Exocytosis and Endocytosis
Exocytosis is the process by which cells release substances outside the cell by vesicle fusion with the cell membrane. On the other hand Endocytosis, on the other hand, involves the uptake of materials into a cell by engulfing them with the cell membrane, forming vesicles. Both processes of exocytosis and endocytosis play crucial roles in cellular transport and maintaining cell homeostasis.
What is Exocytosis?
Exocytosis is a cellular process where a cell releases substances outside itself. Think of it as the cell’s way of sharing or exporting materials. Picture a small bubble, called a vesicle, inside a cell. When the cell wants to release something important, like a protein or signal, it merges the vesicle with its outer layer. This makes the bubble open, letting its contents go into the space outside the cell.
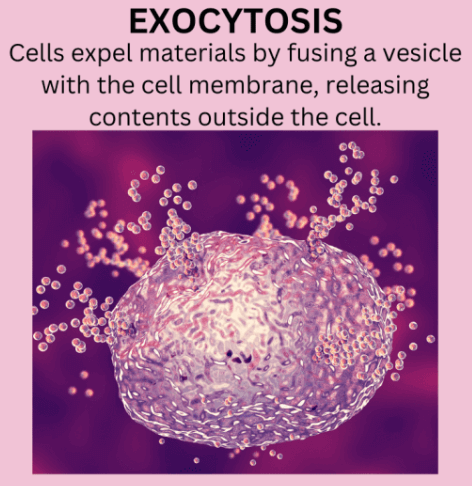
This mechanism is crucial for various functions in the body, such as communication between cells and the release of hormones. Imagine exocytosis as a cellular delivery system, allowing cells to communicate and coordinate activities. It’s like a tiny package being sent out from the cell to deliver its message or contribute to the larger environment outside the cell.
What is Endocytosis?
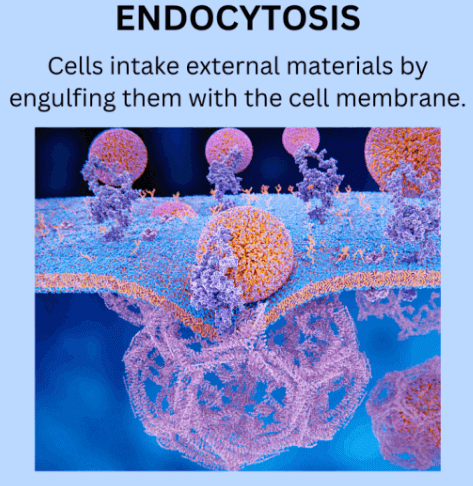
Endocytosis is a cellular process that involves the intake of substances into a cell. It’s like the cell’s way of engulfing external materials. Imagine the cell membrane as a flexible bag. When the cell wants to take in specific molecules or particles from its surroundings, it forms a small pocket in the membrane. This pocket then pinches off, creating a vesicle inside the cell that contains the engulfed material.
There are different types of endocytosis, such as phagocytosis (engulfing solid particles) and pinocytosis (engulfing liquid particles). It’s a vital process for nutrient uptake, regulation of signaling molecules, and overall maintenance of cell function. Essentially, endocytosis allows the cell to bring in necessary substances from the external environment, contributing to its survival and proper functioning.
Difference Between Exocytosis and Endocytosis
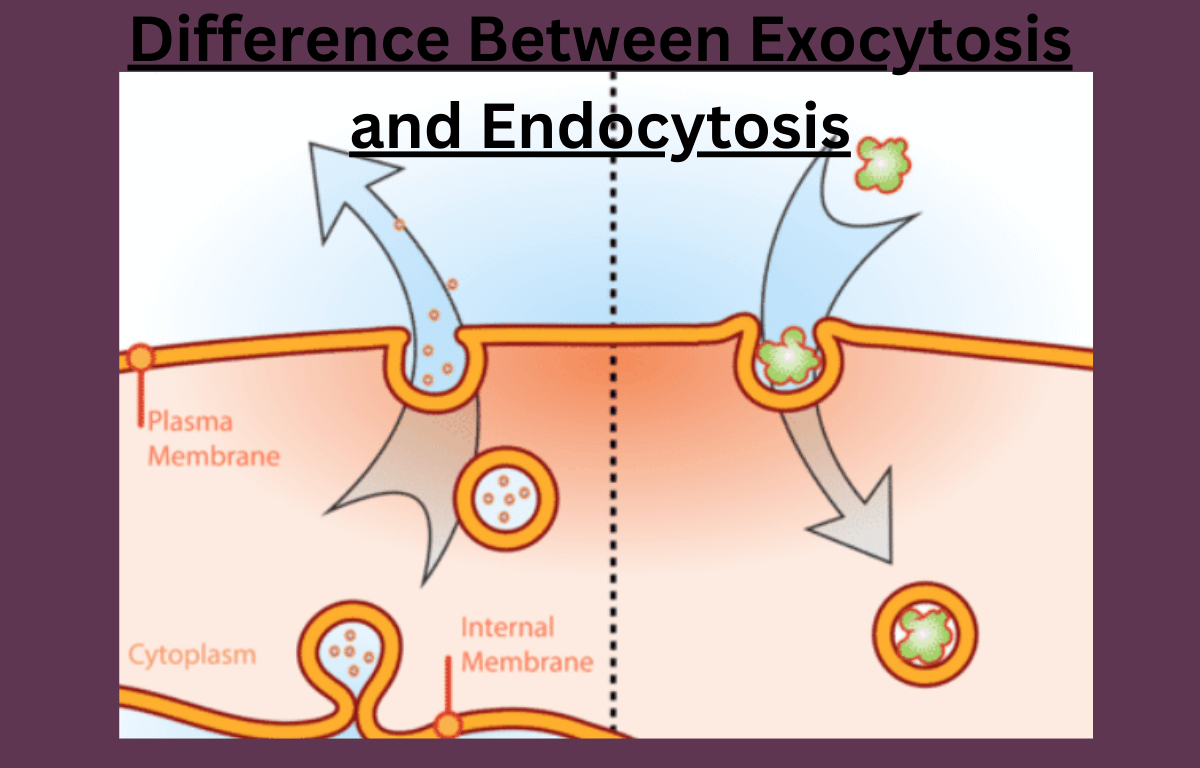
Exocytosis and endocytosis are processes that help cells move materials across their membranes. Exocytosis occurs when a cell pushes substances out, such as waste or signals, allowing them to exit the cell. In contrast, endocytosis is when a cell takes in substances from outside, bringing them inside. You can think of exocytosis as “exit” for materials and endocytosis as “entry” for substances into the cell. For more details about the differences between exocytosis and endocytosis, you must go through the complete table mentioned below.
| Differences Between Exocytosis and Endocytosis | ||
| Features | Exocytosis | Endocytosis |
| Direction of Material Transport | Exocytosis moves materials from the cell’s interior to the external environment. | Endocytosis takes in materials from the external environment into the cell. |
| Vesicle Formation | Exocytosis involves the fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane to release contents. | Endocytosis begins with the formation of vesicles to engulf materials. |
| Purpose | Exocytosis is used for secretion of substances (e.g., hormones and neurotransmitters). | Endocytosis functions in nutrient uptake, defense, and regulation of cell membrane composition. |
| Types | Exocytosis can be constitutive (continuous release) or regulated (triggered by specific signals). | Exocytosis includes phagocytosis (solid particles), pinocytosis (liquids), and receptor-mediated endocytosis (specific molecules). |
| Membrane Fusion | Exocytosis involves the fusion of the vesicle membrane with the cell membrane. | Exocytosis requires the fusion vesicle membrane with the cell membrane to release contents into the cell. |
| Energy Requirement | Exocytosis generally requires energy (ATP) to transport materials out of the cell. | In Endocytosis energy is needed, especially during the formation of vesicles. |
| Examples | Examples of Exocytosis include neurotransmitter release at synapses. | Examples of Endocytosis include the uptake of nutrients by cells |
| Receptor Involvement | Exocytosis does not involve specific receptors on the cell membrane. | Receptor-mediated endocytosis relies on specific receptors to target molecules for uptake. |
| Rate of Occurrence | It is a continuous process in cells for maintaining membrane balance. | Endocytosis can be a rapid, regulated response to external stimuli |
| Cellular Regulation | Exocytosis is controlled by cellular signals and external stimuli. | Endocytosis can be triggered by the presence of specific molecules or signals in the extracellular environment. |
Importance of Exocytosis and Endocytosis
Exocytosis and endocytosis are vital cellular processes that facilitate the exchange of materials between a cell and its environment. In summary, these processes are fundamental for maintaining cellular homeostasis, responding to external stimuli, and supporting various physiological functions in organisms.
Importance of Exocytosis
We have discussed a few points below that will highlight the importance of exocytosis.
- Secretion of Substances: Cells use exocytosis to release various molecules, such as hormones, enzymes, or neurotransmitters, into the extracellular space.
- Membrane Maintenance: Exocytosis helps in maintaining the cell membrane’s integrity by removing excess membrane components and replacing damaged portions.
Importance of Endocytosis
Below are some points that highlight the importance of endocytosis.
- Nutrient Intake: Cells utilize endocytosis to engulf and internalize nutrients, such as proteins or lipids, from the extracellular environment.
- Defense Mechanism: Endocytosis is involved in the uptake of foreign particles, facilitating immune responses and defense against pathogens.
- Cell Signaling: Receptor-mediated endocytosis plays a crucial role in cell signaling by regulating the internalization of specific molecules, allowing cells to respond to their environment.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













