What is Codominance?
Codominance is a genetic concept where two different alleles for a gene are both expressed in an organism, and neither dominates over the other. In simpler terms, if you have a gene with two alleles (versions), instead of one allele masking the effect of the other, both alleles show their traits simultaneously. Imagine a flower with a red allele and a white allele for color. In co-dominance, each allele contributes independently to the phenotype without blending.
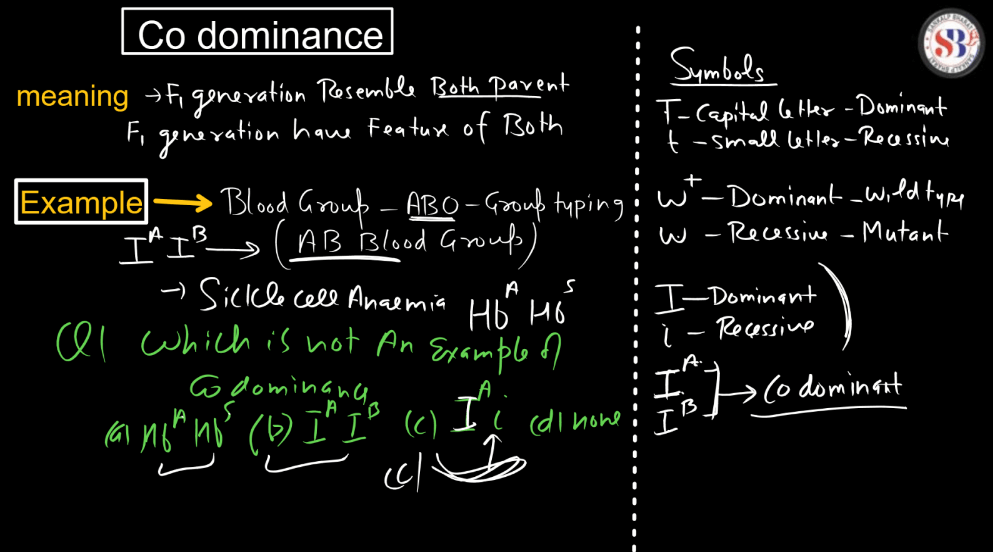
This phenotype is often observed in blood type genetics. For example, in the ABO blood group system, an individual with one A allele and one B allele will express both A and B antigens on their blood cells. This dual expression distinguishes co-dominance from incomplete dominance, where the trait may blend. Co-dominance provides genetic diversity, as both alleles maintain their distinct characteristics. It’s like having a mixed playlist where you can hear each song clearly rather than a blend of different tunes. This concept is crucial in understanding the complexity of genetic traits and how various alleles interact to shape the observable features of organisms.
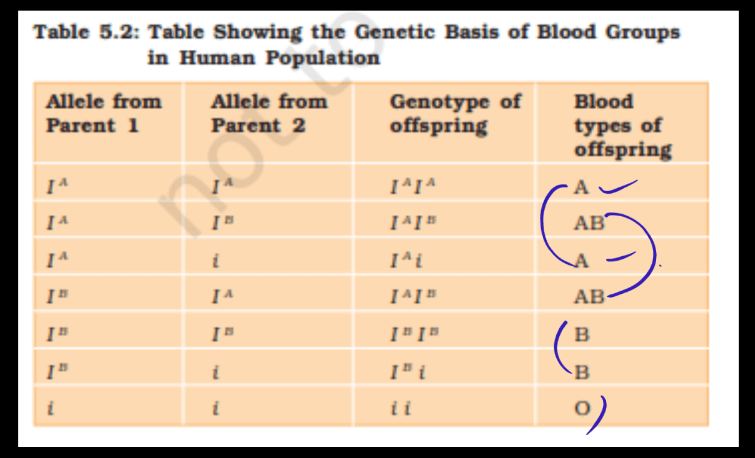
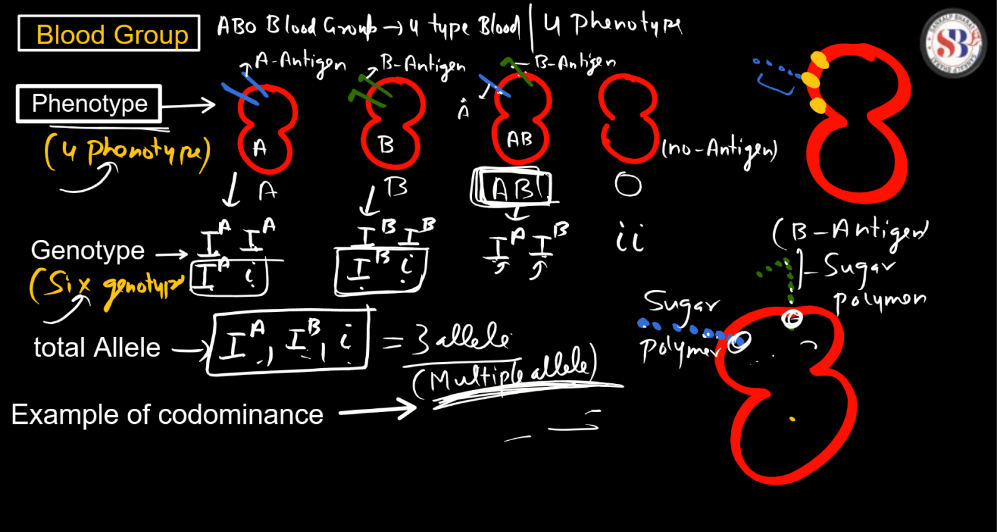
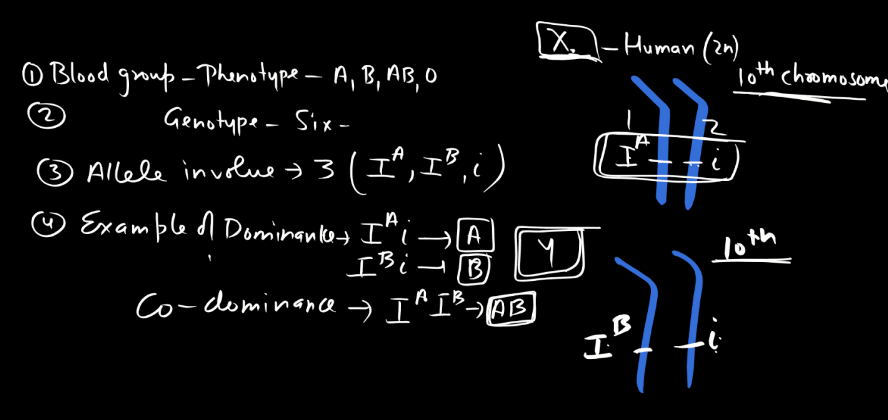
Example of Codominance – Blood Group
Co-dominance is a genetic concept where two alleles of a gene are both expressed in the phenotype, resulting in a combined, distinguishable trait. An example is the blood type AB in humans. If a person inherits an A allele from one parent and a B allele from the other, both alleles are expressed, leading to the co-dominant AB blood type. Unlike other cases where one allele may dominate, here, both contribute equally. This contrasts with incomplete dominance, where a blend of traits occurs. Co-dominance, where a blend of traits occurs. Co-dominance highlights the simultaneous, distinct expression of multiple alleles, providing genetic diversity and illustrating the complexity of inheritance in a straightforward manner.
More Examples of Codominance
Codominance occurs when both alleles in a heterozygous individual express their traits fully. These examples illustrate how co-dominance allows for the simultaneous expression of multiple alleles, producing a distinct phenotype that reflects the contribution of both alleles.
- Roan Cattle Coat Color:
- In cattle, the alleles for red coat color and white coat color are co-dominant.
- Roan cattle have a coat with a mixture of red and white hairs.
- Sickle Cell Anemia:
- In the case of sickle cell anemia, co-dominance is observed in individuals with one allele for normal cell hemoglobin and one allele for sickle cell hemoglobin.
- This results in a condition called sickle cell trait, where both types of hemoglobin are produced.
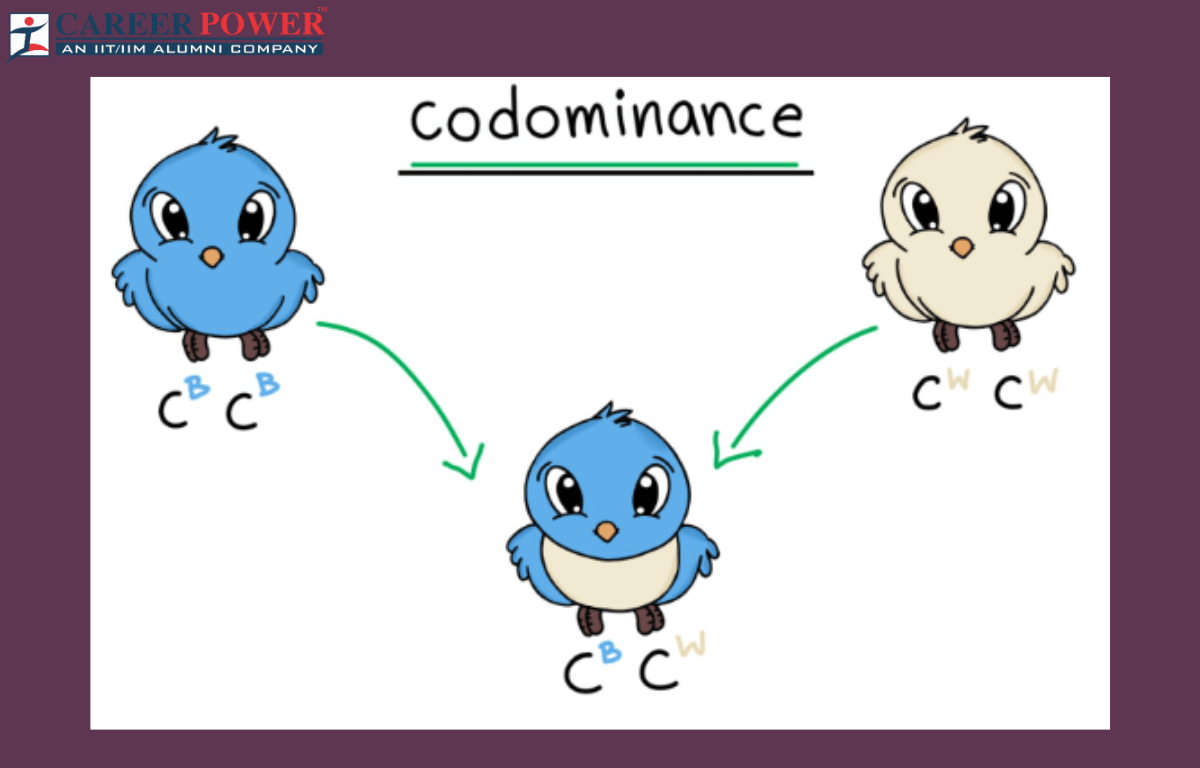
- Chicken Feather Color:
- In some chicken breeds, the alleles for black feathers (B) and white feathers (W) are co-dominant.
- Heterozygous chickens (BW) display a pattern of both black and white feathers.
- Flower Color in Snapdragons:
- In snapdragons, the alleles for red flower color (R) and white flower color (W) are co-dominant.
- Heterozygous individuals (RW) have pink flowers due to the co-expression of both alleles.
- Horse Coat Color – Appaloosa Pattern:
- The Appaloosa pattern in horses is governed by co-dominant alleles.
- Horses with one allele for solid color and one for the spotted pattern (Leopard complex) exhibit a blend of both characteristics.
Facts on Codominance Alleles
As we know co-dominance provides a fascinating example of genetic variation, showcasing the simultaneous expression of multiple alleles and contributing to the diversity within a population
- Co-dominance Definition: Co-dominance is a genetic concept where two different alleles for a gene are expressed independently in a heterozygous individual.
- Distinct Expression: Unlike incomplete dominance, co-dominance involves both alleles maintaining their distinct characteristics without blending.

- Blood Type Example: A classic example is the ABO Blood group system in humans, where the A and B alleles are co-dominant. An individual with an AB genotype expresses both A and B antigens on their red Blood Cells.
- Genetic Variation: Co-dominance contributes to genetic diversity within a population by allowing for the simultaneous expression of multiple alleles.
- Heterozygous Individuals: In co-dominance, heterozygous individuals exhibit a phenotype that reflects the presence of both alleles, highlighting the unique expression pattern.



 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













