As we all know intestines are a part of the digestive system and the digestive system is a very important topic of biology. The intestines, also known as the gastrointestinal tract, play a crucial role in the digestion and absorption of nutrients from the food we consume. It includes the small intestine and the large intestine which is also known as the colon. Various digestive disorders can affect the intestines, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and Crohn’s disease. These conditions can lead to symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and malabsorption.
Small Intestine
The small intestine is a vital part of the digestive system, where most nutrient absorption occurs. It is a long, tube-like organ that is approximately 20 feet (6 meters) in length in adults. The small intestine is located between the stomach and the large intestine. It consisted of three sections: The Duodenum, Jejunum, and Ileum. These segments play a crucial role in breaking down and absorbing nutrients from food, which are then transported into the bloodstream for use by the body.
Diagram of Small Intestine
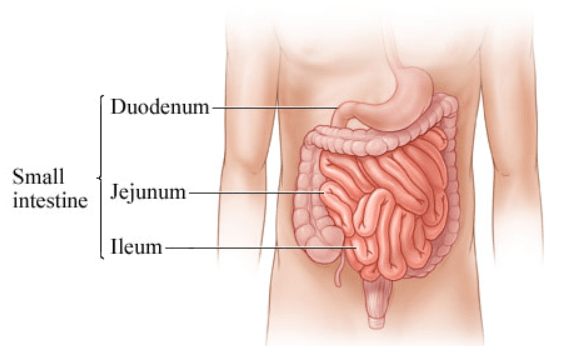
As we already know the small intestine is a long, coiled tube that plays a vital role in the digestion and absorption of nutrients from the food we eat. The small intestine has three main sections: The duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Here we have mentioned a well-labeled diagram of the small intestine.
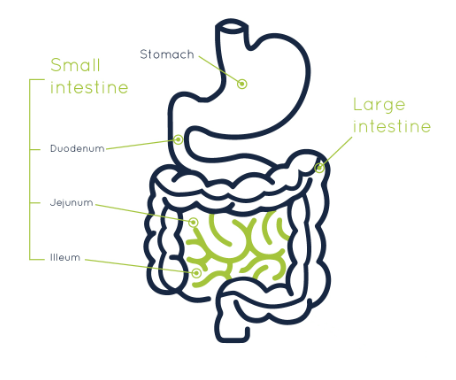
Parts of the Small Intestine
The small intestine consists of three main sections or parts, that are: the Duodenum, Jejunum, and Ileum. These three segments or parts work together to further break down and absorb nutrients from the food we eat. Here we have mentioned some of the characteristic features of all three different parts of the small intestine.
| Characteristics of the three parts of the Small Intestine | |||
| Small Intestine parts | Location | Length | Functions |
| Duodenum | It is the first part of the small intestine and is present in the beginning. | It is about 10 inches. | Receives partially digested food, and mixes it with digestive juices (pancreatic and hepatic). |
| Jejunum | It is the second part and is present in the middle portion of the small intestine. | It is about 08 feet. | Main site of nutrient absorption (e.g., carbohydrates, proteins, and some vitamins). |
| Ileum | It is the third and final part of the small intestine and is present at the end. | It is about 12 feet. | Completes nutrient absorption, especially vitamin B12 and remaining nutrients. |
1. Duodenum
The Duodenum is the first part of the small intestine and is relatively short, about 10 inches (25 cm) long. The duodenum receives digested food from the stomach and mixes it with digestive juices from the pancreas and liver. These juices contain enzymes that further break down food for absorption.
2. Jejunum
The Jejunum is the middle portion of the small intestine, measuring about 8 feet (2.5 meters) in length. The jejunum is that portion of the small intestine where most of the absorption of nutrients from digested food takes place. The walls of the jejunum are lined with finger-like projections called villi and even smaller structures called microvilli. These greatly increase the surface area for absorption of nutrients like sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids into the bloodstream.
3. Ileum
The Ileum is the final and longest section of the small intestine and is approximately 12 feet (3.5 meters) long. The ileum connects to the large intestine (colon) at a valve called the ileocecal valve and is involved in the absorption of remaining nutrients, vitamins, and minerals such as vitamin B12. It also absorbs bile salts, which are recycled into the liver.
Functions of the Small Intestine
The small intestine plays several crucial functions in the digestive process, including:
- Digestion: It continues the digestion of food that begins in the stomach by breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into smaller molecules.
- Absorption: The small intestine is the primary site of nutrient absorption. It absorbs nutrients like glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids into the bloodstream, which are then transported to the cell for energy and growth.
- Villi and Microvilli: Villi and Microvilli in the small intestine increase the surface area for absorption, allowing for efficient nutrient uptake.
- Enzyme Secretion: The small intestine secretes various enzymes and hormones, including pancreatic enzymes and bile, which aid in digestion.
- Nutrient Transport: Nutrients are transported across the intestinal lining into the bloodstream through specialized transport mechanisms.
- Water Absorption: The small intestine absorbs water from the partially digested food, contributing to the maintenance of bloody fluid balance.
- Immune Function: It contains immune cells that help protect the body from harmful microorganisms and foreign substances.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













