Define Biofortification
Biofortification is the process of improving the nutritional content of crops through natural or artificial means. It involves breeding plants to contain higher levels of vitamins, minerals, or other important nutrients. This can be done by traditional breeding techniques or genetic engineering. The goal is to produce crops that help fight malnutrition, especially in areas where people rely heavily on a single type of food.
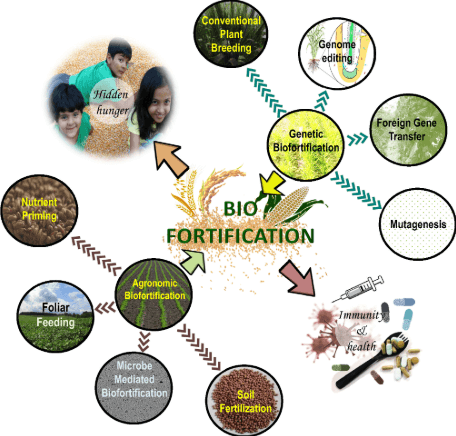
For example, golden rice is biofortified with extra vitamin A to help prevent blindness in children. Biofortification is an important way to improve health and nutrition without needing to change people’s eating habits or introduce expensive supplements. It makes food healthier right from the source, helping to prevent nutrient deficiencies in the population.
Examples of Biofortification
Biofortification is the process of enhancing the nutritional quality of food crops through biological methods, such as selective breeding or genetic modification. These biofortified crops help improve nutritional intake, particularly in areas where people rely on a limited range of staple foods that may lack key nutrients. Here are a few examples:
- Golden Rice: This genetically modified rice is enhanced with beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A. It is aimed at combating vitamin A deficiency, especially in developing countries.
- Biofortified Wheat: Certain varieties of wheat are bred to have higher levels of zinc and iron, addressing deficiencies of these essential minerals in populations with poor diets.
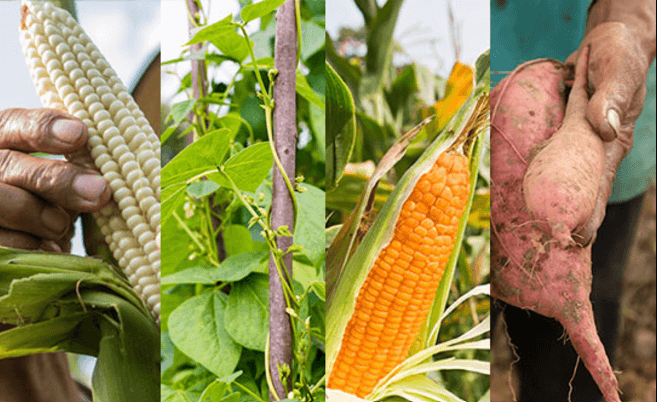

- Sweet Potatoes: Biofortified varieties of sweet potatoes are enriched with higher levels of vitamin A, particularly in regions where the tuber is a staple food.
- Cassava: Some cassava varieties are biofortified with increased levels of essential nutrients like vitamin A, zinc, and iron to combat malnutrition in areas where cassava is a primary food source.
- Maize (Corn): Certain maize varieties are developed to have higher levels of essential vitamins and minerals such as provitamin A (beta-carotene), zinc, and iron.
Methods of Biofortification
There are two different methods of Biofortification, that are: Selective Breeding and Genetic Modification. Selective breeding, is where plants with better nutrition are chosen to reproduce, passing on their traits to future generations. Another method is genetic modification, where scientists change a plant‘s genes in a lab to enhance its nutrients. Both methods help produce crops that are healthier and provide more vitamins and minerals, improving people’s diets, especially in areas where malnutrition is common.
| Different Methods of Biofortification | |
| Methods | Description |
| Selective breeding | Selective breeding is the process of choosing parent plants or animals with specific traits to produce offspring that have those desired characteristics. This is done to improve qualities like size, strength, or resistance to diseases, helping to create better generations over time. |
| Genetic modification | Genetic breeding is the process of improving plants or animals by changing their genes to develop better traits, like higher yield, disease resistance, or faster growth. It involves selecting and combining desirable characteristics to create improved versions of the original species. |
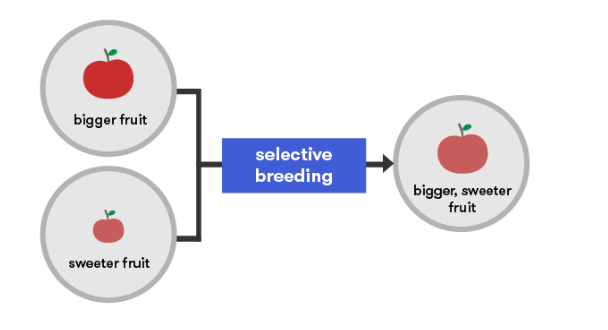
Selective Breeding
Selective breeding is when plants or animals with desirable traits, like better nutrition, are chosen to reproduce. Over time, these traits become more common in the population. For example, crops with higher vitamin content are bred with others that also have that trait to increase the nutrient levels in future generations.
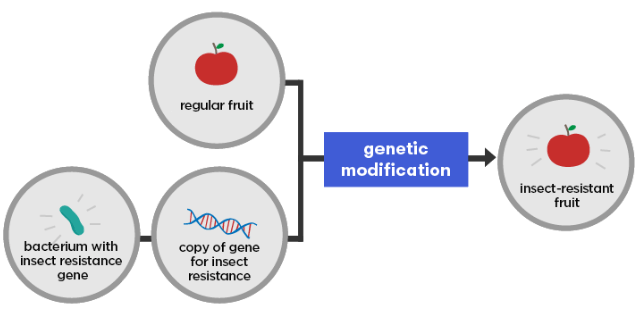
Genetic Modification
Genetic modification involves directly altering an organism’s DNA to add or change traits. Scientists can insert genes from other organisms into crops to improve their nutrient content, like adding a gene that increases vitamins, making them healthier without waiting for natural breeding processes.
How Does Biofortification Work?
Below we have discussed a few steps explaining the working of Biofortification. These methods make food healthier and help fight malnutrition effectively.
- Selecting Nutrient-Rich Crops: Scientists find crops that naturally have more nutrients and breed them to improve their nutritional value.
- Adding Nutrients Using Technology: Modern methods like genetic engineering are used to boost the nutrients in crops, such as adding vitamin A to rice.
- Improving Soil and Fertilizers: Farmers enrich the soil or use special fertilizers to grow more nutritious crops.
- Using Natural Methods: Traditional cross-breeding is done to create new varieties of crops with higher vitamins and minerals.
Benefits of Biofortification
Biofortification helps improve the nutrition of crops by adding vitamins and minerals, making them healthier to eat. It helps fight malnutrition, especially in poor areas, by providing essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and vitamin A. This can reduce health problems such as anemia and vision loss. Biofortified crops are also affordable, offering a cost-effective solution to improve diet. Additionally, farmers benefit from growing more nutritious crops that can add value to their produce.
- Improves Nutrition: It adds important vitamins and minerals to our food, making it healthier to eat.
- Fight Malnutrition: Helps people, especially in poor areas, get the nutrients they need to stay healthy.
- Boosts Health: Reduces diseases caused by a lack of nutrients, like anemia or blindness.
- Affordable Solution: Biofortification is cheaper than taking supplements or medicines for many people.
- Supports Farmers: Crops grown through biofortification can be more nutritious and valuable.
- Improves Health: It helps reduce malnutrition, especially in children and pregnant women.
- Long-Term Impact: Once biofortified crops are grown, they can provide nutrition for years.
Limitations of Biofortification
Addressing the following limitations of Biofortification requires a multi-faceted approach, including education, effective distribution, and complementary nutritional strategies.
- Biofortification is designed to enhance specific nutrients, such as vitamin A, iron, or zinc, in crops. However, it cannot address all nutritional deficiencies, especially those requiring a diverse diet (e.g., essential fatty acids or certain amino acids). Relying solely on biofortified crops may not provide a balanced nutritional profile.
- Farmers may hesitate to adopt biofortified crops if they have lower yields, require different farming techniques, or if their taste, texture, or cooking properties are unfamiliar. This can reduce the spread and effectiveness of biofortification programs.
- Biofortified crops often differ in appearance or taste from traditional varieties, which may discourage consumers from accepting them. For instance, golden rice (enriched with vitamin A) has faced resistance due to its yellowish color, which deviates from the white rice consumers are accustomed to.
- The effectiveness of biofortification can vary with soil quality, climate, and farming practices. For example, crops grown in nutrient-depleted soils may not achieve the desired nutrient levels despite biofortification.
- Low-income populations, who are the primary targets for biofortified crops, may lack access to these varieties due to cost, lack of awareness, or poor distribution networks.
- Since biofortification is a relatively new strategy, there is limited long-term data on its effectiveness in addressing malnutrition and its potential unintended effects, such as the accumulation of other nutrients or anti-nutrients.



 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













