Binary fission is a quick and simple asexual mode of reproduction where a single cell divides into two identical cells. This method is common in organisms like bacteria, amoebas, and some algae. During binary fission, the parent cell copies its genetic material and then splits into two, each getting a copy. It helps organisms grow and multiply rapidly, especially in favorable conditions. This process ensures the survival and expansion of species without the need for a mate. Binary fission is nature’s efficient way for single-celled organisms to reproduce and thrive.
What is Binary Fission?
Binary fission is a simple method of asexual reproduction used by single-celled organisms like bacteria and amoeba. In this process, the cell divides into two identical copies of itself. First, the organism’s genetic material (DNA) is copied. Then, the cell grows and splits into two equal parts, with each part getting one copy of the DNA. These two new cells are called daughter cells and are identical to the parent cell.
Binary fission is a quick and efficient way for these organisms to reproduce, especially in favorable conditions. It helps them grow their population rapidly, which is why bacteria can multiply so fast. This process does not need a partner and is an example of asexual reproduction.
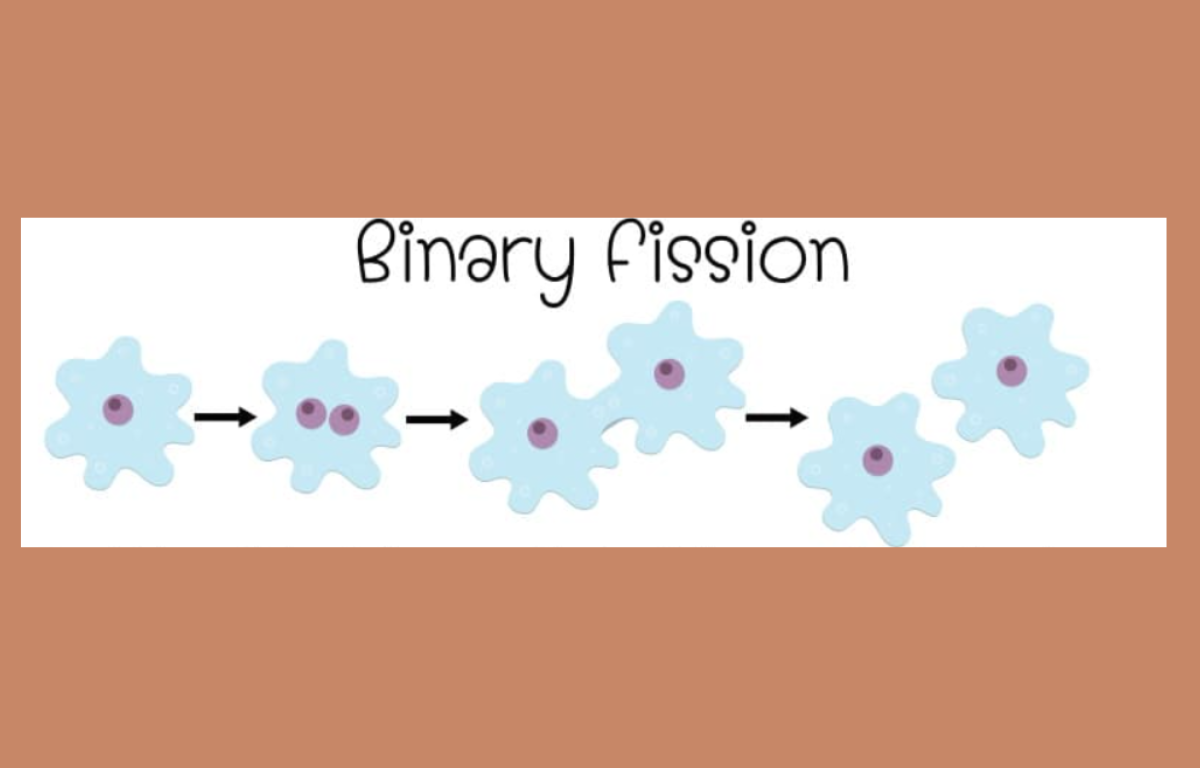
Binary Fission Diagram
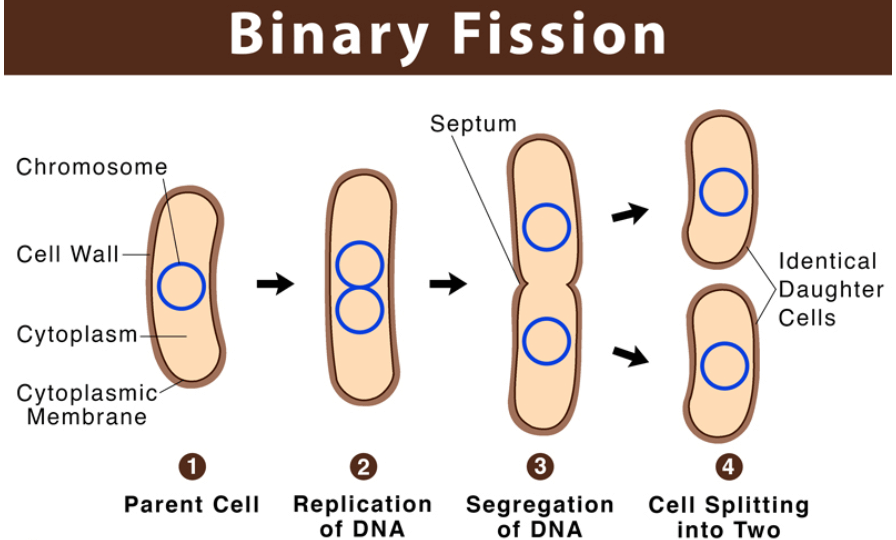
A binary fission diagram shows how a single cell divides into two identical cells. It begins with one cell containing a single loop of DNA. The DNA replicates, creating two identical loops. The cell then elongates, and the DNA moves to opposite ends of the cell. A division line, called a septum, forms in the middle, showing the cell starting to split. Finally, the cell divides completely into two smaller, identical cells, each with its own copy of the DNA. This diagram visually explains the simple and fast process of binary fission in organisms like bacteria.
Step-Wise Process of Binary Fission
Binary fission is a simple method of reproduction used by single-celled organisms like bacteria. This process is quick and efficient, allowing organisms to multiply rapidly under favorable conditions. Binary fission ensures the offspring are genetically identical to the parent. Here’s the process:
Step 1 – DNA Replication: The single DNA molecule in the cell copies itself, creating two identical DNA strands.
Step 2 – Cell Growth: The cell increases in size, stretching the two DNA strands apart.
Step 3 – DNA Segregation: The two DNA strands move to opposite ends of the cell.
Step 4 – Cytokinesis: The cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cytoplasm into two parts.
Step 5- Formation of Daughter Cells: The cell splits into two identical daughter cells, each with its own DNA copy.
Binary Fission in Bacteria
Binary fission is the process by which bacteria reproduce. It is a simple and fast method of cell division. In this process, a single bacterial cell splits into two identical cells. This process helps bacteria multiply quickly, especially in favorable conditions, like warmth and enough nutrients. It’s a common way for bacteria to spread and thrive.
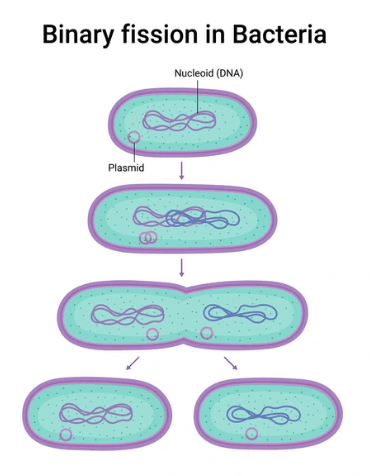
Here’s how it works:
- The bacterial cell makes a copy of its DNA.
- The DNA moves to opposite sides of the cell.
- The cell grows bigger and starts to stretch in the middle.
- Finally, the cell divides into two separate cells, each with a copy of the original DNA.
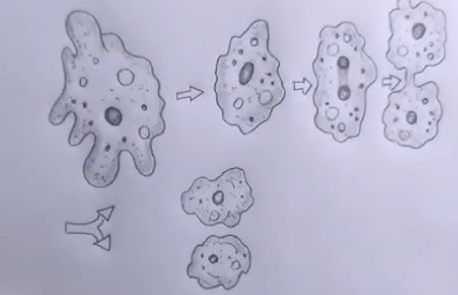
Binary Fission in Amoeba
Binary fission is a simple type of asexual reproduction. In this process, the amoeba’s single cell divides into two identical cells. This simple asexual reproduction helps amoebas multiply quickly under favorable conditions.
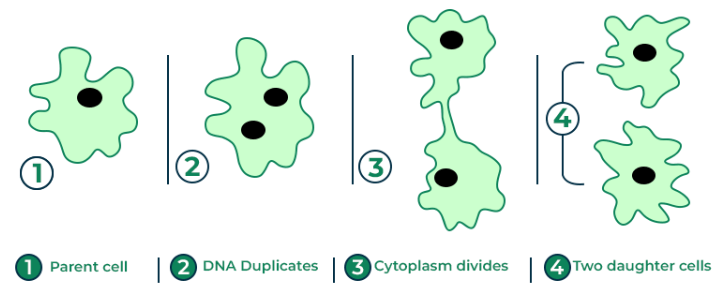
- Preparation for Division: The amoeba grows in size and prepares to divide. Its nucleus begins to duplicate.
- Nuclear Division: The nucleus of the amoeba splits into two through a process called mitosis. Each new nucleus contains the same genetic material.
- Cytoplasmic Division: The cytoplasm, the jelly-like substance in the cell, starts dividing, and the cell membrane stretches.
- Formation of Two Cells: The cell pinches in the middle, separating into two smaller cells.
- Two Identical Amoebas: The parent amoeba is now divided into two new amoebas, each with its own nucleus and cytoplasm. Both are identical to the original parent.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













