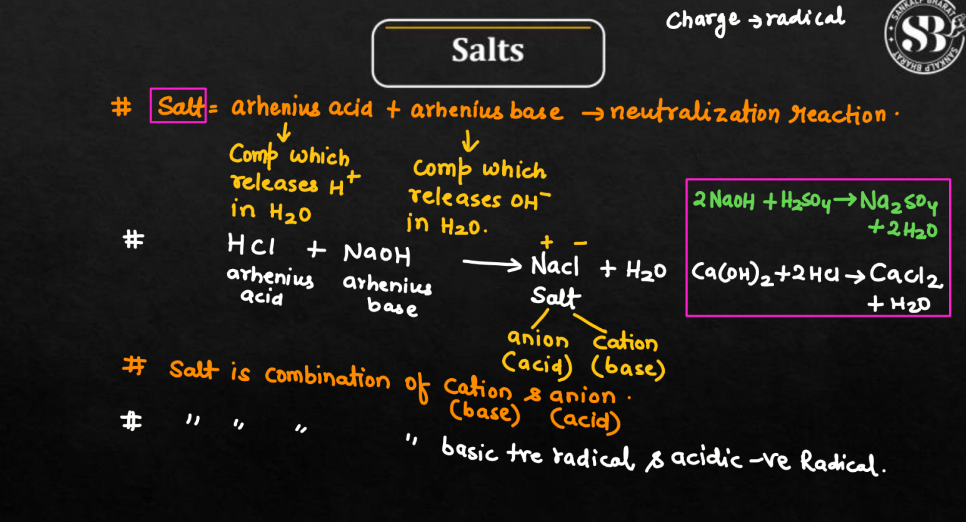
What is Salt Chemistry?
In chemistry, salt refers to a compound formed when an acid reacts with a base. This reaction, known as neutralization, results in the production of salt and water. Salt is composed of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), which come from the acid and base, respectively. Common table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), is a well-known example.

It forms when the hydrogen ions (H+) from an acid combine with the hydroxide ions (OH-) from a base. The positive sodium ions (Na+) from the base and the base and the negative chloride ions (Cl-) from the acid bond together to create a neutral salt. Salt plays a crucial role in various chemical and biological processes and is widely used in cooking, preserving food, and maintaining the balance of fluids in our bodies.
Types of Salts
There are mainly four different types of salts in chemistry namely: Acidic salts, Basic or Alkali salts, Double salts, and Mixed salts. These classifications showcase the diversity of salts based on their composition and formation processes.

| Different Types of Salts | |
| Types | Description |
| Basic or Alkali Salts | Basic or alkali salts are formed when a base reacts with an acid, creating a compound that contains elements of both. These salts can be bitter and often have soapy characteristics. |
| Acidic Salts | Acidic salts form when an acid reacts with a base, resulting in a compound that is part acid and part salt. They can be sour or corrosive and have unique properties. |
| Double Salts | Double salts are compounds formed when two different salts are combined without losing their individual identities. They have a unique crystalline structure and distinct properties from their constituent salts. |
| Mixed Salts | Mixed salts refer to compounds composed of a mixture of different salts. These combinations can exhibit varied properties depending on the specific salts involved, creating diverse chemical characteristics. |
Basic or Alkali Salts
Basic or alkali salts are compounds formed when a metal reacts with a base. In simple terms, picture a metal like sodium joining forces with a substance that feels slippery, like soap. This slippery substance is a base. When they react, they create basic salts. These salts often dissolve in water and can have various uses, like making cleaning products or adjusting the acidity of soil for plants. So, basic salts are like teamwork between metals and bases, resulting in useful compounds with diverse applications in daily life.
Acidic Salts
Acidic salts are formed when a metal or a positive ion reacts with an acid. Imagine it as a partnership between a metal and a sour-tasting substance, like vinegar. When they combine, they create acidic salts. These salts can have unique properties and are often involved in chemical processes. Unlike basic salts, acidic salts may release hydrogen ions in water, making the solution slightly acidic. They can be found in various applications, from industrial processes to some food items. In essence, acidic salts are the result of collaboration between metals and acids, producing compounds with distinctive characteristics.
Double Salts
Double salts are compounds formed by the combination of two different salts, typically through crystallization. Imagine it as a chemical duo where two separate salts join forces to create a new, distinct substance. These compounds retain the properties of both original salts and can have unique colors and structures. Common examples include alum, double salt containing aluminum, and potassium. Double salts are different from mixed salts, as they are different from mixed salts, as they have a specific stoichiometric ratio. While they may dissociate into ions when dissolved in water, they maintain their distinct identity. Double salts play a role in various individual and chemical processes.
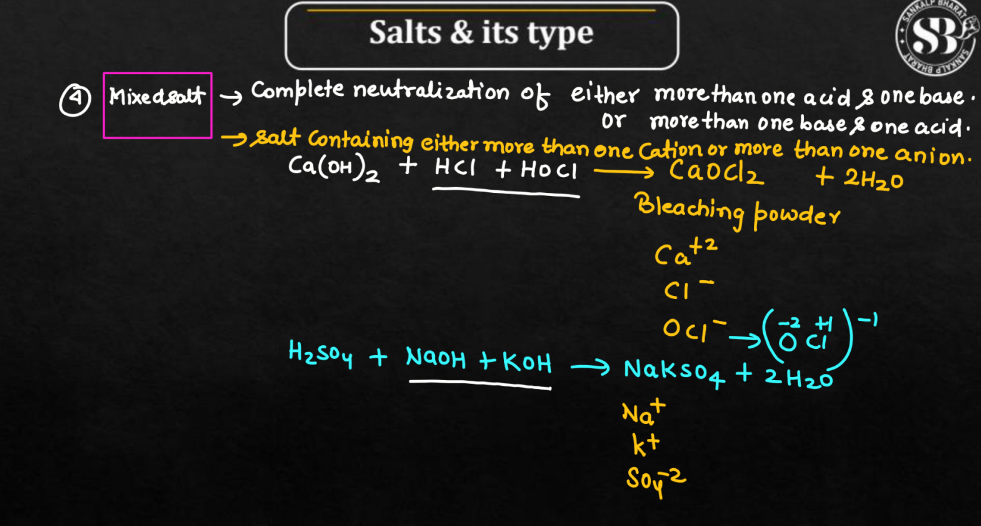
Mixed Salts
Mixed salts are compounds formed when two or more different salts are combined without a specific, fixed ratio. Picture it as a chemical blend where various salts are mixed together, each retaining its individual identity. Unlike double salts, there is no precise stoichiometric proportion between the compounds. These mixtures can exhibit diverse properties based on the combination of salts involved. Mixed salts may dissolve in water and their behavior can vary depending on the ions present. They find applications in fields like chemistry and agriculture, where specific combinations of ions are needed for particular reactions or soil amendments.
Hydrolysis of Salt
Hydrolysis of salt is a chemical process that occurs when a salt, composed of positive and negative ions, is dissolved in water. The ions from the salt interact with water molecules, leading to a change in the solution’s pH. If the salt originates from a strong acid and a weak base, the solution becomes acidic due to the excess of hydrogen ions. Conversely, if the salt comes from a strong base and a weak acid, the solution turns basic as hydroxide ions predominate. This phenomenon is vital in understanding how salts impact the acidity or alkalinity of solutions, influencing various practical scenarios such as cooking, water treatment, and chemical relations in both everyday and scientific contexts.

Different Properties of Salt
Salts are compounds formed by the reaction of an acid with a base. Below we have discussed a few points that will highlight the different properties of salts. Understanding these properties helps in predicting and explaining the behavior of different salts in various contexts.
- Ionic Nature: Salts are typically ionic compounds, consisting of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions) held together by electrostatic forces.
- Solubility: Salts can be soluble or insoluble in water. The solubility depends on the specific ions present in the salt and their interactions with water molecules.
- Melting and Boiling Points: Salts generally have high melting and boiling points compared to molecular compounds. This is due to the strong electrostatic forces between ions.
- Conductivity: When dissolved in water or in a molten state, salts can conduct electricity because their ions are free to move and carry an electric charge.
- Color: Salts can exhibit a variety of colors, influenced by the nature of the cations and anions. Some slats are colorless, while others may be brightly colored.
- pH: When salts dissolve in water, they can affect the pH of the solution. Salts derived from strong acids and strong bases generally result in a neutral solution, while others may be acidic or basic.
- Crystal Structure: Salts often form well-defined crystals with characteristic shapes. The arrangement of ions in the crystal lattice contributes to the overall structure.
- Reactivity: Salts can participate in various chemical reactions, including precipitation reactions, redox reactions, and acid-base reactions.



 Modes of Heat Transfer with Examples
Modes of Heat Transfer with Examples
 Evaporation - Definition, Step-Wise Proc...
Evaporation - Definition, Step-Wise Proc...
 What is Sedimentation, Decantation and F...
What is Sedimentation, Decantation and F...













