Periodic Table of Elements With Names: The periodic table is the systematic arrangement of all chemical elements in the form of a table based on their concerned atomic numbers. The vertical columns of the periodic table are known as Groups while the horizontal rows of the periodic table are known as Periods. The Modern Periodic Law was propounded by the English Physicist Henry Moseley. It states that the properties of chemical elements are periodic functions of their respective atomic numbers. The Modern Periodic Table also follows this law. The properties of all chemical elements can be seen as the periodic functions of the atomic number of elements placed in the groups and the periods of the modern periodic table. Here we will discuss the atomic number, atomic mass number, periodic table of elements, list of names of all elements, and Mendeleev periodic table.
Atomic Number of Elements
The chemical properties of the atoms of all states of matter like solid, liquid, and gas are explained by the number and arrangements of electrons and protons. The electron configuration of all elements follows the quantum mechanics principles. The total number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom is considered its atomic number. The atomic number of the atom is symbolized by the letter Z. In the case of an electrically-neutral atom, the number of electrons is the same as that of protons in the nucleus of that atom. More than 90 elements have been found on Earth. Every chemical element has different protons, electrons, and neutrons numbers. The unique properties of chemical elements like radioactivity, superconductivity, etc. are based on the total number of subatomic particles available in these elements. The proton number present in the nucleus of an atom is known as the atomic number. Not any two different chemical elements possess the same atomic number. The atomic number of chemical elements is always fixed.
Atomic Mass Number
The atomic mass number refers to the combined proton and neutron number in a nucleus of an atom. Some chemical elements possess atoms with different atomic mass numbers. It is due to the different number of neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom. Isotopes of a chemical element refer to those versions of elements having different atomic mass numbers.
Periodic Table of Elements
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of all known chemical elements present in the universe. It makes the arrangement of chemical elements as per their increasing atomic numbers. There is a repetitive function in the properties of chemical elements and this function is known as the Periodic Law which places all chemical elements having similar properties in the same column. It is a general law that metals are placed on the left side within a single row while non-metals are placed on the right side of the row. The rows are called Periods and columns are called Groups in the study of the Periodic Table.
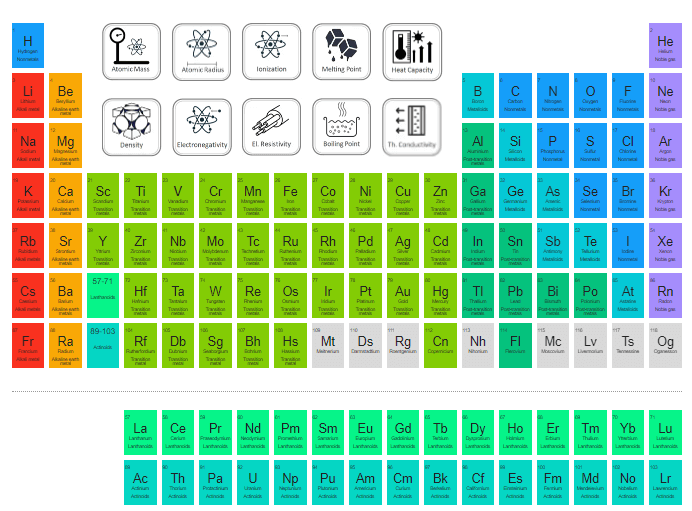
Mendeleev Periodic Table
Dimitri Mendeleev propounded the first iteration of the modern periodic table that we use today. Dimitri Mendeleev came to be recognized as the father of the periodic table. The periodic law of Mendeleev was different from the modern periodic law as Mendeleev drafted his periodic table based on the increasing atomic mass while the modern periodic law was arranged on the basis of increasing atomic numbers. Mendeleev’s periodic table was arranged on the atomic weight of chemical elements. Successfully, he discovered the properties of some chemical elements. The Periodic Table of Mendeleev was released in the German Journal of Chemistry in 1869. It became the basis of today’s periodic table of elements.
List of Chemical Elements
Every element has a particular atomic number (Z) which gives details about the number of protons available in the nucleus of its atom. All isotope versions of an element come within a single cell of the periodic table because all isotopes of that element have the same atomic number. The names of 118 chemical elements of the periodic table organized by their atomic number, atomic weight with their symbols, and discovery year are tabulated below.
| Name of Element | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass | Symbol | Discovery (in Year) |
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1.0079 | H | 1776 |
| Helium | 2 | 4.0026 | He | 1895 |
| Lithium | 3 | 6.941 | Li | 1817 |
| Beryllium | 4 | 9.0122 | Be | 1797 |
| Boron | 5 | 10.811 | B | 1808 |
| Carbon | 6 | 12.0107 | C | Ancient |
| Nitrogen | 7 | 14.0067 | N | 1772 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 15.9994 | O | 1774 |
| Fluorine | 9 | 18.9984 | F | 1886 |
| Neon | 10 | 20.1797 | Ne | 1898 |
| Sodium | 11 | 22.9897 | Na | 1807 |
| Magnesium | 12 | 24.305 | Mg | 1755 |
| Aluminum | 13 | 26.9815 | Al | 1825 |
| Silicon | 14 | 28.0855 | Si | 1824 |
| Phosphorus | 15 | 30.9738 | P | 1669 |
| Sulfur | 16 | 32.065 | S | Ancient |
| Chlorine | 17 | 35.453 | Cl | 1774 |
| Argon | 18 | 39.948 | Ar | 1894 |
| Potassium | 19 | 39.0983 | K | 1807 |
| Calcium | 20 | 40.078 | Ca | 1808 |
| Scandium | 21 | 44.9559 | Sc | 1879 |
| Titanium | 22 | 47.867 | Ti | 1791 |
| Vanadium | 23 | 50.9415 | V | 1830 |
| Chromium | 24 | 51.9961 | Cr | 1797 |
| Manganese | 25 | 54.938 | Mn | 1774 |
| Iron | 26 | 55.845 | Fe | Ancient |
| Cobalt | 27 | 58.9332 | Co | 1735 |
| Nickel | 28 | 58.6934 | Ni | 1751 |
| Copper | 29 | 63.546 | Cu | Ancient |
| Zinc | 30 | 65.39 | Zn | Ancient |
| Gallium | 31 | 69.723 | Ga | 1875 |
| Germanium | 32 | 72.64 | Ge | 1886 |
| Arsenic | 33 | 74.9216 | As | Ancient |
| Selenium | 34 | 78.96 | Se | 1817 |
| Bromine | 35 | 79.904 | Br | 1826 |
| Krypton | 36 | 83.798 | Kr | 1898 |
| Rubidium | 37 | 85.4678 | Rb | 1861 |
| Strontium | 38 | 87.62 | Sr | 1790 |
| Yttrium | 39 | 88.906 | Y | 1794 |
| Zirconium | 40 | 91.224 | Zr | 1789 |
| Niobium | 41 | 92.906 | Nb | 1801 |
| Molybdenum | 42 | 95.94 | Mo | 1781 |
| Technetium | 43 | 98 | Tc | 1937 |
| Ruthenium | 44 | 101.07 | Ru | 1844 |
| Rhodium | 45 | 102.91 | Rh | 1803 |
| Palladium | 46 | 106.42 | Pd | 1803 |
| Silver | 47 | 107.87 | Ag | Ancient |
| Cadmium | 48 | 112.411 | Cd | 1817 |
| Indium | 49 | 114.82 | In | 1863 |
| Tin | 50 | 118.71 | Sn | Ancient |
| Antimony | 51 | 121.76 | Sb | Ancient |
| Tellurium | 52 | 127.6 | Te | 1783 |
| Iodine | 53 | 126.9045 | I | 1811 |
| Xenon | 54 | 131.293 | Xe | 1898 |
| Cesium | 55 | 132.91 | Cs | 1860 |
| Barium | 56 | 137.327 | Ba | 1808 |
| Lanthanum | 57 | 138.91 | La | 1839 |
| Cerium | 58 | 140.12 | Ce | 1803 |
| Praseodymium | 59 | 140.9077 | Pr | 1885 |
| Neodymium | 60 | 144.24 | Nd | 1885 |
| Promethium | 61 | 145 | Pm | 1945 |
| Samarium | 62 | 150.36 | Sm | 1879 |
| Europium | 63 | 151.964 | Eu | 1901 |
| Gadolinium | 64 | 157.25 | Gd | 1880 |
| Terbium | 65 | 158.9253 | Tb | 1843 |
| Dysprosium | 66 | 162.5 | Dy | 1886 |
| Holmium | 67 | 164.9303 | Ho | 1867 |
| Erbium | 68 | 167.259 | Er | 1842 |
| Thulium | 69 | 168.9342 | Tm | 1879 |
| Ytterbium | 70 | 173.04 | Yb | 1878 |
| Lutetium | 71 | 174.967 | Lu | 1907 |
| Hafnium | 72 | 178.49 | Hf | 1923 |
| Tantalum | 73 | 180.9479 | Ta | 1802 |
| Tungsten | 74 | 183.84 | W | 1783 |
| Rhenium | 75 | 186.207 | Re | 1925 |
| Osmium | 76 | 190.23 | Os | 1803 |
| Iridium | 77 | 192.22 | Ir | Ancient |
| Platinum | 78 | 195.08 | Pt | 1803 |
| Gold | 79 | 196.97 | Au | 1735 |
| Mercury | 80 | 200.59 | Hg | Ancient |
| Thallium | 81 | 204.3833 | Tl | 1861 |
| Lead | 82 | 207.2 | Pb | Ancient |
| Bismuth | 83 | 208.9804 | Bi | Ancient |
| Polonium | 84 | 209 | Po | 1898 |
| Astatine | 85 | 210 | At | 1940 |
| Radon | 86 | 222 | Rn | 1900 |
| Francium | 87 | 223 | Fr | 1939 |
| Radium | 88 | 226 | Ra | 1898 |
| Actinium | 89 | 227 | Ac | 1899 |
| Thorium | 90 | 232.0381 | Th | 1829 |
| Protactinium | 91 | 231.0359 | Pa | 1913 |
| Uranium | 92 | 238.0289 | U | 1789 |
| Neptunium | 93 | 237 | Np | 1940 |
| Plutonium | 94 | 244 | Pu | 1940 |
| Americium | 95 | 243 | Am | 1944 |
| Curium | 96 | 247 | Cm | 1944 |
| Berkelium | 97 | 247 | Bk | 1949 |
| Californium | 98 | 251 | Cf | 1950 |
| Einsteinium | 99 | 252 | Es | 1952 |
| Fermium | 100 | 257 | Fm | 1952 |
| Mendelevium | 101 | 258 | Md | 1955 |
| Nobelium | 102 | 259 | No | 1958 |
| Lawrencium | 103 | 262 | Lr | 1961 |
| Rutherfordium | 104 | 267 | Rf | 1964 |
| Dubnium | 105 | 268 | Db | 1967 |
| Seaborgium | 106 | 269 | Sg | 1974 |
| Bohrium | 107 | 270 | Bh | 1981 |
| Hassium | 108 | 269 | Hs | 1984 |
| Meitnerium | 109 | 277 | Mt | 1982 |
| Darmstadtium | 110 | 281 | Ds | 1994 |
| Roentgenium | 111 | 282 | Rg | 1994 |
| Copernicium | 112 | 285 | Cn | 1996 |
| Nihonium | 113 | 286 | Nh | 2003 |
| Flerovium | 114 | 290 | Fl | 1998 |
| Moscovium | 115 | 290 | Mc | 2010 |
| Livermorium | 116 | 293 | Lv | 2000 |
| Tennessine | 117 | 294 | Ts | 2010 |
| Oganesson | 118 | 294 | Og | 2006 |
