What is Biological Evolution?
Biological evolution is a gradual change in living organisms over time. It occurs through the process of natural selection, where traits that help an organism survive and reproduce are passed on to the next generation. Random mutations in the genes contribute to this variation. Over generations, organisms with advantageous traits thrive, while those with less favorable traits may struggle to survive. This leads to the accumulation of beneficial characteristics in a population, shaping the diversity of life on Earth. Evolution doesn’t have a specific goal; it’s simply the result of ongoing adaptation to environmental challenges, driving the continuous development and diversity of living species.
Origin of Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
Eukaryotes and prokaryotes represent two major categories of cells. Prokaryotes, such as bacteria and archaea, are simpler cells lacking a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They likely appeared around 3.5 billion years ago. Eukaryotes, more complex Cells with a nucleus and organelles, likely originated through endosymbiosis, where simpler cells engulfed others, forming a mutualistic relationship. This process, occurring around 1.5 billion years ago, led to the evolution of diverse eukaryotic organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi.
Origin of Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are simple cells like bacteria and archaea, originated around 3.5 to 4 billion years ago, making them among the earliest life forms on Earth. These cells lack a Nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, distinguishing them from more complex Eukaryotic Cells. The exact origin is not fully clear, but it likely involved a gradual process of chemical evolution. Early Earth had a harsh environment with volcanic activities and extreme temperatures. In this setting, simple organic molecules formed and eventually gave rise to self-replicating entities-Proto-Cells.
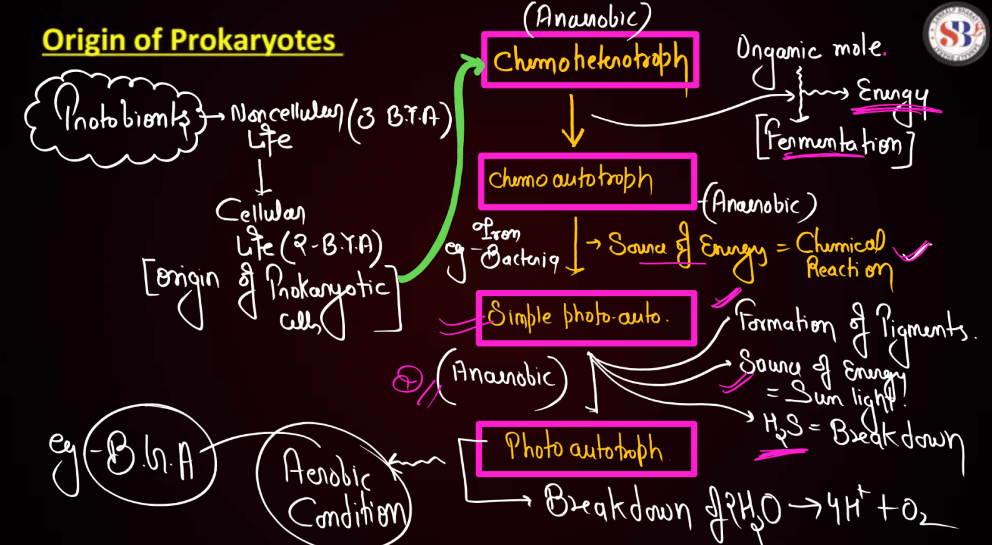
These proto-cells lacked the intricate structures we see today but represented a crucial step toward life as we know it. Over time, through natural selection, these primitive forms of life developed mechanisms for survival and adaptation, leading to the diverse array of prokaryotes that exist today. Their resilience and adaptability played a pivotal role in shaping the Earth’s ecosystems, and they remain fundamental to the planet’s biological processes.
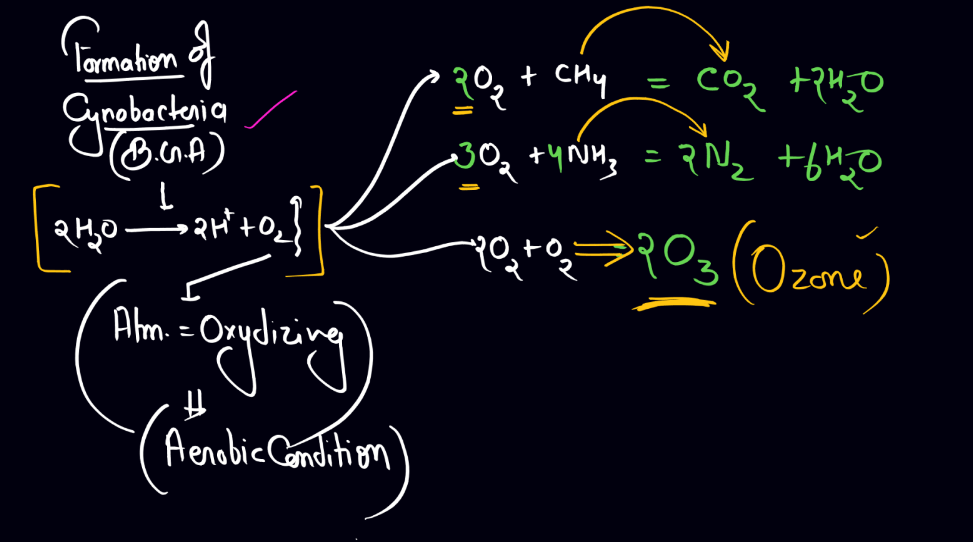
Origin of Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes, the complex cells that make up plants, animals, and fungi, have an intriguing origin. About 2 billion years ago, simpler cells, called prokaryotes, dominated Earth. The transition to eukaryotes likely occurred through a process called endosymbiosis. This theory proposes that the host cell engulfed a free-living bacterium. Instead of being digested, a mutually beneficial relationship developed, with the host providing protection and resources while the engulfed bacterium contributed specialized functions, eventually evolving into Mitochondria, the cell’s energy powerhouse. Another such event may have led to the development of Chloroplast in the Plant Cells.
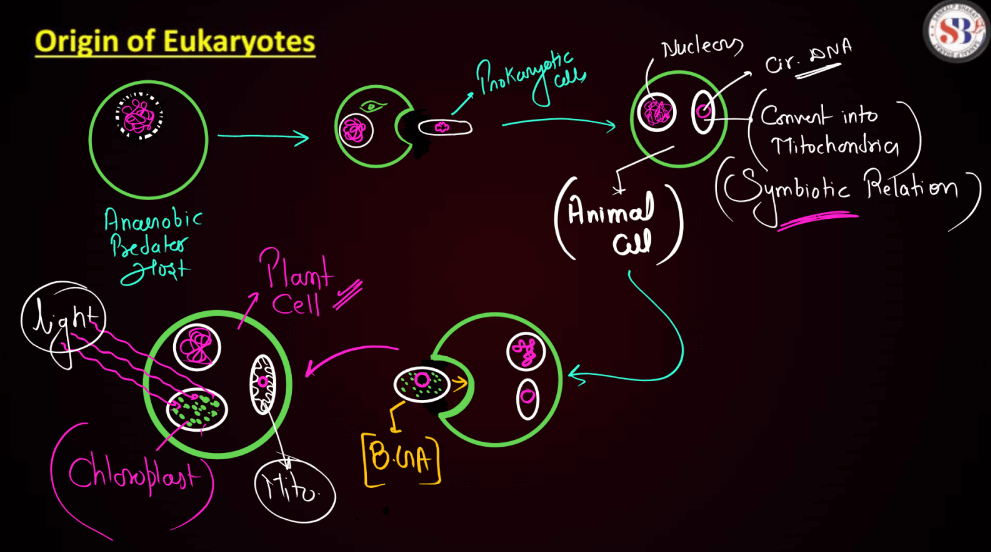
Over time, these collaborative partnerships formed more complex cells with distinct organelles, marking the emergence of eukaryotes. This evolutionary leap allowed for increased cellular specialization, leading to the diverse and sophisticated life forms we see today. The origin of eukaryotes is a testament to the dynamic interplay of life’s building blocks, shaping the biological world we inhabit.
Evidence in Favor of Evolution
Numerous lines of evidence support the theory of evolution, including fossil records documenting transitional species, comparative anatomy revealing structural similarities among diverse species, molecular Biology demonstrating shared genetic codes, and observed instances of natural selection in various populations.
| Evidence in Favor of Evolution | |
| Evidence of Evolution | Description |
| Paleontological Evidence | Fossil records show a progression of life forms over geological time, indicating the emergence and extinction of species. Transitional fossils, like Archaeopteryx, demonstrate intermediate features. |
| Evidence from Comparative Anatomy and Morphology | Similarities in anatomical structures across different species suggest a common ancestry. Homologous structures (e.g., vertebrate limbs) and vestigial organs (e.g., the human appendix) support evolutionary relationships. |
| Embryological Evidences | Similarities in early developmental stages among different organisms point to shared ancestry. For instance, vertebrate embryos often exhibit comparable structures during embryogenesis. |
| Evidence from Physiology and Biochemistry | Molecular similarities, such as DNA and protein sequences, provide evidence for common ancestry. Genetic homologies and shared biochemical pathways support the idea of a universal common ancestor. |



 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













