Chordates and non-chordates represent two major groups in the Animal Kingdom. The key distinction lies in the presence of a notochord – a flexible, rod-like structure providing skeletal support – in chordates. This notochord, usually replaced by a backbone in invertebrates, sets chordates apart. Non-chordates lack this feature, relying on alternative support structures like exoskeletons or hydrostatic skeletons. Additionally, chordates typically exhibit a dorsal nerve cord and gill slits at some stage, features absent in non-chordates. Here we have discussed a few more differences between chordates and non-chordates with their importance.
Chordates and Non-Chordates
Chordates and Non-chordates represent two major groups of animals with distinct characteristics. Chordates, including vertebrates like mammals, birds, and fish, play a crucial role in ecosystems as diverse contributors to biodiversity. They often occupy top positions in food chains, influencing the balance of ecosystems.
Non-chordates, such as arthropods (like insects and crustaceans) and mollusks, also contribute significantly to biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Many non-chordates serve essential roles as pollinators, decomposers, and prey in various ecosystems, influencing nutrient cycling and ecosystems.
What are Chordates?
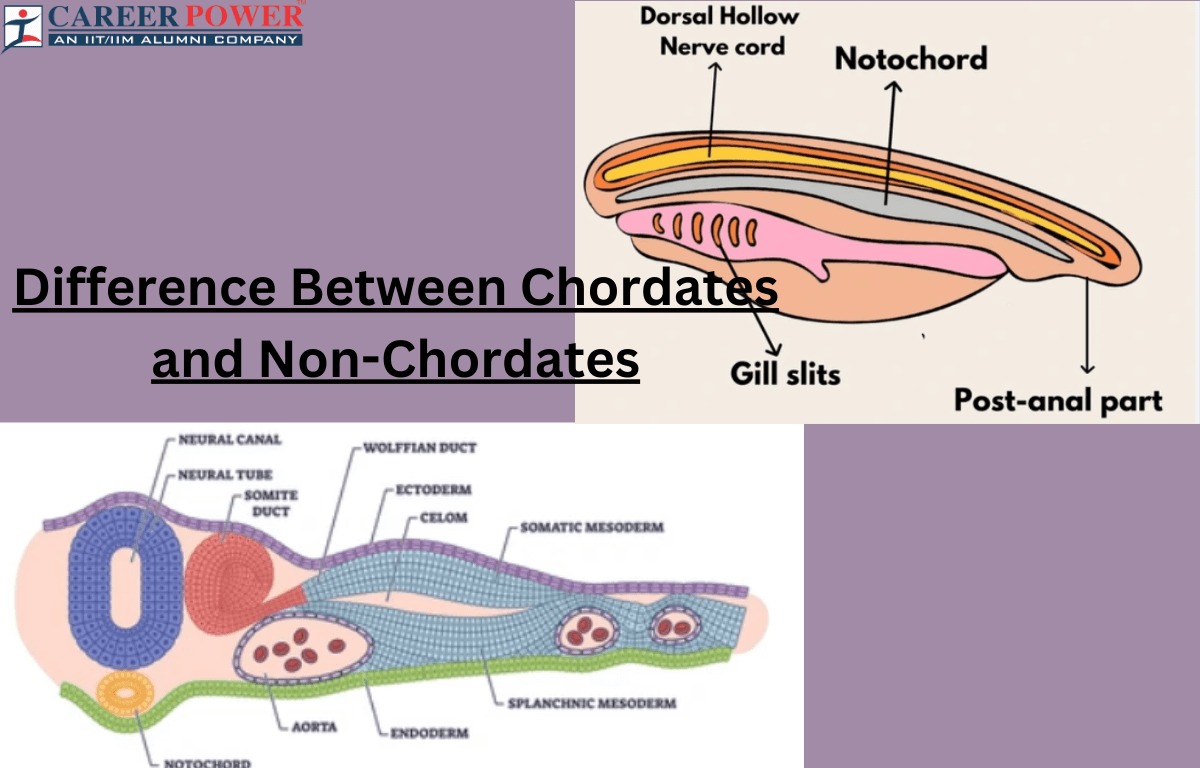
Chordates are animals that belong to the phylum Chordata, and they share a set of distinctive features. At some point in their life, chordates typically exhibit a notochord – a flexible, rod-like structure that provides support. In vertebrates, like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, the notochord is often replaced by a spine during development.

Chordates also have a hollow nerve cord running along their back, which develops into the spinal cord in vertebrates. They possess gill slits in the pharynx, which may be present only during embryonic development in some species or persist throughout life in others. Chordates usually have a muscular tail, although this feature may be more prominent in certain stages of their life cycle.
The group Chordata includes a diverse array of organisms, from simple sea squirts to complex mammals. Humans are also chordates, sharing these fundamental characteristics with other members of the phylum. The presence of these key features unites chordates, showcasing their evolutionary connections and diverse adaptation across the Animal Kingdom.
What are Non-Chordates?
Non-chordates are a diverse group of animals that lack a notochord, a flexible rod-like structure found in chordates (animals with backbones). This group includes a wide range of creatures such as insects, worms, mollusks, and jellyfish. Unlike chordates, non-chordates don’t have a spinal column or a backbone. Instead, they exhibit varied body structures and can be found in different environments and can be found in different environments around the world. Insects, for instance, have exoskeletons, while worms have soft bodies. Mollusks, like snails and clams, possess a muscular foot and a mantle that may secrete a protective shell.

Non-chordates play crucial roles in ecosystems; insects are pollinators and decomposers, worms contribute to soil health, and mollusks serve as both prey and predators in aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, jellyfish, belonging to the phylum Cnidaria, exhibit radial symmetry and stinging cells called cnidocytes. Understanding non-chordates helps scientists explore the incredible diversity of life on Earth, highlighting the adaptability of different organisms to their environments.
Difference Between Chordates and Non-Chordates with Examples
Chordates are animals with a notochord, a dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail at some stage of their development. Non-chordates lack these characteristics. Chordates include vertebrates like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, while non-chordates encompass a diverse group such as Arthropods, mollusks, and annelids.
| Difference Between Chordates and Non-Chordates | ||
| Characteristics | Chordates | Non-Chordates |
| Notochord | Chordates have a notochord, a flexible rod-like structure providing skeletal support. | Non-chordates lack a notochord throughout their life cycle. |
| Dorsal Nerve Cord | Chordates possess a dorsal nerve cord, typically part of the central nervous system. | Non-chordates lack a dorsal nerve cord in the characteristic chordate manner. |
| Pharyngeal Slits | Chordates exhibit pharyngeal slits or pouches in their throat region at some stage. | Non-chordates generally lack pharyngeal slits. |
| Post-anal Tail | Chordates have a post-anal tail, an extension beyond the anal opening. | Non-chordates lack a post-anal tail. |
| Segmentation | Chordates often display a segmented body plan. | Non-chordates may or may not exhibit segmentation. |
| Endoskeleton | Chordates typically have an internal endoskeleton, often composed of bone or cartilage. | Non-chordates usually have exoskeletons (external skeletal structures) or no true skeleton. |
| Circulatory System | Chordates commonly possess a closed circulatory system with a heart. | Non-chordates may have an open circulatory system in many cases. |
| Respiratory Structures | Chordates employ various respiratory structures, including lungs or gills. | Non-chordates use diverse respiratory mechanisms, such as tracheae or diffusion through the body surface. |
| Body Symmetry | Chordates often exhibit bilateral symmetry. | Non-chordates can have bilateral, radial, or asymmetrical body symmetry. |
| Examples | Chordates include vertebrates like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. | Non-chordates encompass arthropods, mollusks, annelids, and other invertebrates. |
Importance of Chordates and Non-Chordates
Both chordates and non-chordates are essential for comprehending the complexity and diversity of life on Earth, contributing to ecological stability and the overall health of ecosystems.
Importance of Chordates
- Chordates represent a diverse group including vertebrates like mammals, birds, and fish.
- The chordates play crucial roles in ecosystems as top predators, influencing Food Chains.
- Chordates contribute significantly to biodiversity, adding complexity to ecosystems.
- Chordates often have well-developed sensory and nervous systems, enhancing adaptability.
Importance of Non-Chordates
- Non-chordates include diverse groups like arthropods (insects, crustaceans) and mollusks.
- Non-chordates serve essential ecological roles such as Pollination, decomposition, and as prey.
- Non-chordates contribute significantly to biodiversity, with vast species diversity.
- Non-chordates influence nutrient cycling and ecological interactions in various ecosystems.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













