Antigen and Pathogen
Antigens are molecules that trigger an immune response in the body. They can be part of pathogens, like bacteria or viruses, and help the immune system recognize and neutralize them. Pathogens, on the other hand, are disease-causing agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, that invade the body and can lead to illness. Understanding and responding to antigens is crucial for the immune system to recognize and combat pathogens effectively.
Define Antigen
Antigens are like identification tags for the immune systems. They are molecules, often found on the surface of pathogens like bacteria or viruses, that trigger the body’s defense fingerprints that help the immune system distinguish between the body’s own cells and invaders. When the immune system detects foreign antigens, it launches an attack to eliminate the threat. Antigens can also be present on non-threatening substances, like pollen or certain foods, causing allergic reactions.
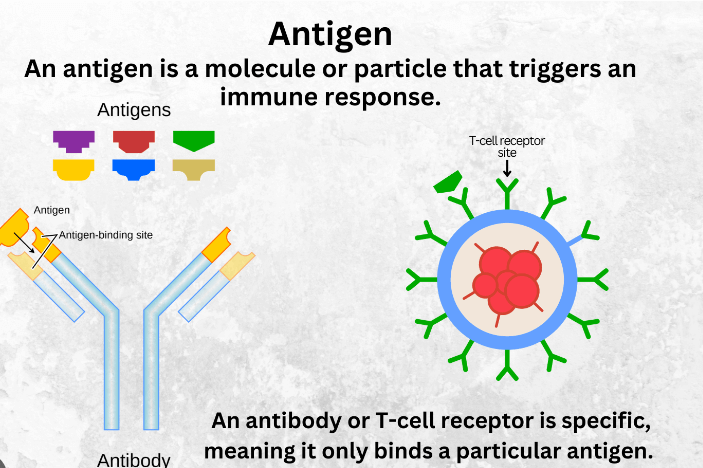
The immune system learns to recognize and remember these antigens, providing protection against future encounters. Vaccines work by introducing harmless forms of antigens to train the immune system, allowing it to build a memory and respond more effectively if exposed to the actual pathogen later on. In summary, antigens are vital for immune recognition and response, playing a crucial role in maintaining the body’s health.
Define Pathogen
Pathogens are tiny troublemakers that can make us sick. These microscopic organisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, have the potential to cause diseases. Think of them as unwelcome guests that sneak into our bodies and disrupt the usual harmony. Pathogens are often found in contaminated water, food, or in the air, waiting for an opportunity to invade. Once inside, they can multiply and interfere with our body’s normal functions, leading to illnesses.

Your body’s immune system acts like a superhero, working hard to identify and eliminate these invaders. Sometimes, though, pathogens can outsmart our defenses, causing infections and making us feel unwell. To stay healthy, it’s crucial to practice good hygiene, like washing hands regularly, and to use vaccines that train our immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens. Understanding and guarding against these sneaky troublemakers is key to maintaining well-being.
Difference Between Antigens and Pathogens
Below we have discussed a few points that will highlight the differences between Antigens and Pathogens.
| Difference Between Antigens and Pathogens | ||
| Aspects | Antigens | Pathogens |
| Definition | Antigens are molecules that elicit an immune response; can be part of pathogens or other substances. | Pathogens are microorganisms causing disease, like bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. |
| Nature | Antigens can be diverse, including proteins, carbohydrates, or other molecules. | Pathogens are living organisms or infectious agents causing diseases. |
| Role | Antigens elicit an immune response; can be harmless or harmful. | Pathogens actively cause diseases in the host organisms. |
| Source | Antigens can come from pathogens, allergens, or substances introduced into the body. | Pathogens originate as infectious agents capable of replicating within a host. |
| Examples | Antigens are proteins on the surface of bacteria, viral coat proteins, or allergens like pollen. | Pathogens are bacteria (for example E.coli), viruses (for example influenza), fungi (for example candida), and parasites (for example Plasmodium causing malaria). |
| Function | Antigens activate the immune system, leading to the production of antibodies or cell-mediated responses. | Pathogens invade host tissues, replicate, and cause disease symptoms. |
| Response Trigger | Antigens trigger immune responses, whether from pathogens or other sources. | Pathogens activate the immune system in response to infection. |
| Presence | Antigens can be present on the surface of cells, viruses, or in soluble form. | Pathogens exist as complete organisms or particles causing infection. |
| Specificity | Antigens can be specific or nonspecific; the immune system recognizes and responds to specific antigens. | Specific pathogens elicit tailored immune responses. |
| Outcome | The immune response aims to neutralize or eliminate antigens, providing immunity. | Immune responses work to eliminate or control the infection caused by pathogens. |
Functions of Antigens and Pathogens
Antigens are molecules that trigger an immune response, often found on the surface of pathogens like bacteria or viruses. Pathogens are disease-causing agents, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. The immune system recognize antigens as foreign and mounts a defense against the invading pathogens.
Functions of Antigens
Antigens play crucial roles in the immune system. In summary, antigens serve as triggers for the immune system, initiating responses that are essential for protecting the body against infections and diseases.
- Recognition by the Immune System: Antigens are recognized by the immune system as foreign substances, triggering an immune response.
- Immune Response Trigger: Antigens trigger the activation of immune cells, such as B cells and T cells, leading to the production of antibodies and the initiation of cellular immune responses.
- Memory Formation: Exposure to antigens induces the immune system to create memory cells, enhancing the speed and efficiency of future immune responses against the same antigen.
- Specificity: Antigens exhibit specificity, as each antigen is recognized by a specific antibody or T cell receptor. This specificity allows the immune system to target and eliminate specific pathogens.
Functions of Pathogens
Pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, have various functions that contribute to their ability to cause diseases. Some key functions include:
- Attachment and Entry: Pathogens often possess structures or proteins that enable them to attach to host cells and enter the body, allowing them to establish infection.
- Evading the Immune System: Pathogens can evade the host’s immune response through mechanisms like antigenic variation, hiding within host cells, or suppressing immune system, functions.
- Reproduction and Multiplication: Pathogens reproduce within the host, increasing their numbers and spreading to other tissues or individuals. This is essential for their survival and the progression of the infection.
- Damage to Host Cells: To sustain themselves, pathogens may damage host cells directly or indirectly. This damage can contribute to the symptoms and severity of the disease.
- Toxin Production: Some pathogens produce toxins that directly harm host cells. These toxins can interfere with the cellular functions, leading to tissue damage and contributing to the overall impact of infection.
- Immune System Manipulation: Pathogens may manipulate the host’s immune response, altering the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals to their advantage.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













