Compounds of D-block Elements
The d-block elements, also known as transition metals, are a group of metallic elements located in the central block of the periodic table. These elements exhibit unique properties due to the presence of partially filled d orbitals in their electron configuration. Transition metal compounds often display variable oxidation states, forming colorful complexes. Their ability to form coordination compounds with ligands makes them crucial in catalysis and industrial processes. Additionally, d-block elements contribute to the diverse properties of alloys, providing strength and durability in materials such as steel. Overall, the compounds of d-block elements play vital roles in a wide range of chemical and industrial applications.
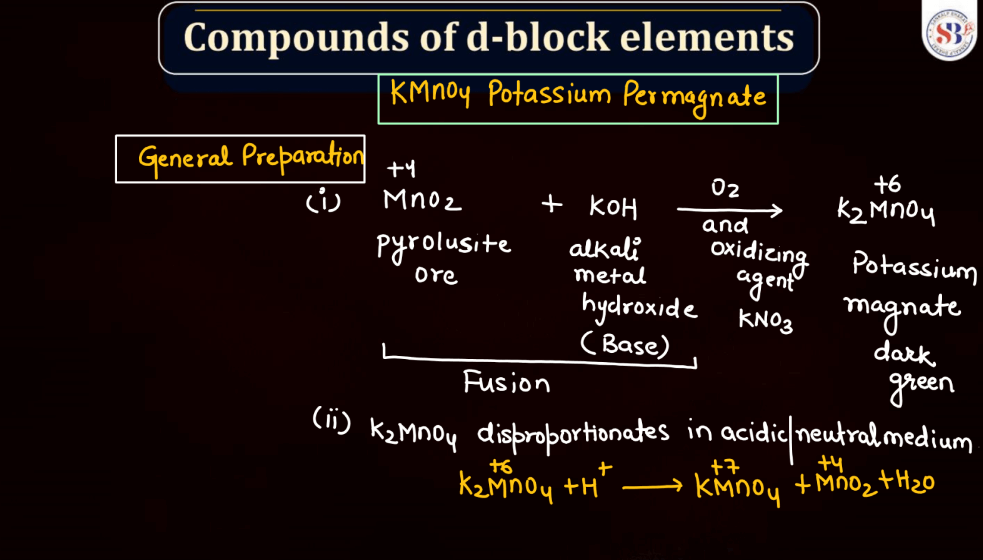
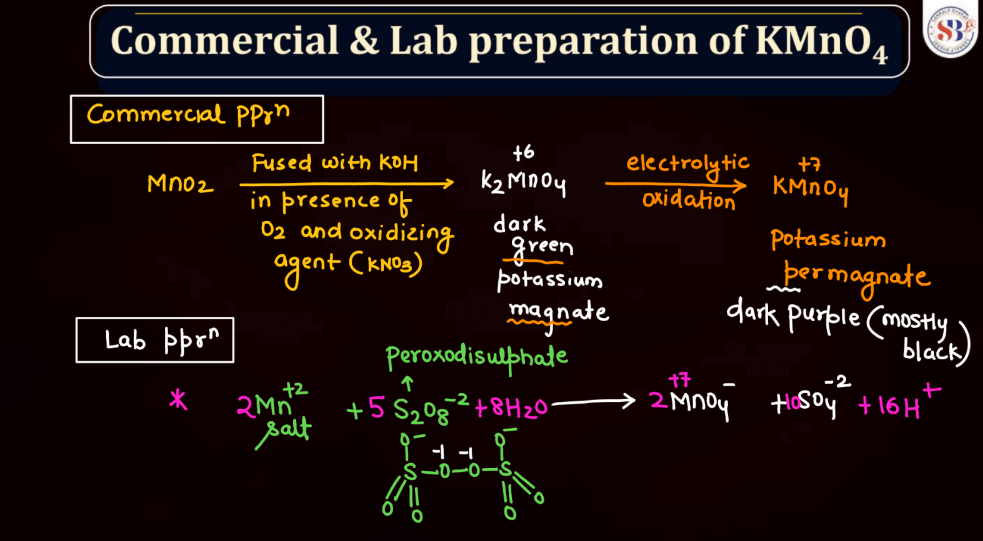
Commercial and Lab Preparation of KMnO4
Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) holds significance in both commercial and laboratory settings. In commercial applications, it is often utilized as a strong oxidizing agent in industries such as water treatment, where it helps eliminate impurities. Its striking purple color makes it useful in dyeing and tanning processes as well. In laboratories, KMnO4 is a versatile chemical employed in various experiments. Its ability to undergo color changes during reactions makes it a valuable indicator and its oxidizing properties play a crucial role in titrations. Whether in water treatment plants or scientific laboratories, potassium permanganate serves as a versatile compound with distinct applications.
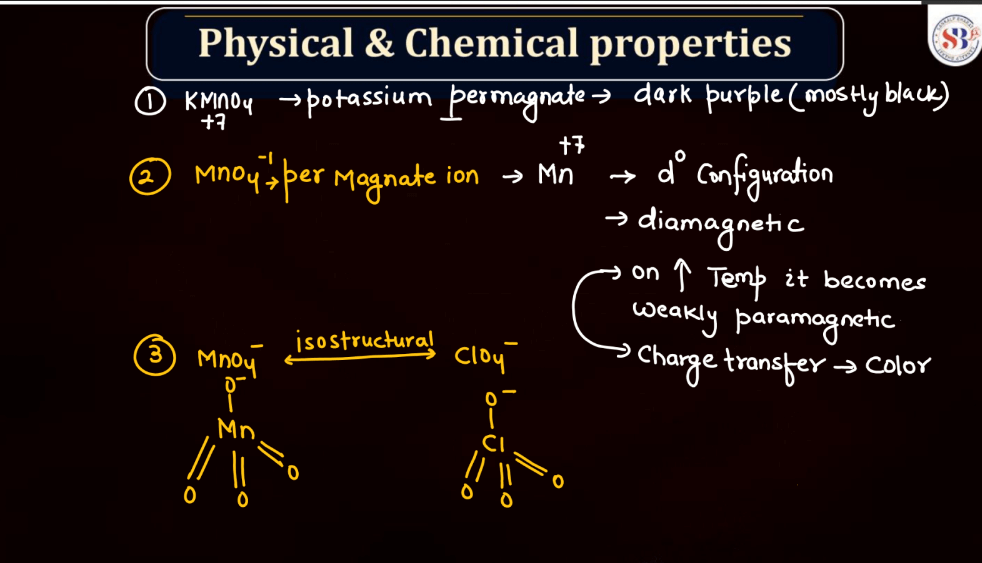
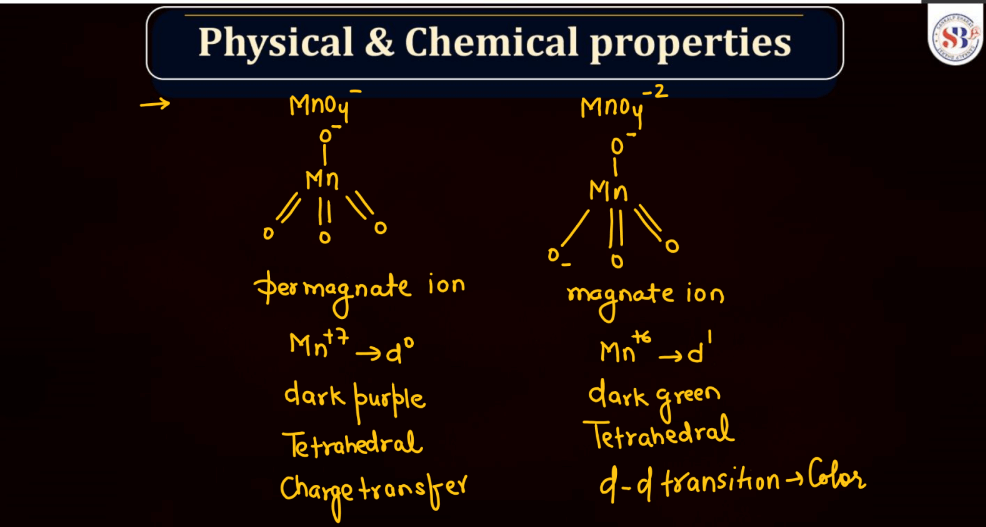
Physical and Chemical Properties of KMnO4
Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) is a powerful oxidizing agent with distinct physical and chemical properties:
Physical Properties of KMnO4
- Color: The color of Potassium permanganate is deep purple crystals or dark purple powder.
- Solubility: Soluble in water, producing a vibrant purple solution.
- Density: The density of KMnO4 is around 2.70 g/cm³.
- Melting point: The Potassium permanganate decomposes before melting.
Chemical Properties of KMnO4
- Oxidizing Agent: KMnO4 is a strong oxidizing agent, capable of accepting electrons during redox reactions.
- Decomposition: It decomposes upon heating, releasing oxygen, and forming manganese dioxide (MnO2).
- Reaction with Organic Compounds: It can react vigorously with organic compounds, often resulting in the combustion or oxidation of the organic material.
- Stoichiometry in Reactions: Its reactions often involve stoichiometric quantities, making it useful in titrations.
- Applications: Used in various applications such as water treatment, analytical chemistry, and as a laboratory reagent.
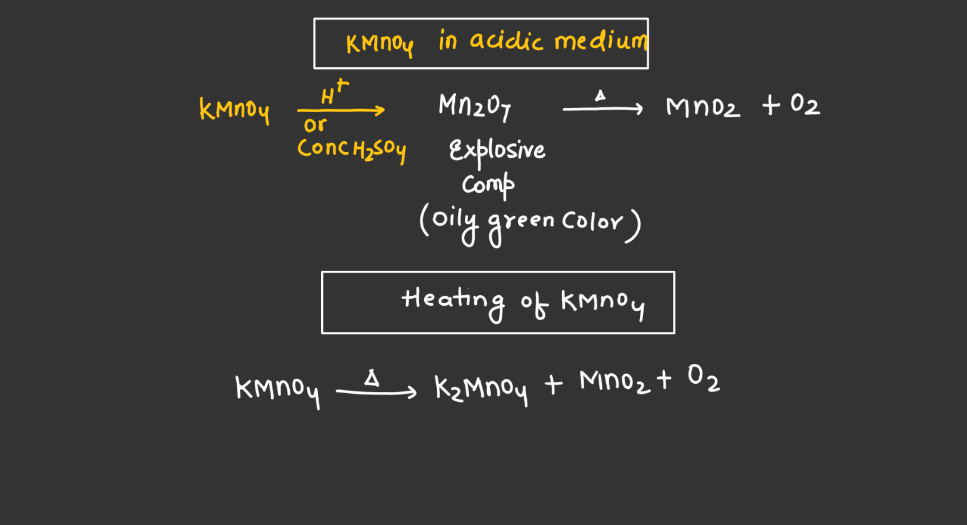

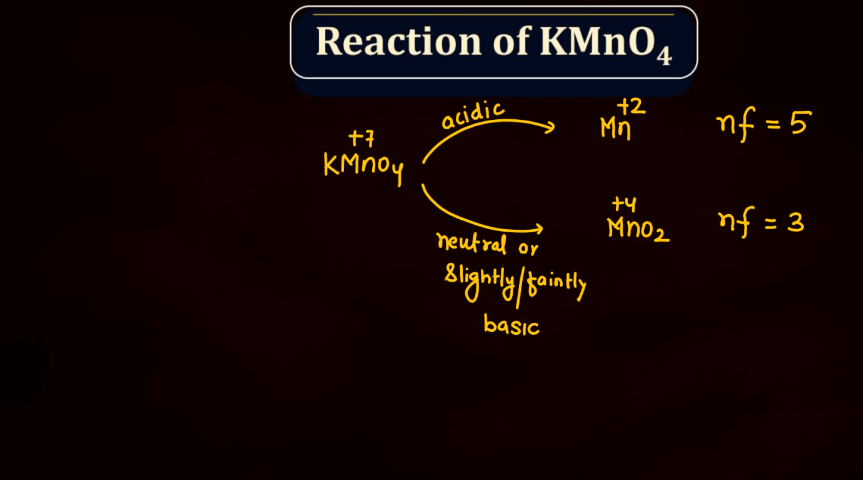
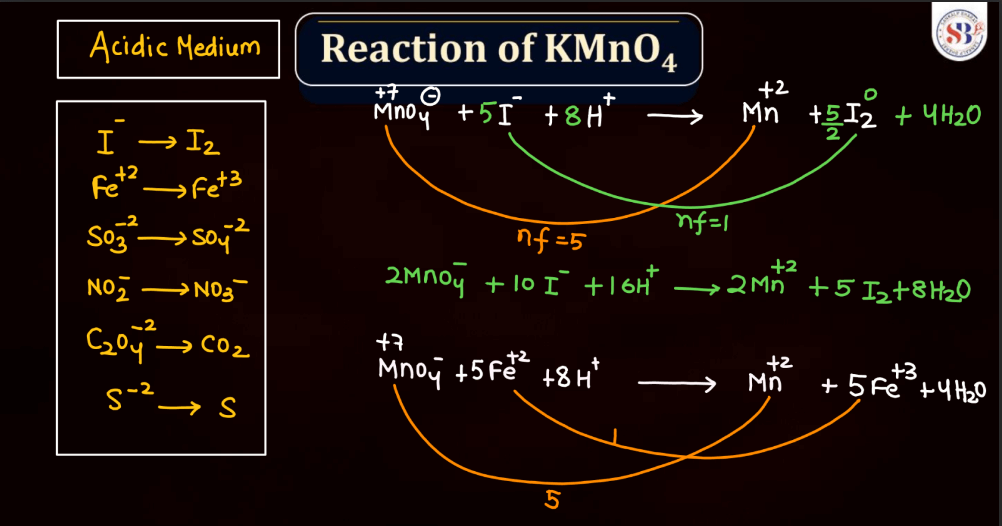
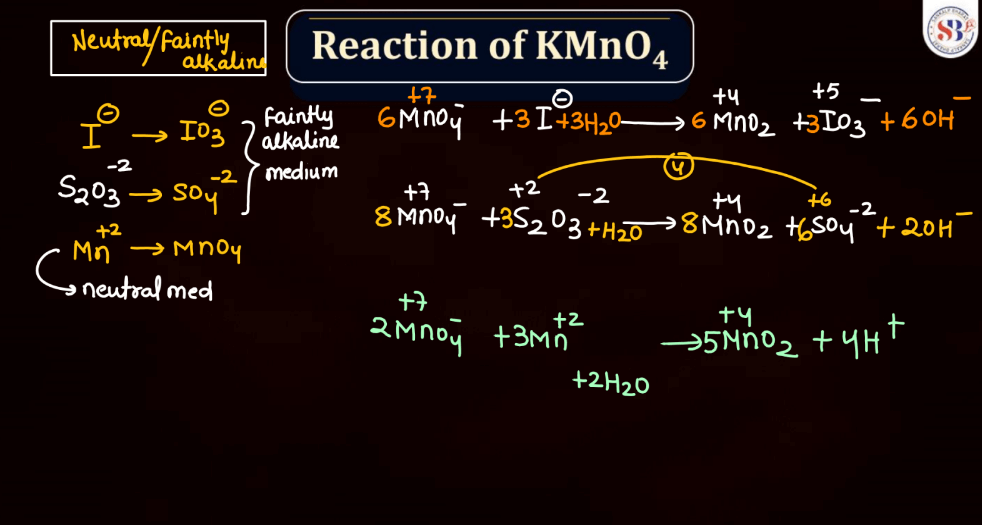
Reaction of KMnO4
As we know Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) is a strong oxidizing agent and is widely used in most chemical reactions. When it reacts, it undergoes reduction, releasing manganese dioxide (MnO2) and oxygen gas (O2). In acidic conditions, it oxidizes various organic compounds, turning from its purple color to colorless. For example, in the presence of oxalic acid, KMnO4 forms carbon dioxide, water, and manganese (II) ions. In alkaline solutions, the reaction produces brown manganese (IV) oxide and oxygen gas. This versatile compound is employed in titrations, water treatment, and laboratory experiments due to its potent oxidizing properties and distinctive color changes during reactions.



Potassium Dichromate (K2Cr2O7)
Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) is a bright orange-red chemical compound with a crucial role in various industrial processes and laboratory applications. It is a strong oxidizing agent and is commonly employed in oxidizing organic compounds during chemical synthesis. Its distinctive color makes it easily recognizable in the laboratory settings. Beyond its utility in chemical reactions, potassium dichromate is also used in qualitative analysis to detect the presence of certain substances. However, it is toxicity and potential environmental impact, as chromium compounds can pose health and environmental risks if not managed properly.
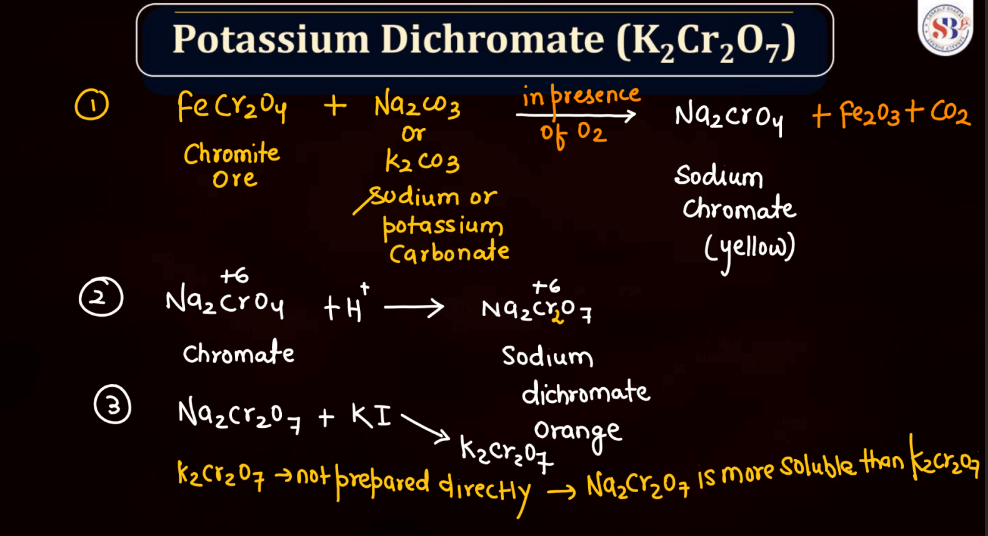

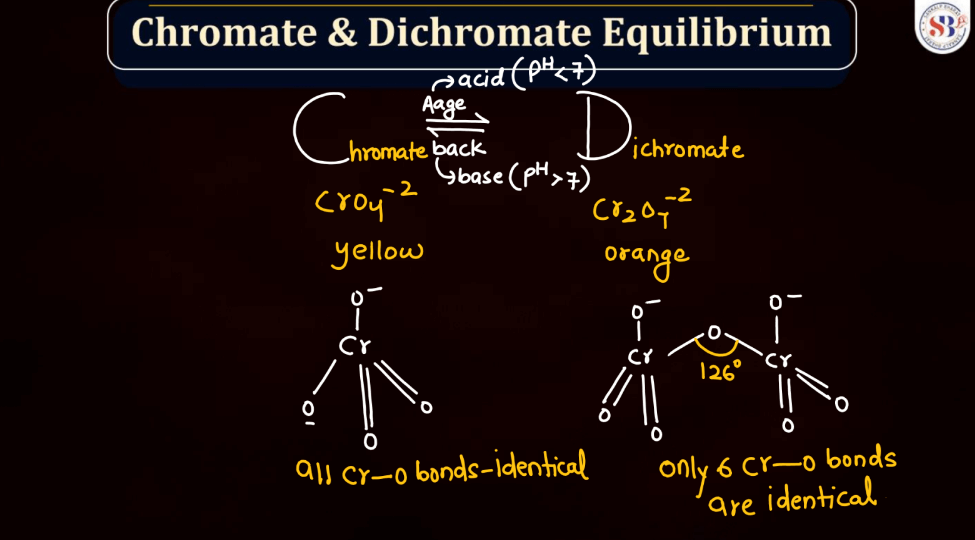

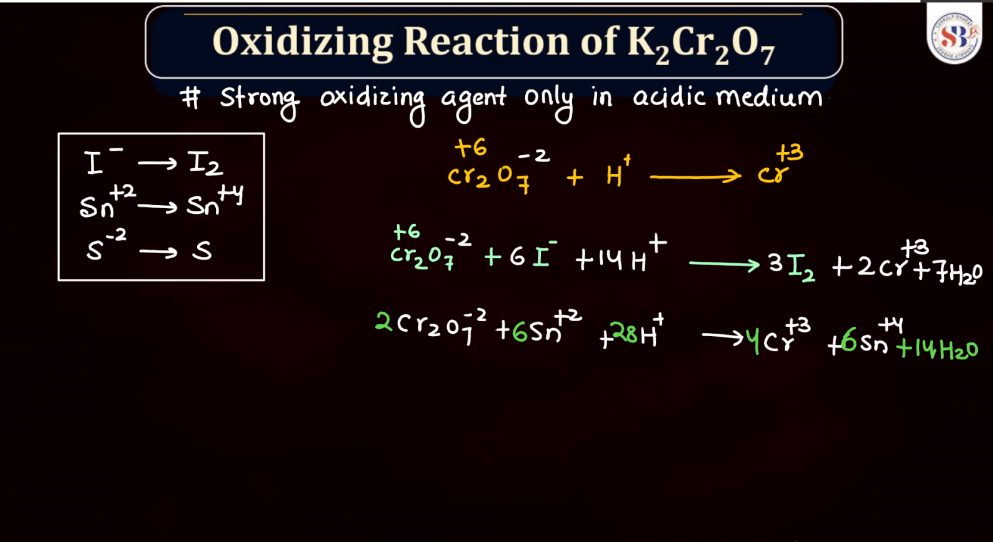
Oxidation Reaction of K2Cr2O7
The oxidation reaction of potassium dichromate is commonly observed in acidic or alkaline conditions. In an acidic environment, it serves as a powerful oxidizing agent. For instance, in the presence of acid and heat, it can oxidize alcohol to form a corresponding aldehyde or ketone, depending on the nature of the alcohol. The dichromate ion (Cr2O7^2-) undergoes reduction, changing its oxidation-reduction, changing its oxidation state from +6 to +3 or +4, depending on the specific reaction. The resulting products vary based on the starting material and reaction conditions. This versatile compound is widely utilized in organic chemistry for its ability to facilitate oxidation reactions.



To know more about the KMnO4 and K2Cr2O7, Watch the video as given below:


 Modes of Heat Transfer with Examples
Modes of Heat Transfer with Examples
 Evaporation - Definition, Step-Wise Proc...
Evaporation - Definition, Step-Wise Proc...
 What is Sedimentation, Decantation and F...
What is Sedimentation, Decantation and F...













