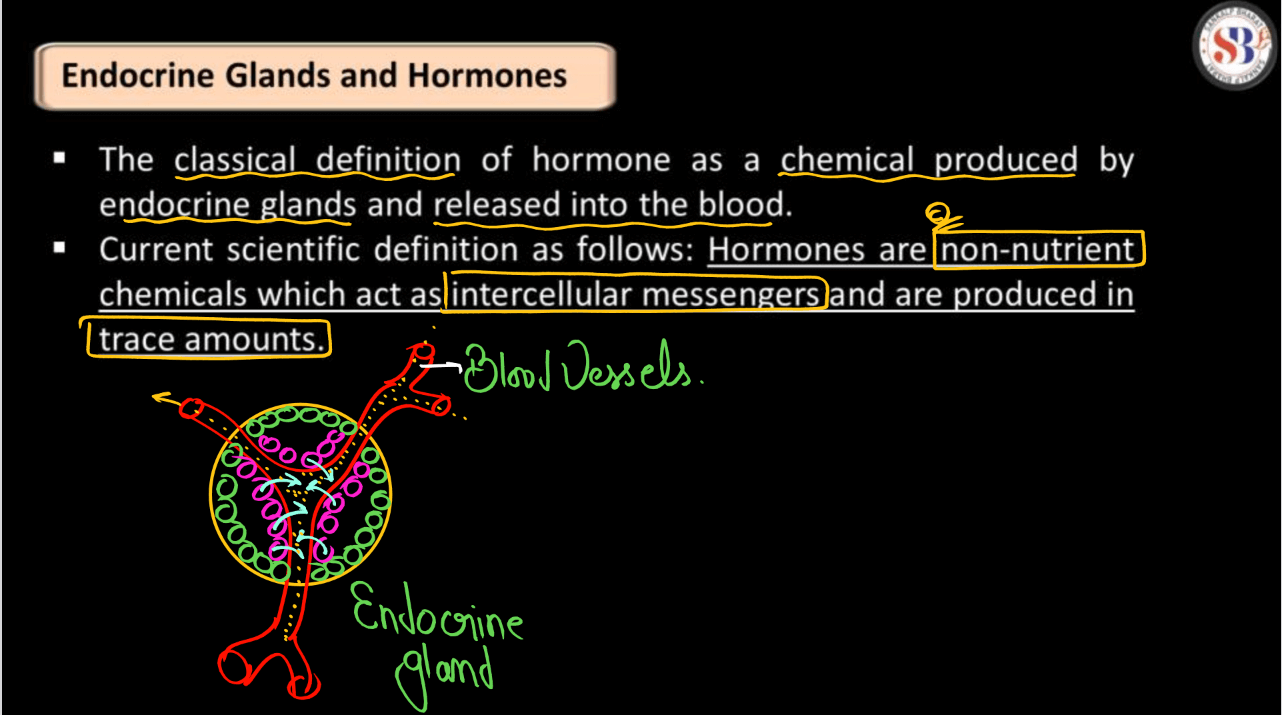
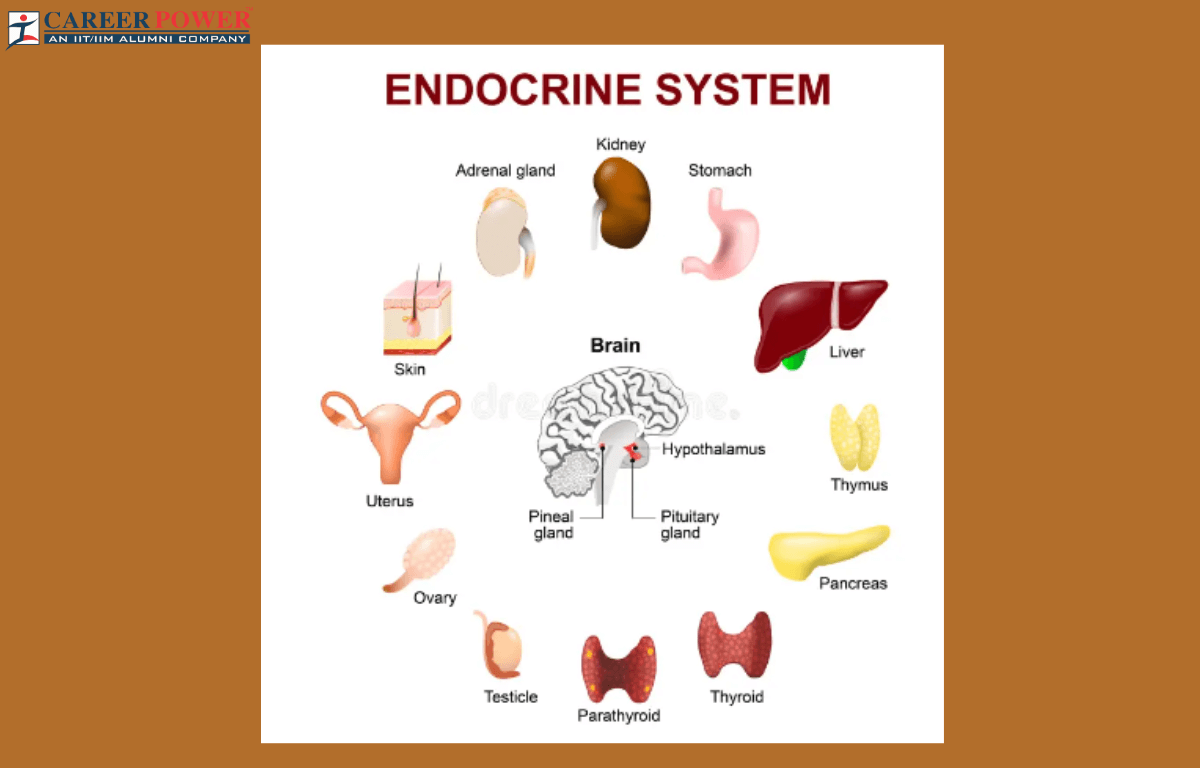
Endocrine glands are special organs in your body responsible for producing hormones, which act as messengers to regulate various functions like growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Unlike exocrine glands that release substances through ducts, endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones travel throughout the body, targeting specific cells and organs to initiate responses. Examples of endocrine glands include the thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, and pituitary gland. Together, they help maintain the body’s internal balance, known as homeostasis, by coordinating processes such as blood sugar levels, stress response, and sleep patterns. Essentially, endocrine glands play a crucial role in keeping our body functioning properly.
List of Endocrine Glands
Endocrine glands are glands in the body that produce hormones, which are chemical messengers that regulate various physiological functions. Some of the major endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, pancreas, pineal gland, etc. These glands work together to maintain homeostasis and regulate various bodily functions.
| List of Endocrine Glands | |
| Glands | Description |
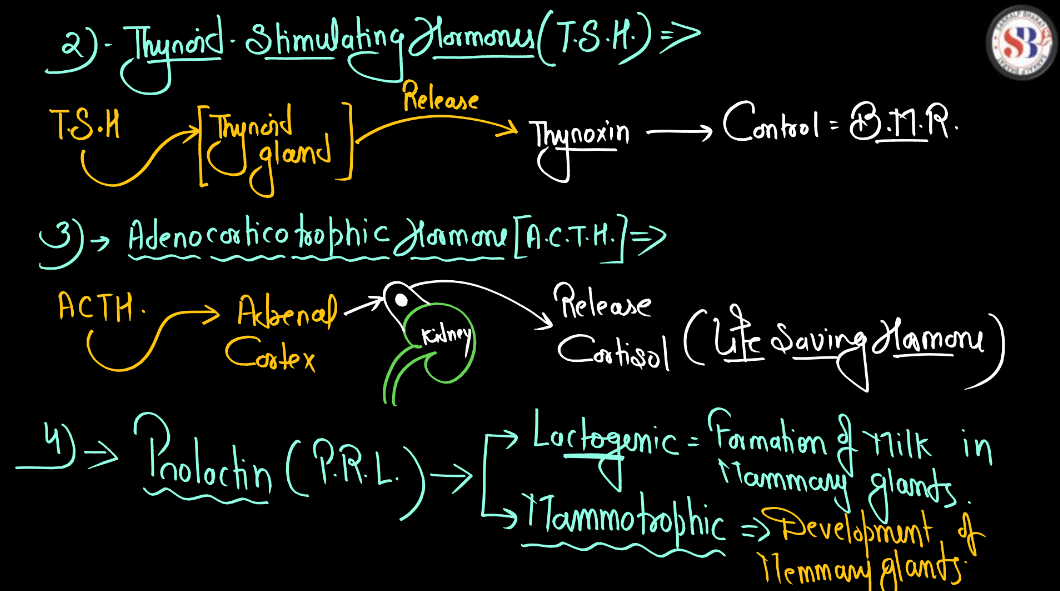
| Pituitary Gland | Often called the “master gland”, it produces hormones that control other glands, growth, and various bodily functions. |
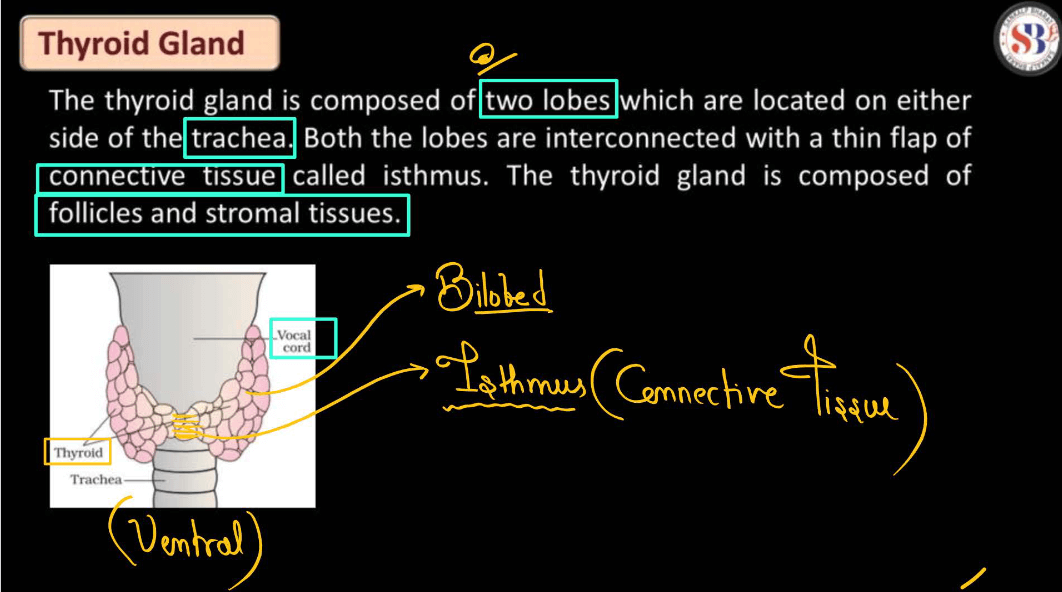
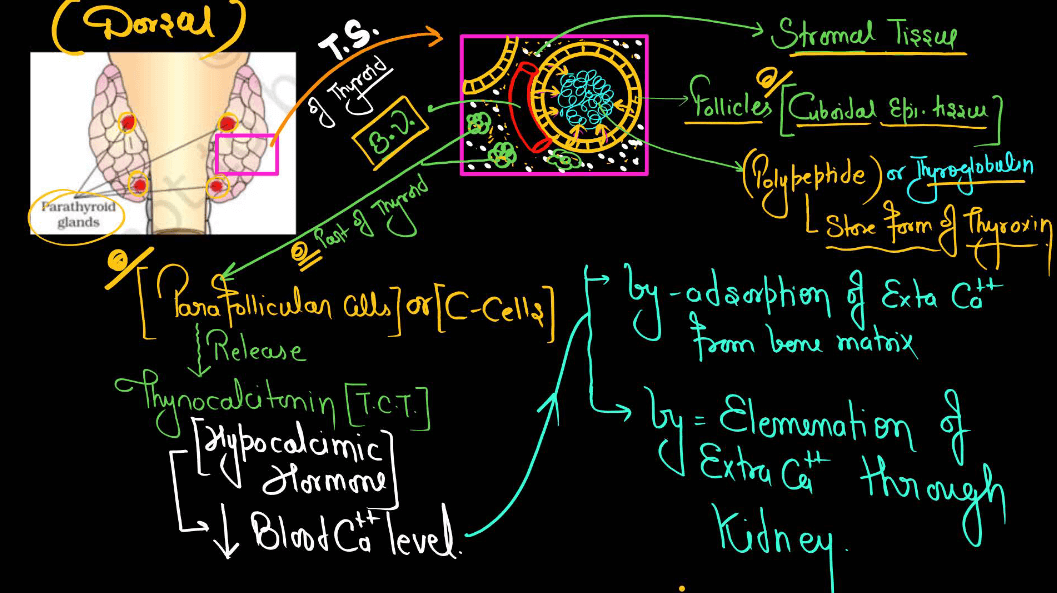
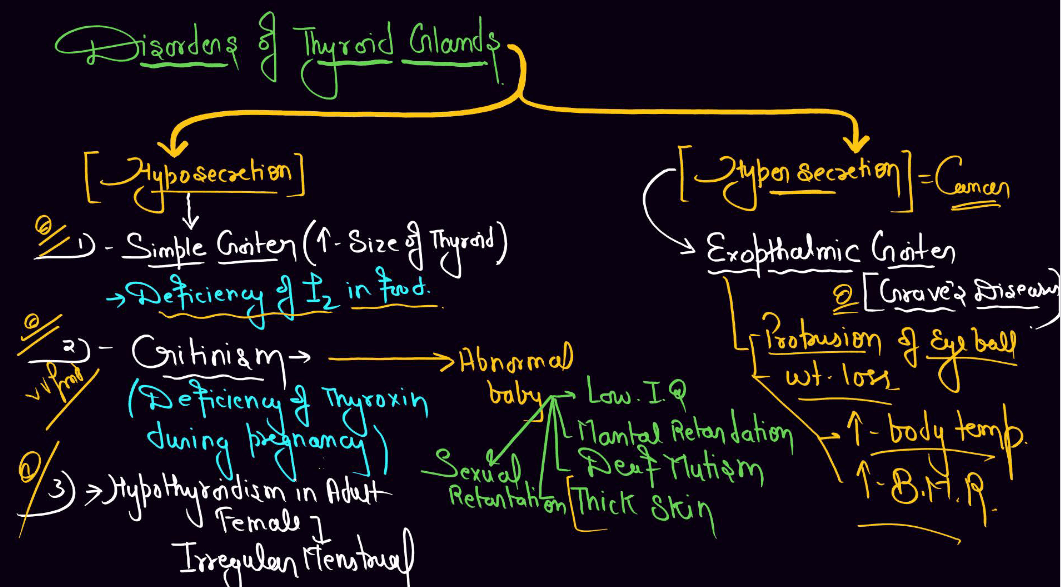
| Thyroid Gland | Produces hormones that regulate metabolism and energy levels. |
| Adrenal Gland | Produces hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, which help regulate stress response, metabolism, and immune functions. |
| Pancreas | Produce insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels. |
| Pineal Gland | Produces melatonin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles. |
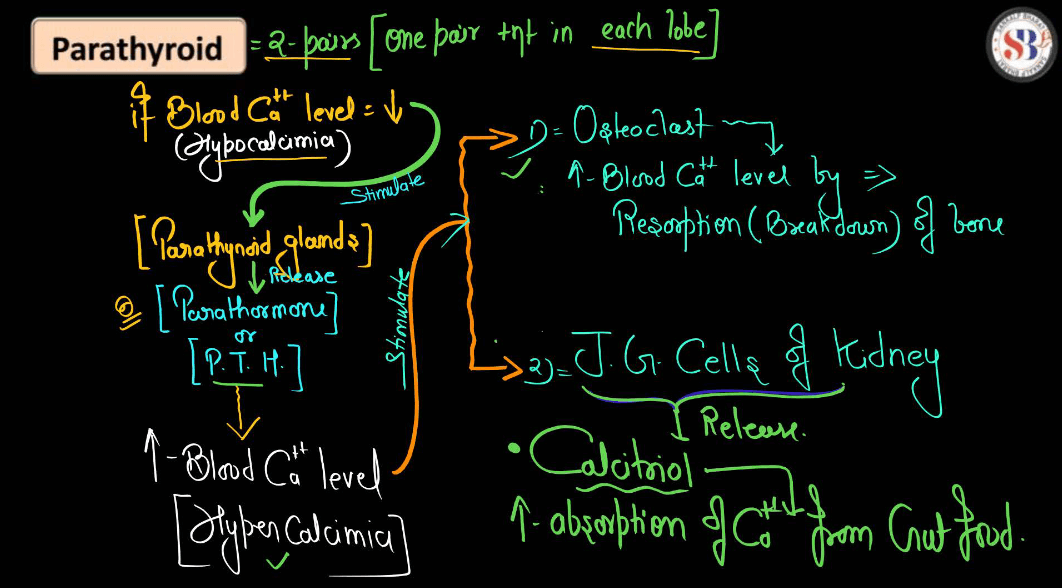
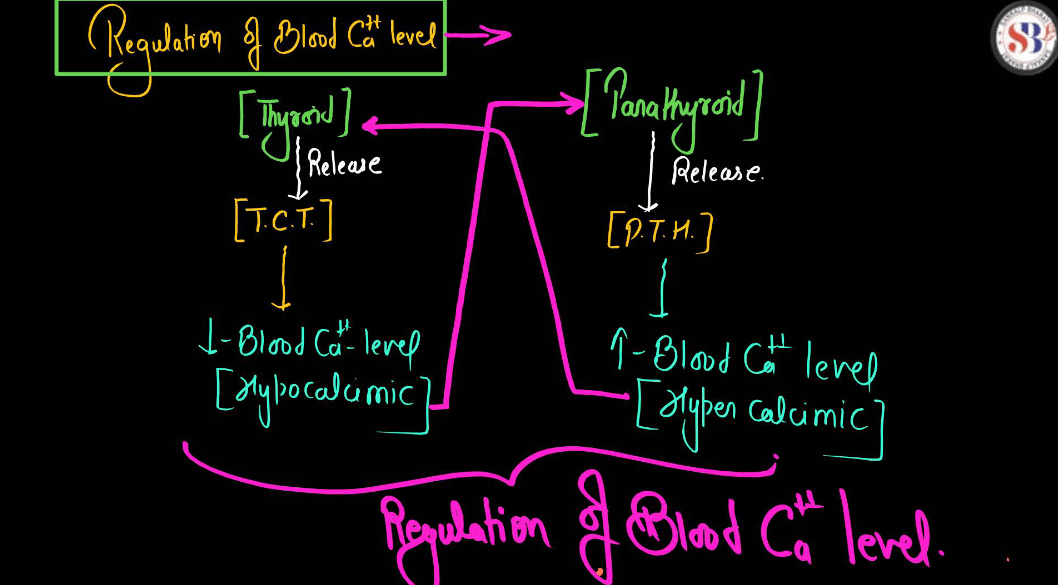
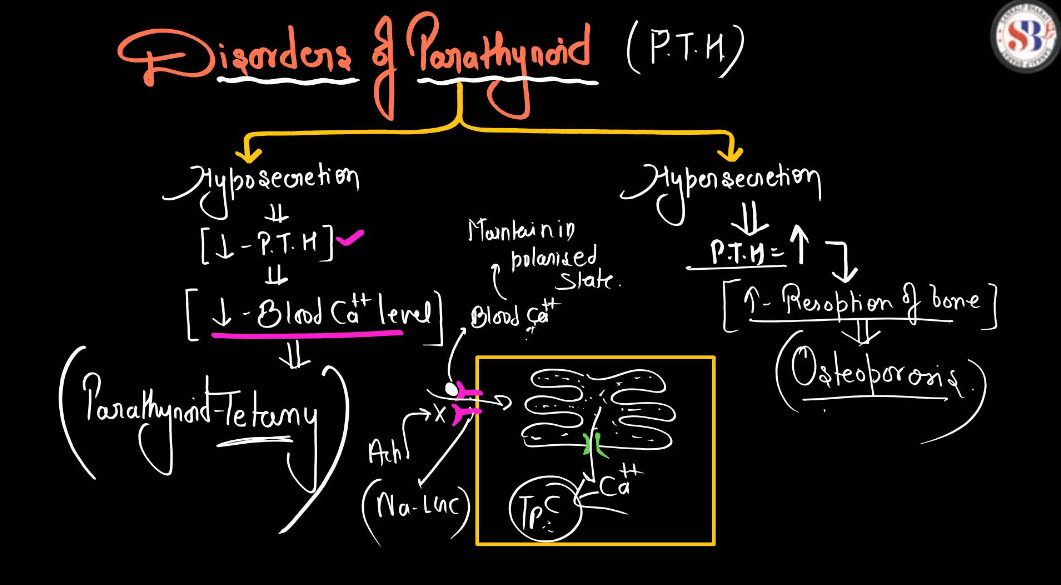
| Parathyroid Gland | Produce hormones that regulate calcium and phosphorus levels in the body. |
| Thymus Gland | Produces hormones involved in immune functions and the development of T-cells. |
| Gonads | Produce sex hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, which regulate reproductive functions and secondary sexual characteristics. (ovaries in females |

Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland is like the boss of our body’s hormones. It is a tiny pea-sized gland located at the base of our Brain, but its job is super important. Think of it as a control center that sends out signals to other glands in our body to tell them when to release hormones. These hormones regulate things like growth, metabolism, reproduction, and stress response. So basically, the pituitary gland helps keep everything in balance and working smoothly. If it doesn’t do its job properly, it can cause all sorts of problems with our body’s functions. So, it might be small, but it’s definitely mighty.
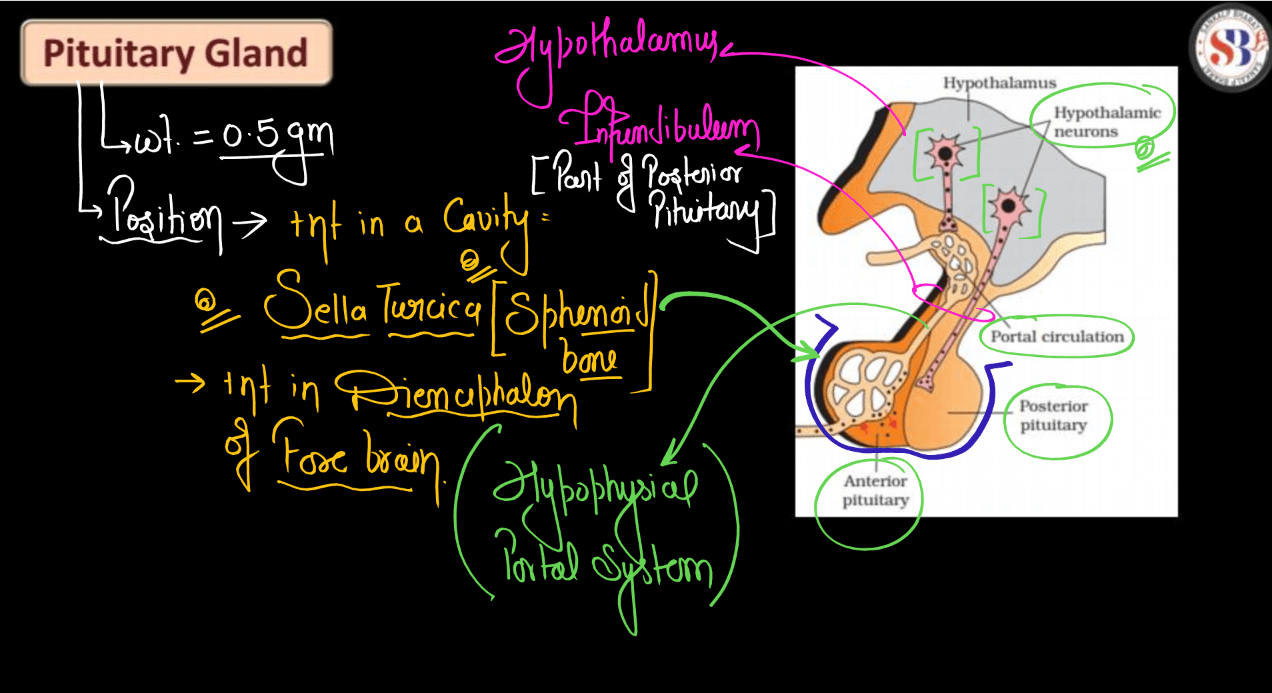
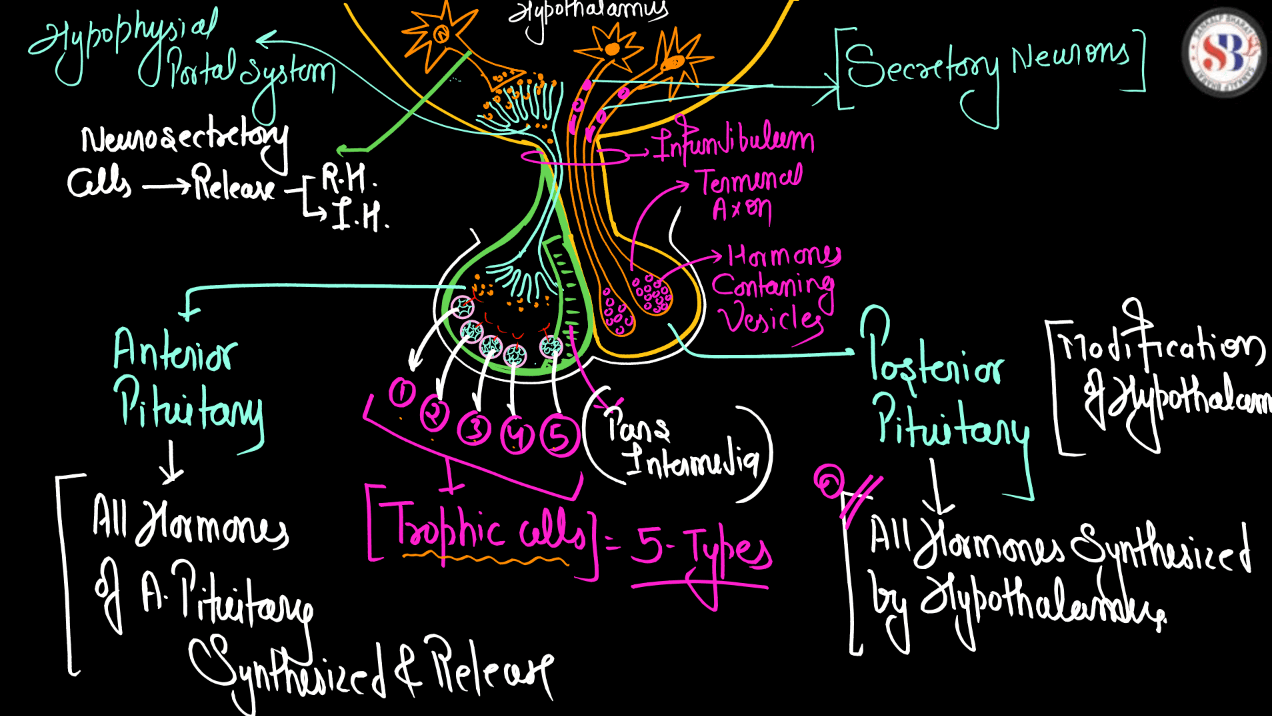
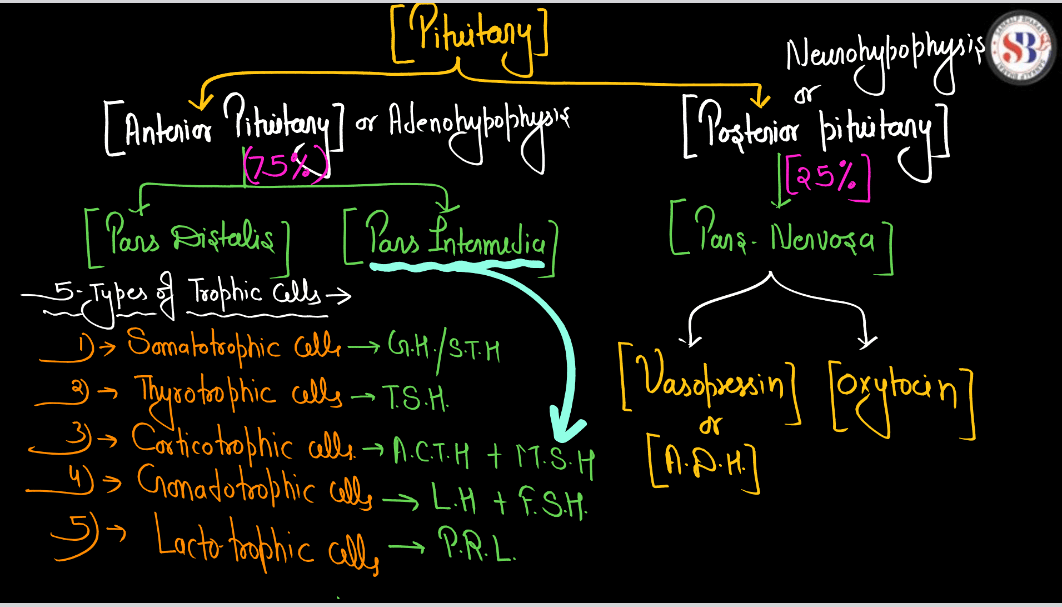
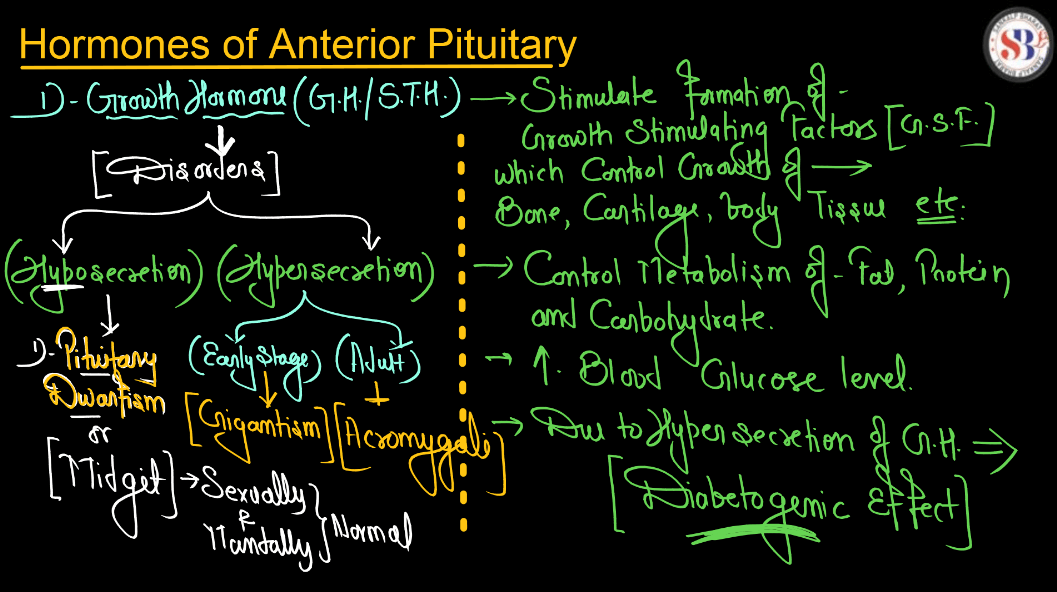
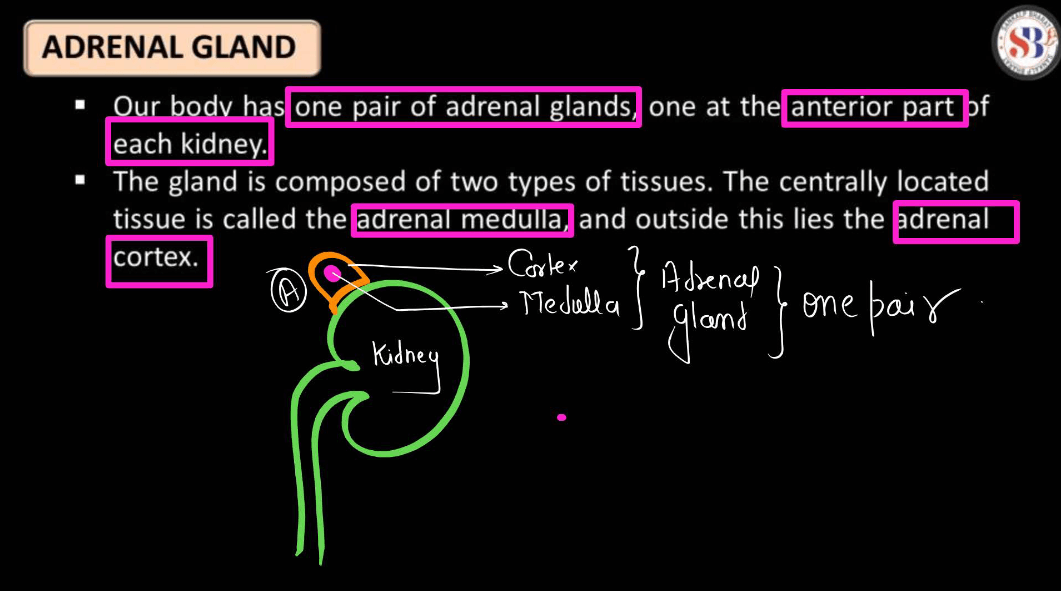
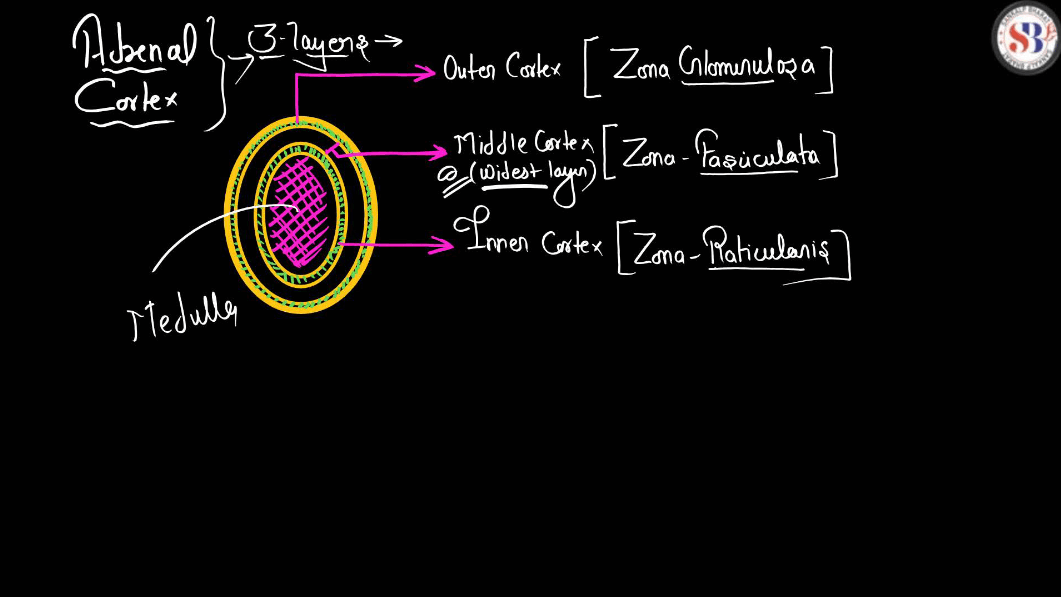
Adrenal Gland
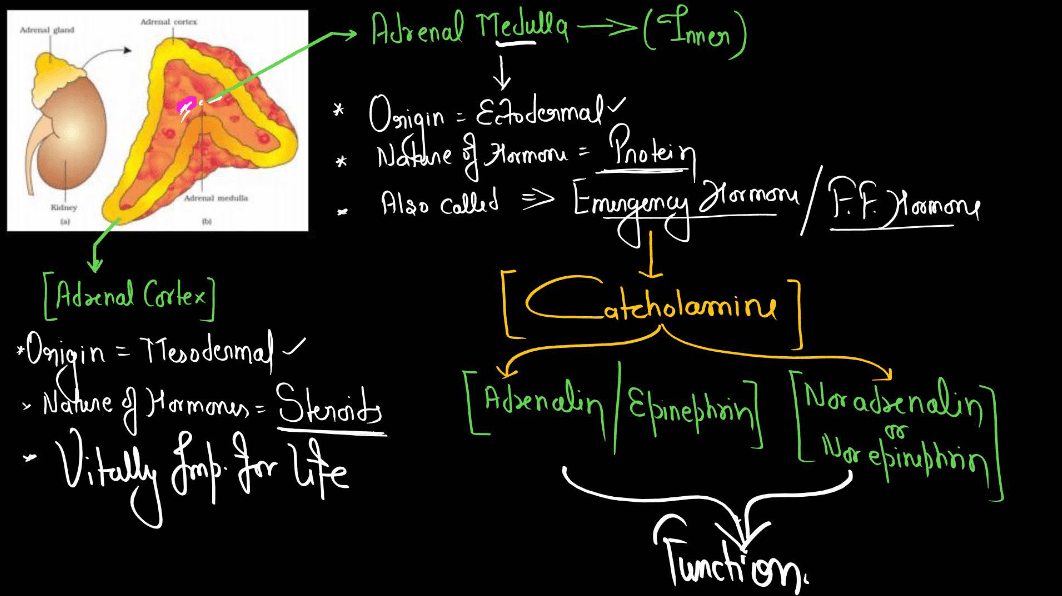
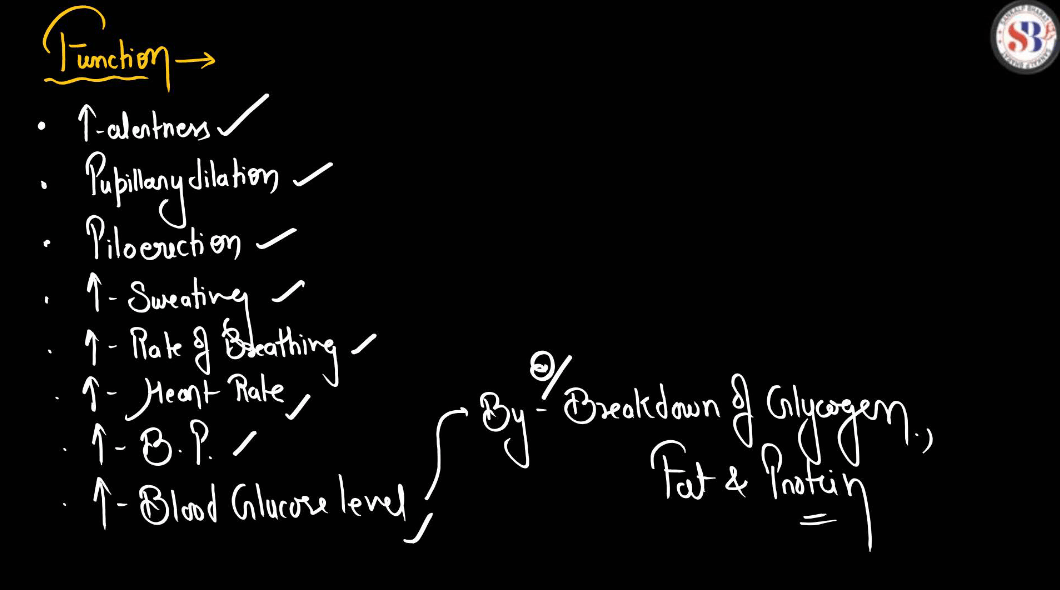
The adrenal glands are small, triangle-shaped glands located on top of each Kidney. They produce hormones that are vital for regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, immune response, and stress management. The adrenal glands secrete hormones like adrenaline, which triggers the body’s fight-or-flight response in stressful situations, and cortisol, which helps regulate metabolism and manage stress. These hormones play crucial roles in maintaining balance within the body and responding to changes in the environment.
Pancreas
The Pancreas is a gland located behind the stomach that plays a vital role in Digestion and blood sugar regulation. It produces enzymes that help break down food in the small intestine, allowing the body to absorb nutrients. Additionally, the pancreas produces hormones like insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin helps Cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream, lowering blood sugar levels, while glucagon raises blood sugar levels by releasing stored glucose into the bloodstream when needed. Essentially, the pancreas acts as an endocrine gland, ensuring the body receives essential nutrients and maintains proper blood sugar balance for overall health.
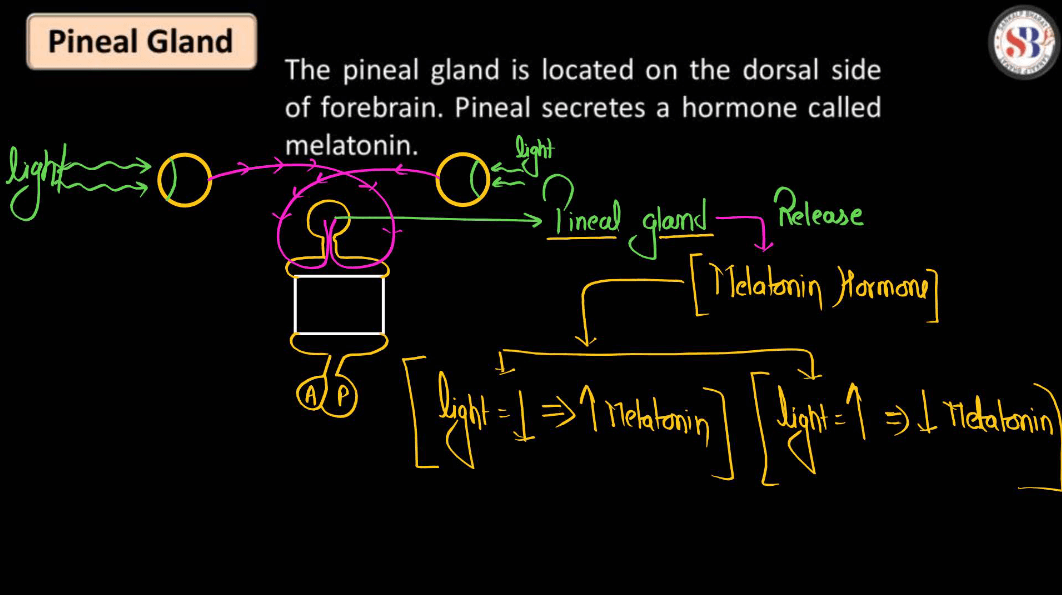
Pineal Glands
The pineal gland is a small gland located deep in the brain, between the two hemispheres. Despite its tiny size, it has significant roles in regulating the body’s internal clock and producing melatonin, a hormone that helps control sleep patterns and circadian rhythms. Often referred to as the “third eye” due to its unique structure and function, the pineal gland receives signals from light-sensitive cells in the eyes to help regulate the sleep-wake cycle. Additionally, it is believed to play a role in various physiological processes, including mood regulation and the body’s response to stress. Overall, the pineal gland acts as a crucial regulator of sleep and other physiological functions in the body.



 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













