Many people, especially those new to the English language, often confuse the words “where” and “were”. It is a common mistake. If you are asked how these words differ, here’s what you can say: “Where” is used to ask about a place or location. For example, “Where are you going?” “Were” is the past tense of the verb “to be” used with plural subjects. For example, “They were at the park.” Understanding their distinct uses can help avoid confusion. We have discussed more about where, were, and the differences between them in the article below.
Meaning of Where
“Where” is an equation word used to ask about a location or place. It helps to find out the specific place something or someone is was, or where an event happened or will happen. For example, if you ask, “Where is the store?” you want to know the location of the store. Similarly, “Where are you going?” asks about the destination. Where can also be used in statements to describe a place, such as “This is where I grew up.” It helps in providing directions, locating objects or people, and describing settings in conversations. Understanding “Where” helps people communicate about places’ location making it easier to navigate and share information about different places.
Meaning of Were
“Were” is the past tense form of the verb “are” and is used to describe actions, events, or states that happened in the past. It is commonly used with plural subjects, such as “we,” “you,” and “they,” as well as with singular “you.” For example, in the sentence “They were happy,” ‘were’ indicates that the happiness occurred in the past. In “You were late,” it shows that the lateness happened before now. “Were” can also be used in conditional sentences, such as “If I were you,” to express hypothetical situations. Understanding “were” is essential for speaking and writing about past events accurately.
Difference Between Where and Were
Both “Where” and “Were” are two commonly confused words in English, but they have distinct meanings and uses. “Where” asks about or indicates a place, on the other hand, “Were” is the past tense form of “to be” for certain subjects. Using them correctly depends on the context of the sentence.
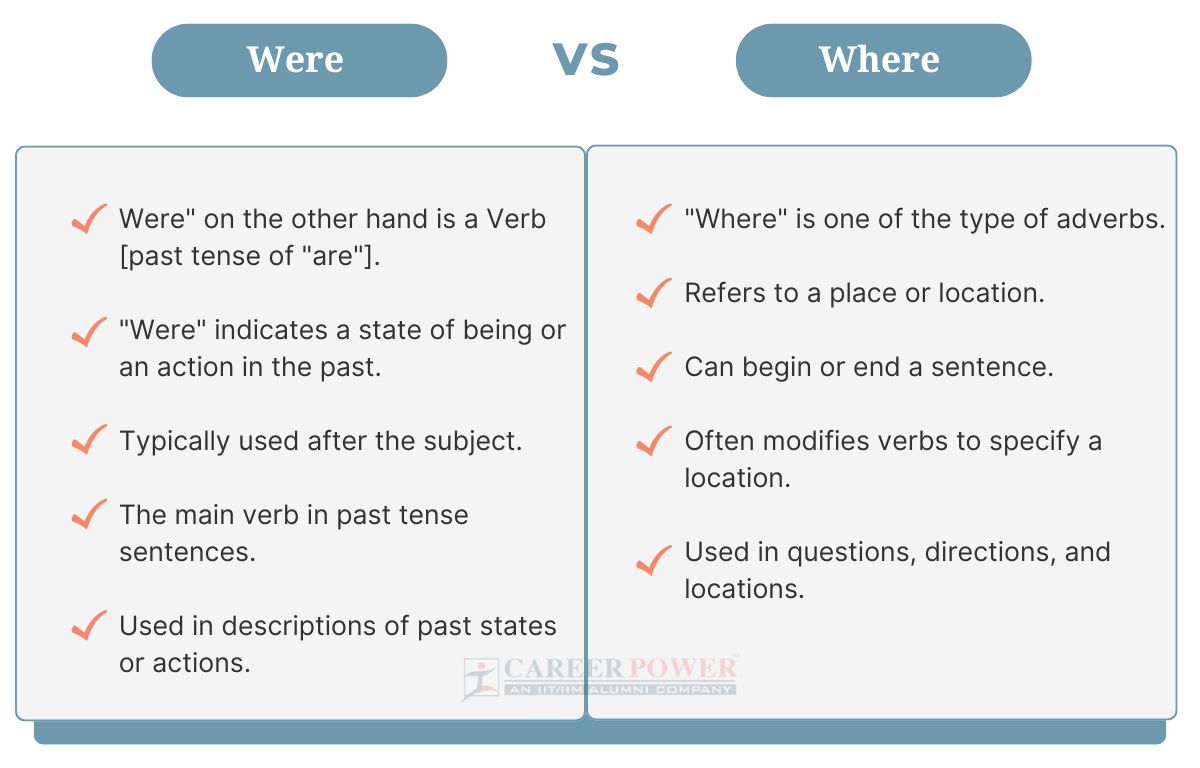
| Difference Between Where and Were | ||
| Aspect | Where | Were |
| Part of Speech | “Where” is one of the type of adverbs. | “Were” on the other hand is a Verb [past tense of “are”]. Used as the past tense of “are” or “to be” [used with subjects like you, we, they]. |
| Meaning | Refers to a place or location. | “Were” indicates a state of being or an action in the past. |
| Question Form | Used in questions to ask about location. | Not used in forming questions. |
| Example Sentence |
|
|
| Position in Sentence | Can begin or end a sentence. | Typically used after the subject. |
| Related Words | Here, there, everywhere. | Are, was, being. |
| Usage Context | Used in questions, directions, and locations. | Used in descriptions of past states or actions. |
| Common Phrases | “Where is it?” OR “Where are you?” | “We were there.” OR “They were excited.” |
| Homophones | Wear [same pronunciation but different meaning.] | None. |
| Grammar Role | Often modifies verbs to specify a location. | The main verb in past tense sentences. |
Examples of Where
The word “where” can be used in various contexts to denote different meanings or situations. Each use of “where” depends on the context in which it is used, indicating either a place, situation, reason, or relationship between things.
- “Where is the nearest grocery store?” – Here, “Where” asks for a specific place or location.
- “Tell me where it hurts.” – In this case, “where” refers to the specific condition or situation causing discomfort.
- “The house where I grew up.” – Here, “where” indicates the context or circumstances under which something happens or is located.
- “That’s where I lost my keys.” – This usage of “where” indicates the place or point in time where an event occurred.
Examples of Were
“Were” is the past tense form of the verb “to be” in the plural [you, we, they] and the singular second person [you] in formal English. In each case, “were” serves as the past tense form of “to be,” used to indicate the existence, states, conditions, or actions that occurred in the past.
- “They were at the park yesterday.” – Here, “were” indicates that a group of people [they] existed or were located at the park in the past.
- “If I were you, I would apologize.” – Here ‘were’ is used to express a hypothetical situation or condition, indicating what someone would do in another person’s place.
- “You were late for the meeting.” – In this sentence, ‘were’ is used to indicate that the person being addressed [you] was not punctual for the meeting.
- “They were playing football when it started raining.” – In this example ‘were’ is part of the past continuous tense, indicating an action that was ongoing in the past.
Uses of Where and Were
“Where” and “were” are often confused because they sound similar, but they have different meanings and uses. Remembering these differences can help you use each word correctly in sentences.
Where:
- Usage: Refers to a place or location.
- Examples:
- Where are you going?
- Do you know where the library is?
- This is the place where we met.
Were:
- Usage: The past tense form of the verb “to be” is used with subjects like you, we, and they.
- Examples:
- You were at the meeting yesterday.
- We were excited about the trip.
- They were happy with the results.


 Independence Day Speech in English, 15 A...
Independence Day Speech in English, 15 A...
 50+ Rhyming Words in English List, Check...
50+ Rhyming Words in English List, Check...
 Essay Writing Format for Students in Eng...
Essay Writing Format for Students in Eng...













