Respiration is a biological process through which living organisms, including humans, obtain energy from the food they consume. Respiration is counted as one of the most important topics in biology. The process of respiration involves the exchange of gases, primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the body and the environment. Respiration is mainly of two types namely: Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration. Aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen. Here in the article, we have briefly discussed the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration
Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration are two different metabolic processes that organisms use to obtain energy from nutrients, primarily glucose. They differ in the presence or absence of oxygen during the energy extraction process:
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a metabolic process that occurs in the presence of oxygen. It involves the breakdown of glucose (other organic compounds or molecules) to produce energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) along with carbon dioxide and water as byproducts. It is a highly efficient process and is the primary way organisms including humans, generate energy during normal, everyday activities. Examples of Aerobic respiration are Plant cells, Aerobic bacteria, Animal cells, Human muscle cells, Kingdom Fungi, etc.
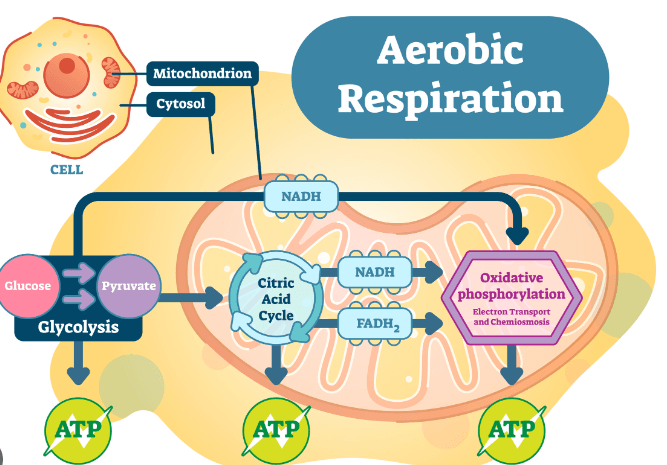
What is Anaerobic Respiration?
Anaerobic respiration, on the other hand, is a metabolic process that occurs in the absence or limited presence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration is less efficient than aerobic respiration and usually occurs when oxygen supplies are scarce or during intense physical activities. Anaerobic respiration results in the production of ATP, but it also produces other byproducts such as lactic acid (in humans) or ethanol (in some microorganisms). Examples of Anaerobic respiration are Human cells during short bursts of activity, Plant roots, Yeast Fermentation, Certain bacteria, Lactic acid fermentation, etc.
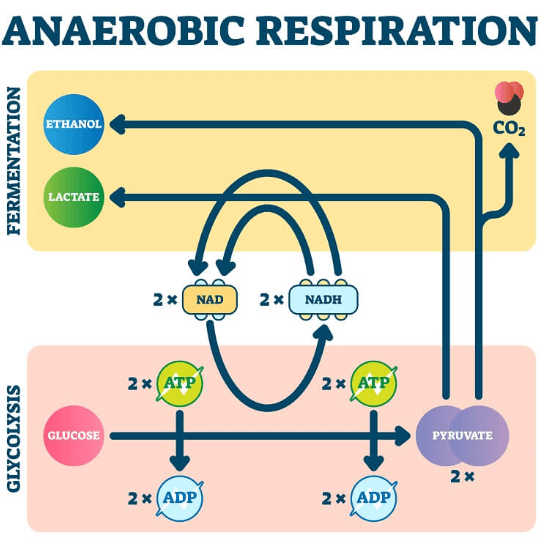
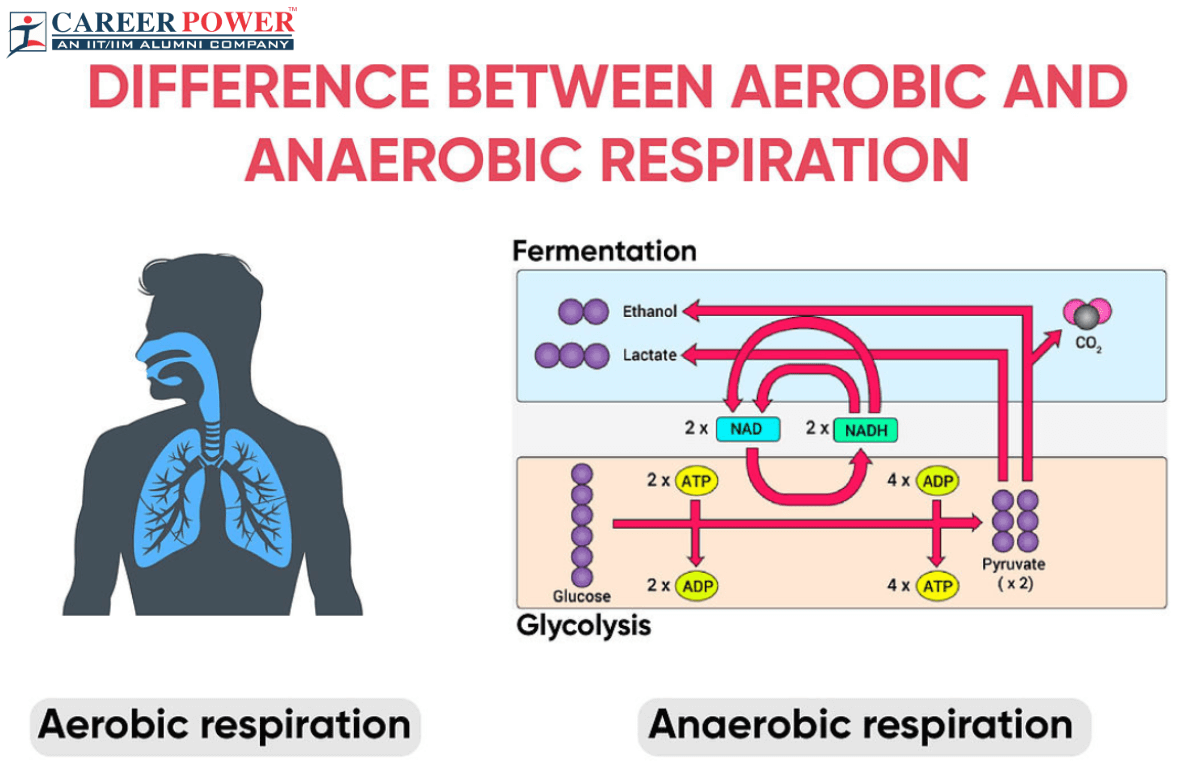
Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Both Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration are two different metabolic processes that cells use to produce energy. Aerobic respiration is more efficient, produces more energy, and requires oxygen; while anaerobic respiration is less efficient, produces less energy, and can occur in the absence of oxygen, with different products depending on the organism and conditions.
| Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration | ||
| Characteristics | Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| Oxygen Requirements | Aerobic respiration requires oxygen. | Anaerobic respiration does not require any oxygen. |
| Chemical equation | C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP (Energy) | C6H12O6 → 2C3H6O3 + 2 ATP (Energy) |
| Location | Aerobic respiration takes place in the mitochondria. | Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm. |
| Efficiency | Aerobic respiration is more efficient, producing more ATP (energy) per glucose molecule. | Anaerobic respiration is less efficient, producing fewer ATP (energy) per glucose molecule. |
| End Products | Aerobic respiration produces carbon dioxide and water as end products. | Anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid or other byproducts. |
| ATP Yield | It generates up to 36-38 ATP per glucose molecule in eukaryotes. | It generates 2 ATP per glucose molecule (in lactic acid fermentation. |
| Examples | This type of respiration is common in aerobic organisms like humans, plants, and animals. | It occurs during strenuous exercise when oxygen is limited. |
| Duration | Sustainable energy production for a longer period. | Provides quick bursts of energy for a shorter period. |
| Efficiency | Aerobic respiration produces more energy but the process is slower. | Anaerobic respiration produces less energy but the process is faster. |
Importance of Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Both types of respiration are important in their own ways. As aerobic respiration produces more energy (ATP) in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic respiration provides quick energy without oxygen, both crucial for cellular functions.
Importance of Aerobic Respiration
- Energy Production: It is the primary process by which cells generate energy (ATP) in the presence of oxygen. This energy is essential for the functioning of all living organisms.
- Efficiency: Aerobic respiration yields a large amount of ATP per glucose molecule compared to anaerobic processes, making it a highly efficient energy production method.
- Oxygen Utilization: Aerobic respiration helps in the efficient utilization of oxygen, which is vital for most complex life forms. Oxygen is necessary for the final electron transport chain, which generates the majority of ATP.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal: It helps in the removal of carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular metabolism, preventing its accumulation, which can be harmful.
- Evolutionary Advantage: The evolution of aerobic respiration played a critical role in the development of complex life forms, allowing for greater energy storage and utilization.
Importance of Anaerobic Respiration
- Energy Production: It allows cells to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell when oxygen is scarce or unavailable. This is crucial for organisms to maintain basic cellular functions even in low-oxygen environments.
- Muscle Activity: During intense physical activity, muscles may rely on anaerobic respiration when oxygen cannot be supplied to them fast enough. This provides a quick burst of energy for activities like sprinting or lifting heavy weights.
- Metabolic Flexibility: Anaerobic pathways provide metabolic flexibility, enabling cells to adapt to changing conditions. Cells can switch between aerobic and anaerobic respiration depending on oxygen availability.
- Microbial Decomposition: Anaerobic bacteria play a crucial role in the decomposition of organic matter in environments devoid of oxygen, such as the bottom of lakes and in the human digestive system.
- Biotechnological Applications: Anaerobic fermentation by microorganisms is used in various biotechnological processes, including the production of ethanol in the brewing and biofuel industries.


 50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
50 Vegetables Name for Kids in English a...
 Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples,...
 Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...
Human Respiratory System: Definition, Di...













