Genes are segments of DNA that codes for specific traits. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that carries genetic instructions. In simpler terms, think of DNA as a complete instruction manual for an organism, and genes as individual chapters that provide details about particular features. DNA contains all the information, while genes are specific sections that genes are specific sections that guide the development of distinct characteristics. Other details about the Genes and DNA have been discussed below.
Gene and DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and Reproduction of all living organisms. Genes are specific sequences of DNA that encode instructions for building proteins, which play crucial roles in various biological processes. Genes serve as the blueprint for the traits and characteristics inherited from one generation to the next.
Define Gene
A gene is a biological instruction manual that guides the development and functioning of living organisms. Found within the DNA of cells, genes contain the information needed to create proteins, the building blocks of life. Think of genes as sentences composed of a sequence of “letters” called nucleotides. These nucleotides form the genetic code, determining the characteristics and traits of an organism. Genes play a crucial role in passing traits from parents to offspring during reproduction. Changes in genes, known as mutation, can lead to variations in traits and contribute to the diversity of life. In essence, genes are the fundamental units of heredity, influencing everything from eye color to susceptibility to certain diseases.
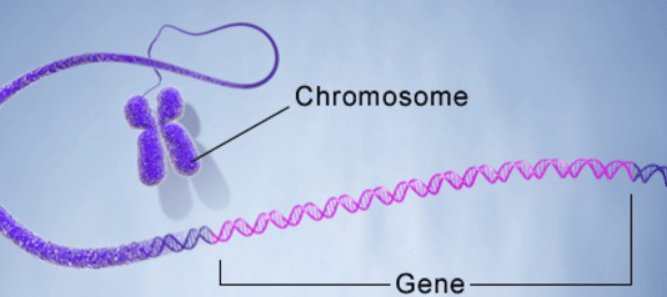
Define DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is like a biological instruction manual that guides the development and functioning of living organisms. It’s a complex molecule found in the cells of all living lings, from tiny bacteria to large mammals like humans. Imagine DNA as a string of letters, A, T, C, and G, representing the building block of life. These letters form sequences called genes, which hold the information needed to create and maintain an organism. Think of genes as chapters in a book, each containing specific details about different aspects of the organism, such as eye color or how the immune system works.
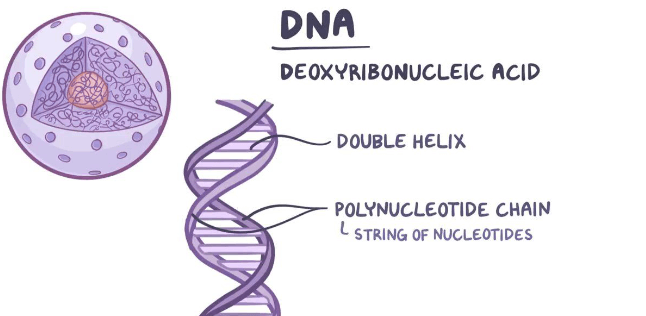
What’s fascinating is that DNA carries hereditary information from one generation to the next. When cells divide, they replicate this genetic code, ensuring that traits are passed down. This remarkable molecule plays a crucial role in determining who we are, influencing our physical traits, susceptibility to certain diseases, and even aspects of our behavior. In essence, DNA is the fundamental code of life, orchestrating the symphony of living organisms.
Difference Between Gene and DNA
Here we have discussed a few points that highlights the difference between Gene and DNA:
| Difference Between Gene and DNA | ||
| Aspects | DNA | Gene |
| Definition | DNA is a molecule carrying genetic instructions. | Genes are segments of DNA containing instructions. |
| Composition | DNA is made up of nucleotides (adenosine, thymine, cytosine, guanine). | Genes are made up of specific sequences within the DNA molecules. |
| Functions | DNA stores genetic information and instructions. | Gene codes for the synthesis of proteins or functional RNA. |
| Locations | DNA is found in the cell’s nucleus (nuclear DNA and mitochondrial DNA). | Genes are found within the DNA molecule, usually on chromosomes. |
| Role in Inheritance | DNA is passed from parents to offspring, determining genetic traits. | Genes are inherited and influence specific traits or functions. |
| Structure | The structure of DNA is like a double-stranded helix. | The genes have a specific sequence of nucleotide bases. |
| Variability | DNA sequences can vary widely between individuals. | Gene sequences can vary, contributing to genetic diversity. |
| Copying Process | DNA replicates during cell division. | Genes are transcribed into DNA during gene expression. |
| Number in a Cell | Multiple copies in a cell, depending on the type (nuclear, mitochondrial). | Multiple genes in a cell, each with unique functions. |
| Examples | Examples of DNA include Nuclear DNA and Mitochondrial DNA. | Examples of Genes include genes for eye color, enzymes, etc. |
Importance of Genes and DNA
DNA and genes are crucial components of living organisms, serving fundamental roles in genetics and Biology. DNA contains the genetic instructions necessary for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known living organisms.
- Genetic Information Storage: DNA carries the genetic information in the form of genes, which are specific sequences of nucleotides. Genes encode instructions for synthesizing proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of cells.
- Inheritance: DNA is passed from parents to offspring during reproduction. This inheritance is the basis for the transmission of genetic traits, determining the characteristics and traits of an organism.
- Protein Synthesis: Genes within DNA provide the instructions for synthesizing proteins. Proteins are vital for the structure and function of cells, tissues, and organs. They play roles in enzymatic reactions, transport, signaling, and structural support.
- Cellular Functions: DNA directs cellular processes by controlling the synthesis of proteins. This regulation is crucial for the proper functioning of cells and the coordination of various physiological activities.
- Biomedical Applications: Understanding DNA and genes is central to advancements in medicine, including genetic disorders, gene therapy, and personalized medicine. It enables researchers and healthcare professionals to study and treat various diseases.
- Biotechnology and Agriculture: Genetic engineering, based on the understanding of DNA and genes, allows for the development of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) with desired traits, improving crop yields, pest resistance, and other agricultural characteristics.



 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













